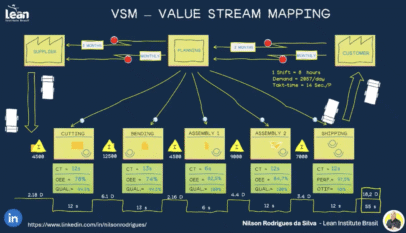
The world of lean manufacturing is always evolving, and today, we will introduce a groundbreaking concept set to revolutionize the industry: SMED v2.
Single Minute Exchange of Die (SMED) has been a cornerstone of lean manufacturing since its inception. This new iteration, SMED v2, promises to take efficiency and waste reduction to new heights. In this blog post, we will discuss the origins of SMED, the key differences between SMED and SMED v2, and how to implement SMED v2 in your organization effectively.
A Brief History of SMED
SMED, or Single Minute Exchange of Die, is a lean manufacturing method developed by Dr. Shigeo Shingo in the 1950s. This revolutionary approach aimed to reduce manufacturing processes’ setup and changeover times, thereby increasing efficiency and reducing waste. The core principles of SMED include the following:
- Separating internal and external setup operations.
- Converting internal to external setup operations.
- Streamlining all aspects of the setup process.
Over the years, SMED has been successfully implemented in various industries, delivering impressive results. However, as technology and manufacturing processes have evolved, a growing need for a more advanced approach to changeover times has been needed – enter SMED v2.
Introducing SMED v2
SMED v2 takes the foundational principles of SMED and elevates them to a whole new level. By incorporating cutting-edge technology and advanced data analysis techniques, SMED v2 allows organizations to achieve greater efficiency and waste reduction. The key differences between SMED and SMED v2 are:
- Enhanced data analysis: SMED v2 uses advanced data analysis tools to gain deeper insights into the setup process, identifying bottlenecks and areas for improvement more effectively.
- Digitalization of setup processes: SMED v2 embraces the power of digital technology to streamline and automate setup operations, reducing human error and enhancing overall efficiency.
- Integration of Industry 4.0 technologies: SMED v2 incorporates Industry 4.0 technologies, such as IoT, AI, and machine learning, to optimize the setup process and enable real-time decision-making.
In order to get the most out of SMED v2, it’s important to focus on optimizing three key aspects of the setup process: reducing the time it takes for internal setup, reducing the time it takes for external setup, and improving verification and iteration. This section provides strategies for improving each component to help your organization achieve the best possible results from implementing SMED v2.
- Shortening Internal Setup
Internal setup refers to the tasks that must be completed while the machine is stopped. To reduce the time spent on internal setup, consider the following strategies:
- Standardize and simplify: Create standardized procedures for all internal setup tasks, and simplify these tasks wherever possible to minimize time and effort.
- Implement parallel operations: Identify opportunities for team members to perform tasks simultaneously rather than sequentially to shorten overall setup time.
- Utilize quick-change tooling: Invest in quick-change tooling and fixtures that can be easily and quickly installed or removed, reducing the time needed for changeovers.
- Shortening External Setup
External setup encompasses tasks that can be completed while the machine runs. Improving external setup efficiency involves the following strategies:
- Prepare in advance: Ensure that all necessary tools, equipment, and materials are prepared and easily accessible before the machine stops to minimize downtime during changeovers.
- Develop standard work instructions: Establish clear, standardized work instructions for external setup tasks to ensure consistency and minimize the potential for errors.
- Leverage automation and robotics: Incorporate automation and robotics into external setup processes, where feasible, to improve efficiency and reduce manual labour.
- Enhancing Verification and Iteration
Verification and iteration involve confirming the accuracy and effectiveness of the setup process and making ongoing improvements as needed. To optimize this aspect of SMED v2, consider these strategies:
- Implement real-time monitoring: Utilize sensors and data analytics tools to monitor the setup process, allowing for instant identification of issues or inefficiencies.
- Foster a culture of continuous improvement: Encourage team members to actively identify opportunities for improvement and provide a structured process for reporting and addressing these suggestions.
- Conduct regular reviews: Schedule regular reviews of the setup process to assess performance, identify areas for improvement, and implement necessary changes.
Implementing SMED v2 in Your Organization
Now that we’ve explored the differences between SMED and SMED v2 let’s discuss how to implement SMED v2 in your organization:
- Assess your current setup process: The first step in implementing SMED v2 is thoroughly analyzing your existing setup process. Identify areas where digitalization, data analysis, and Industry 4.0 technologies could be integrated to enhance efficiency.
- Develop a comprehensive implementation plan: Once you’ve identified areas for improvement, develop a comprehensive plan outlining the steps and resources needed to implement SMED v2. This plan should include timelines, budget considerations, and anticipated results.
- Train your team: Successful implementation of SMED v2 requires your organization’s buy-in. Invest in training and development to ensure your team is well-equipped to embrace the new technologies and methodologies associated with SMED v2.
- Monitor progress and continuously improve: As with any lean manufacturing initiative, continuous improvement is key. Monitor the progress of your SMED v2 implementation, using data to identify areas for further optimization and streamlining.
Conclusion
SMED v2 represents the future of lean manufacturing, allowing organizations to achieve unprecedented efficiency and waste reduction levels. By embracing advanced data analysis techniques, digitalization, and Industry 4.0 technologies, SMED v2 takes the core principles of traditional SMED and elevates them to new heights. If your organization wants to stay competitive in an ever-evolving manufacturing landscape, implementing SMED v2 is essential to success. Remember to assess your current processes, develop a comprehensive implementation plan, invest in training, and continually monitor progress to ensure lasting results. Embrace the power of SMED v2 and revolutionize your organization’s approach to lean manufacturing today.