1) Opening
The global market has been expanding for some time now. As a result, each company has expanded its sales and profits at the same time. However, the market is declining in many countries and companies and future expansion is unlikely.
In this situation, companies are facing many problems such as:
- Sales are growing, but profits are stagnant;
- Sales are not growing and cost reductions are not progressing enough;
- There seem to be unprofitable products and inefficient operations, but it is difficult to locate and address;
- Managers want to move from sales-focused management to profit-focused management.
2) From Outside-in Approach….
Is your company facing the following vicious circle from both an operational and improvement perspective? Is this vicious circle a structural problem that stands in the way of profit growth?
This vicious circle is operationally characterized by:
- Sales-oriented management has been used so far and sales volume was what brought the desired profit;
- Sales has a strong voice in deciding which products to sell. In reality, the product range is determined by customer requirements. Basically sales focuses on items that sell “almost by themselves” rather than items that make a profit;
- Production: with many losses and waste;
- Responsibility for the lack of price competitiveness and slow profit growth is pushed onto the purchasing department. Often the variety of products is increased, even if the quantities of raw materials are not available;
- Logistics makes inefficient deliveries and does not make any significant progress in reducing costs.
It is natural for procurement to make efforts to reduce costs in order to increase product competitiveness, but it is also necessary to create an environment in which procurement can more easily achieve cost reduction. To do this, consolidating profitable items and product ranges is an important perspective, simultaneously with the adherence to the Strategic Kaizen Transformation.
Furthermore, having multiple product ranges, operations tend to become inefficient and inventories tend to increase. In addition, it is difficult to consolidate raw material quantities, which makes it difficult to reduce procurement costs.
Regarding the service activities performed by logistics, these services are set the same for both important customers and general customers, which hinders the increase in logistics efficiency and prevents the reduction of logistics costs.
In this context, it can be said that:
if customers do not report problems or elements that need to be improved, then this does not mean that our operations are productive and profitable enough to successively achieve ROI targets. Creating profit through continuous productivity growth and cost reduction is the core mission of any management team. (Alin POSTEUCĂ, 2023, “Beyond Strategic Kaizen”, p. 9-11).
The continuous strategic improvement of companies’ productivity to achieve annual and especially multi-annual operational profit targets is the responsibility of each company, beyond customer requests.
The improvements made in this vicious circle can be characterized as follows:
- Empirical approach based on business improvement plan;
- Current state of systematic improvements;
- Problem definition & process analysis to perform synchronous operations;
- Waste identification;
- Identify and implement the improvement ideas;
- Carrying out activities in the new way.
In conclusion, it can be said that: sales-oriented management is the main cause of slow cost reduction!
3) …To Inside-out Approach
The key to improving profits is to create a virtuous cycle centered on managing profit per item and strategically improving productivity to achieve target profits.
At the operational level, this virtuous circle (by Strategic Kaizen Transformation) is characterized by:
- Management focused on increasing profits (intentional profit creation through Takt Profit). Visibility of profit and losses by product, product family and process;
- Production: with losses and waste controlled and eliminated continuously;
- Procurement aims to consolidate profitable products and seeks to achieve cost reduction targets by consolidating target volumes;
- Logistics continuously seeks to improve the efficiency of logistics operations and improve logistics services;
- Sales focuses on profitable products.
If products and product ranges are consolidated simply for the convenience of procurement or logistics, sales may decline, so decisions must be made with the prospect of profitable sales in mind.
It would be desirable to achieve the narrowing of items and ranges with clear objectives and arguments, to create profitable products and to achieve a virtuous cycle of operational and improvements.
In order to have profitable products with such clear objectives and reasons and to achieve profit-oriented management, close cooperation between top management, sales, purchasing, production and strategic productivity improvements is essential. Strategic Kaizen Transformation does this.
The improvements made in this virtuous circle (by Strategic Kaizen Transformation) can be characterized as follows:
- Scientific approach based on high productivity improvement strategic plan;
- Current state of strategic systematic improvements;
- Goal setting for lowering costs for synchronous profitable operations;
- Ideal way of productivity improvement towards ideal takt profit;
- Analysis and improvement of the cost of losses and targeted waste;
- The future reality strategically revised.

4) Strategic Kaizen Transformation
In today’s fast-paced business environment, Strategic Kaizen stands out as a robust methodology that not only enhances operational efficiency but also aligns closely with strategic goals, fosters innovation, and embraces digital transformation.
The target of the Strategic Kaizen Transformation is: Cost Reduction of 6% per year for 5 consecutive years and achieving sales volume targets.
Strategic Kaizen Transformation can be characterized by the following 10 basic elements:
- Long-term Focus: Strategic Kaizen not only enhances immediate efficiency but also ensures that every improvement contributes to long-term profitability;
- Alignment with Strategy: By synchronising operational enhancements with strategic goals, Strategic Kaizen transforms every action into a step towards overarching success;
- Adaptability & Responsiveness: In a rapidly changing market, Strategic Kaizen empowers organisations to adapt swiftly while maintaining profitability at the forefront;
- Data-driven Improvements: Utilising real-time data, Strategic Kaizen converts insights into actionable improvements, driving measurable results;
- Performance Metrics: Strategic Kaizen redefines performance metrics, ensuring that every improvement is a step towards comprehensive operational excellence;
- Holistic Approach: With a holistic perspective, Strategic Kaizen ensures that every improvement resonates throughout the organisation, fostering unity and purpose;
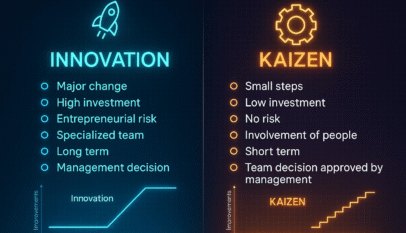
- Type of Improvements: Strategic Kaizen champions a culture of innovation, where every improvement – large or small – fuels competitive advantage;
- Involvement of Managers: By engaging managers at every level, Strategic Kaizen cultivates a culture of shared responsibility and collective success;
- Innovation and Creativity: Strategic Kaizen unleashes creativity, transforming innovative ideas into profitable realities;
- Digital Transformation: Embracing digital transformation, Strategic Kaizen positions organisations at the forefront of innovation and profitability.
5) Conclusion
In conclusion, Strategic Kaizen Transformation prioritizes holistic optimization over isolated departmental improvements. By enhancing the synergy between sales, production, purchasing, and logistics, it elevates the entire management system.
Embracing Strategic Kaizen for Takt Profit empowers managers to secure a competitive edge and drive sustained profitability for their organizations.
Thank you for dedicating your valuable time to read this article. I genuinely hope it serves as a source of inspiration for your endeavours.
Dr. Alin Posteucă