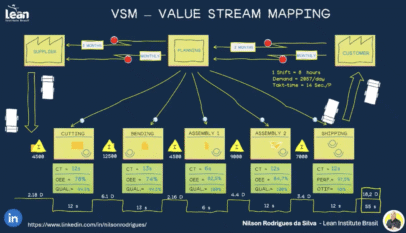
In the field of industrial facility design, selecting the appropriate plant layout is essential for optimizing operational efficiency, enhancing workflow, and ensuring effective material handling. Each layout type, whether U-shaped, O-shaped, S-shaped, L-shaped, I-shaped, or T-shaped, offers unique benefits and potential drawbacks. Understanding these characteristics allows businesses to make informed decisions that align with their production needs and spatial constraints, ultimately leading to improved productivity and streamlined processes.
U-Shaped Layout:
The U-shaped plant layout is an industrial facility arrangement where production areas are organized in the shape of the letter “U”, with machinery and workstations along the arms of the U and an open space in the center.
Benefits:
- Efficient material flow
- Enhanced communication
- Space optimization
- Reduces material handling distances
Drawbacks:
- Potential congestion in central space
- Difficulties in scaling operations
Ideal for: Automotive assembly plants
O-Shaped Layout:
The O-shaped plant layout refers to an industrial facility layout where production processes are arranged in a circular or oval shape, with machinery and workstations along the perimeter.
Benefits:
- Continuous material flow
- Clear production layout
- Safety
- Centralized control
Drawbacks:
- High space requirement
- Complex to modify layout
Ideal for: Chemical processing plants
S-Shaped Layout:
The S-shaped plant layout arranges production areas in an S configuration, with machinery and workstations along its curves, aiming to optimize workflow and offer flexibility for complex manufacturing processes.
Benefits:
- Space optimization
- Flexibility
- Efficient material flow along curves
Drawbacks:
- Potential for complex material handling
- May require more space
Ideal for: Food processing plants
L-Shaped Layout:
The L-shaped plant layout arranges production areas in an L configuration, maximizing space efficiency and facilitating workflow optimization.
Benefits:
- Streamlined workflow
- Function separation
- Space efficiency
- Easy supervision
Drawbacks:
- Limited scalability
- Potential dead space
Ideal for: Small manufacturing workshops
I-Shaped Layout:
The I-shaped plant layout organizes production areas in a linear configuration to streamline workflow and material flow.
Benefits:
- Sequential flow
- Simplifies material handling
- Improves efficiency and reduces bottlenecks
Drawbacks:
- Limited flexibility
- May lead to bottlenecks in high-volume production
Ideal for: Conveyor belt assembly lines
T-Shaped Layout:
The primary goal of the T-shaped layout is to optimize space utilization, facilitate efficient workflow, and provide flexibility for various manufacturing processes.
Benefits:
- Efficient material handling
- Space optimization
- Flexibility for expansion or rearrangement
Drawbacks:
- Potential complexity in layout design
- May require significant space
Ideal for: Warehouses / Distribution centers
Choosing the right plant layout is a strategic decision that can significantly impact the efficiency and productivity of manufacturing processes. By carefully evaluating the pros and cons of each layout type, businesses can tailor their production environments to meet specific operational goals and challenges. Whether prioritizing space optimization, material flow, or flexibility, the ideal layout will facilitate smoother operations and contribute to overall organizational success.