The Six Sigma quality improvement methodology uses a problem-solving technique called DMAIC. It stands for Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. Here is a quick summary of each stage of the DMAIC process:
- Define: This stage defines the project’s scope and problem precisely. Ensuring that everyone participating in the project has a clear grasp of the issue and what needs to be done is the goal of this phase.
- Measure: Information is gathered during this stage to comprehend how the process is performing right now. Establishing the process’s baseline and identifying the critical process variables that will be used to monitor progress are the goals of this phase.
- Analyze: The data gathered in the previous step is examined in this phase to determine the problem’s underlying causes. This phase aims to understand the connection between the main process factors and the issue.
- Improve: In this stage, the problem’s solutions are found and implemented. This phase aims to adjust the process to boost productivity and reduce the risk of the issues.
- Control: The process is reviewed and managed at this stage to maintain earlier advancements. This stage’s goal is to maintain process stability and ensure that any potential future issues are avoided.
In general, the DMAIC process is a systematic approach to problem-solving that assists businesses in streamlining their operations, lowering waste and variability, and boosting productivity.



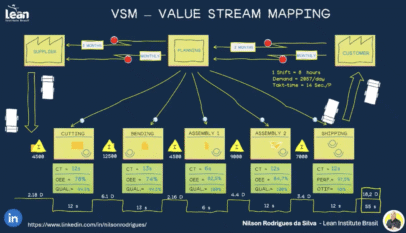

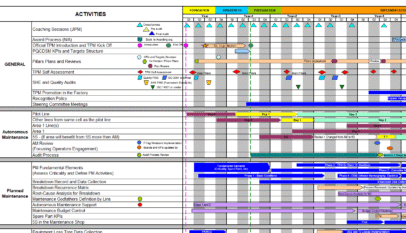













Please we need more information
Hi Mohamed,
What information are you looking for?
I am a seasoned Facilitator and Assessor with 8 years training experience with blue chip companies
Expert in Manufacturing Management and Continuous Improvement
Any opportunities for online facilitation
CV available request