Objective and Importance
- Understand different methodologies to manage our equipment suppliers
- Understand how can we put our equipment suppliers in our current management program
- Quick overview about Materials Suppliers
- Avoid delays and “surprises” related to suppliers
- Closer relationships with our suppliers
How to put our suppliers in the innovation funnel?
Suppliers can be divided in 2 classes: based on the Innovation Funnel
- Selected Suppliers – since project begging
- When you already know your supplier
- Typical situations:
- Corporate / Regional projects
- Corporate / Regional suppliers agreement
- Attend factories standards
- Technical Projects (specific technology)
- Examples of existing suppliers:
- KHS Fillers
- Bosch Case Packers
- Tetra Pak Process Equipment
- Strong Point Palletizing Equipment
- Non Selected Suppliers – chosen after bidding
- You don’t know your supplier
- Bidding process needed
- Regular flow in the company
- Generally regional or local suppliers
- Examples:
- Electrical
- Automations
- Mixers
- Examples:
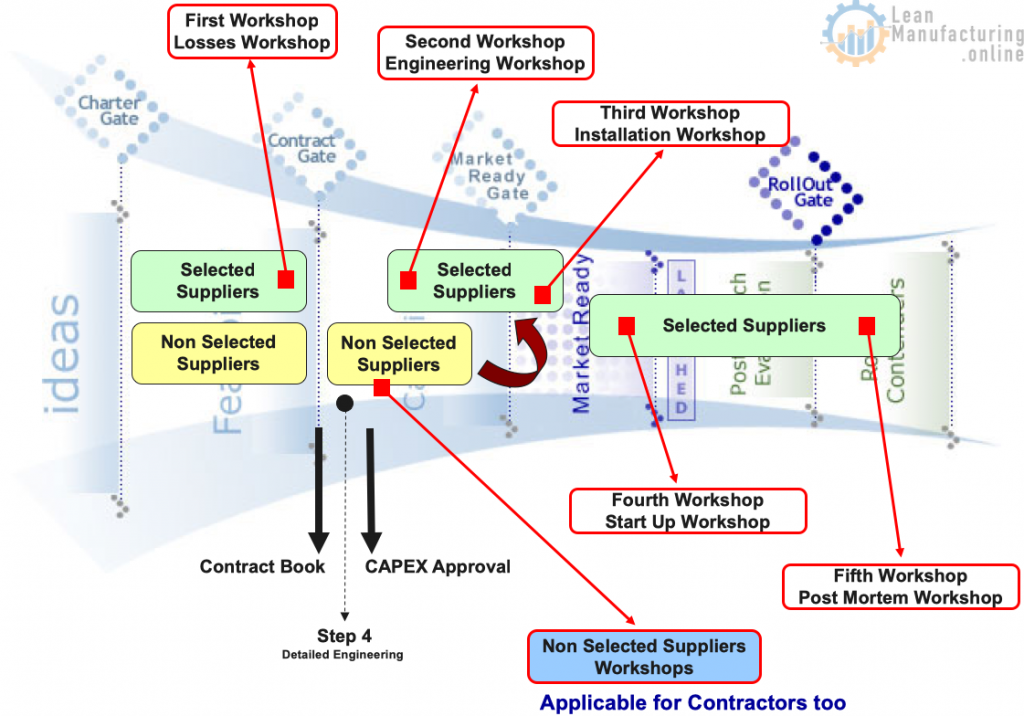
Selected Suppliers:
- Join Company EEM Process
- Join workshops and share actions
- Run Supplier EEM Process
- Workshops in the suppliers using our methodology
- Loss Management
- Risks Management
- Workshops in the suppliers using our methodology
Non Selected Suppliers:
- Suppliers workshops
- Technical inputs to selection
- Join part of Company EEM Process
- Engineering activities – equipment assessments
- Installations & Start-up workshops
Selected Suppliers
- Join Company EEM Process
- Real partners Suppliers
- Join all workshops since the EEM first step
- Part of the engineer team
- Some suppliers have their resources allocated in Company factories
- Responsible for actions in the Master Spreadsheet
- BUT, engineers are accountable for the overall delivery
- Run Supplier EEM Process
- Apply similar methodology for suppliers process
- Link with supplier service level
- It will be the supplier loss tree
- Focusing on these points below:

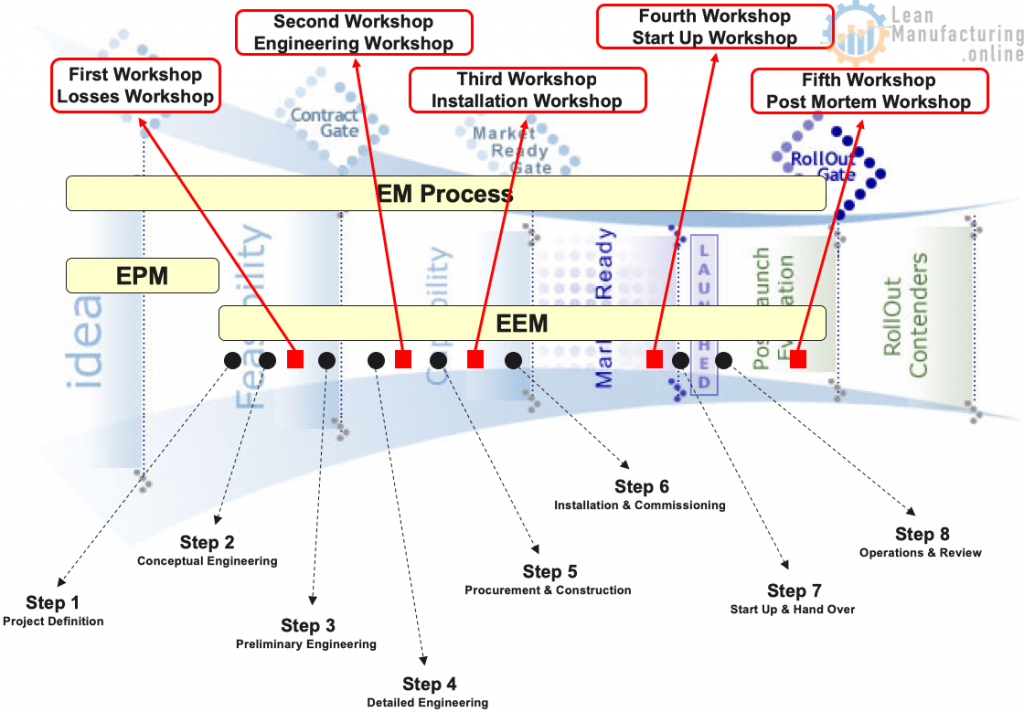
Losses Workshop
- Most important
- Company people could facilitate the exercise
- Deliverables: Company requirements
- KPI’s
- Risks and Actions from Company exercises
- Work:
- Project Capabilities: 4M exercise
- Losses exercise
- Outputs:
- Supplier master spreadsheet
- Actions for Company Master Spreadsheet
Engineering Workshop
- Company people could facilitate the exercise
- Work:
- Suppliers best practices
- From other supplier facilities
- From other supplier lines
- Company expertise – inputs
- Tagging process
- Outputs:
- Supplier master spreadsheet
- Actions for Company Master Spreadsheet
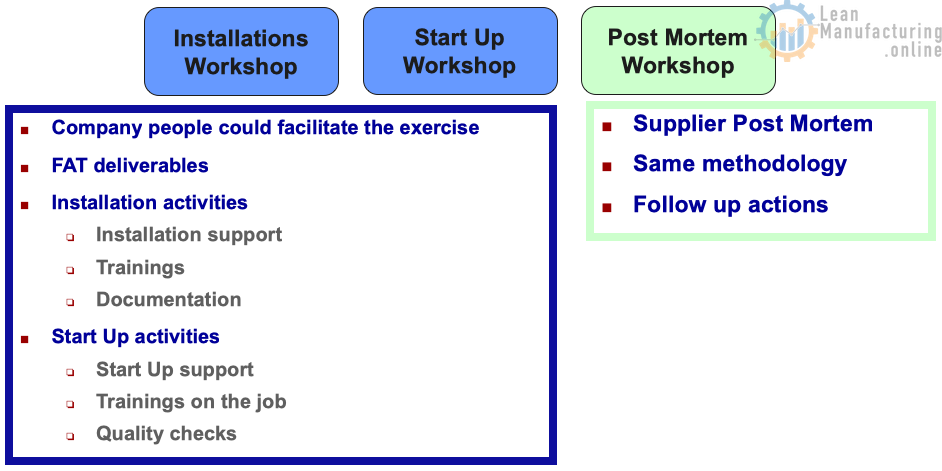
Installation and Startup Workshop
- Company people could facilitate the exercise
- FAT deliverables
- Installation activities
- Installation support
- Trainings
- Documentation
- Start Up activities
- Start Up support
- Trainings on the job
- Quality checks
Post Mortem Workshop
- Supplier Post Mortem
- Same methodology
- Follow up actions
Important:
- Internal Company Post Mortems
- Not recommended Suppliers participation
Non Selected Suppliers
- Suppliers workshops
- Suppliers joining the bidding process
- Objective: inputs for chosen suppliers
- Analysis:
- Total Cost of Ownership – TCO

- Suppliers workshops ways of working
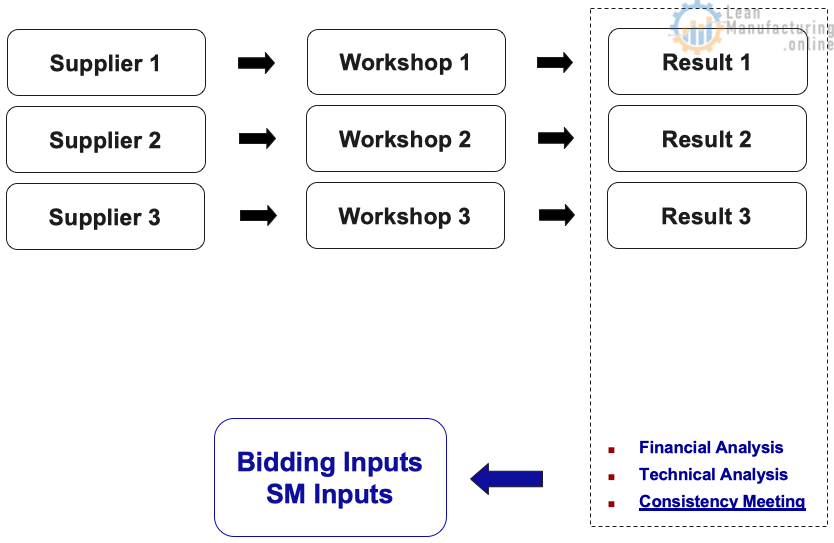
- Join part of Company EEM Process
- Engineering activities – equipment assessments
- Installations & Start Up workshops
Important Considerations:
- This is a VERY important activity during project execution
- However:
- It’s a time consuming process
- Many workshops
- Time to analyze and agree information
- Training and coaching new methodologies for suppliers
- It’s a time consuming process
- So,
- Prioritize main equipments
- Empowered people
- We have to facilitate and coaching, not do all the work!!
Materials Suppliers

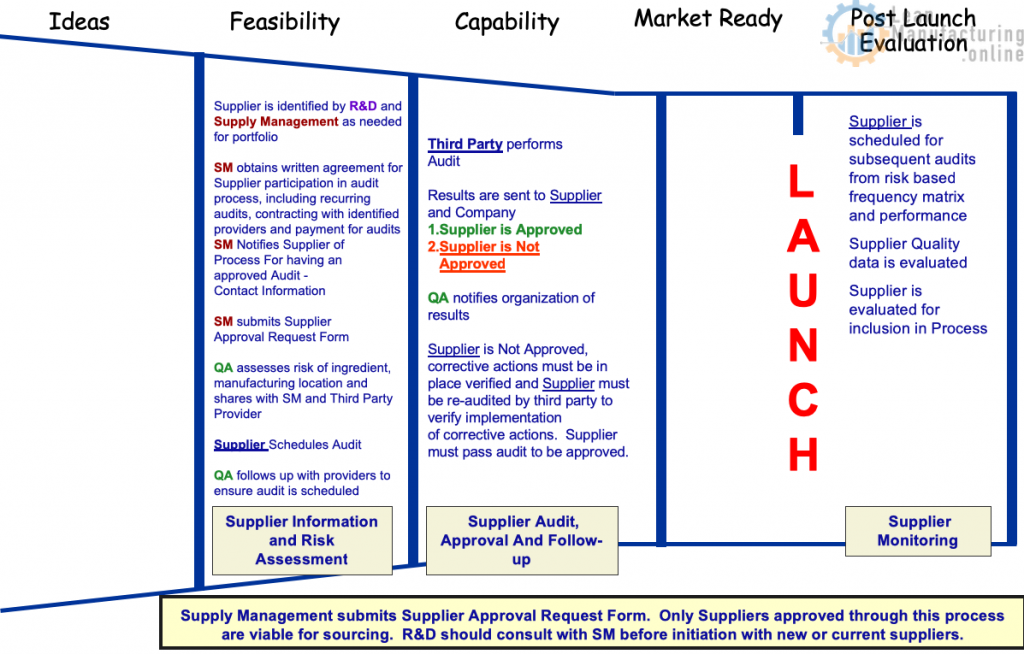
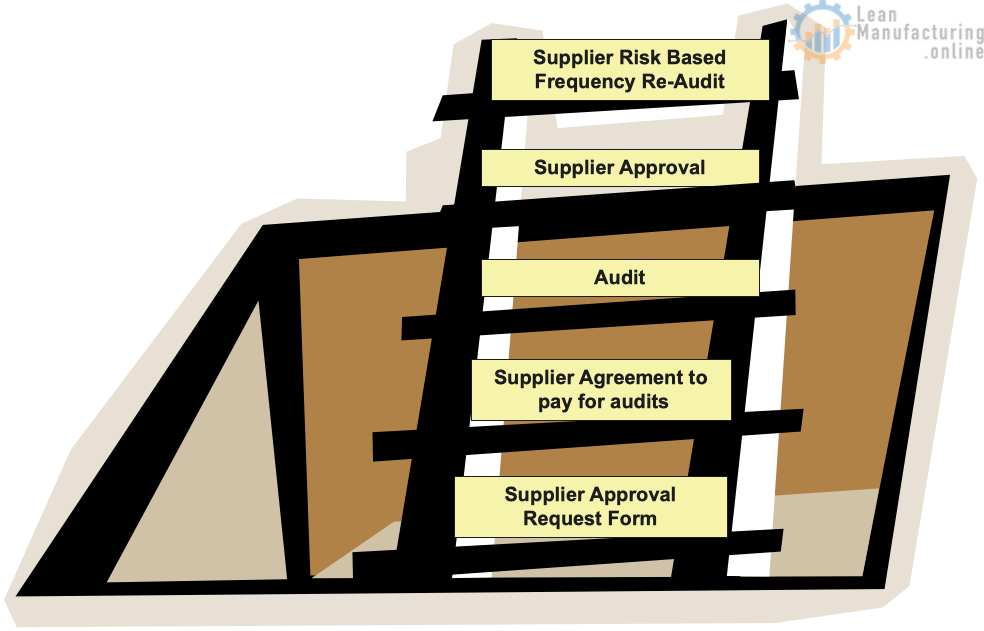
Step 1: Agreement From The Supplier To Schedule And Pay For Initial Audit
Supply Management obtains commitment from the supplier to participate in audit process. This is for all manufacturing locations/sites that ship to Company. **
- Scheduling of Audit
- Payment for audits
- Initial
- Follow-up
- Risk Based Frequency
- Release of Information to Company
**If a supplier will use more than one location/site to manufacture product, all sites must be approved prior to use. Suppliers are not approved, their individual manufacturing sites are approved.
Step 2: Supplier Approval Request Form must be completed and issued by Supply Management to start the Supplier Approval Process.
Supply Management submits Supplier Approval Request Form for all suppliers new and existing (ingredients, commodities, packaging etc.)
Step 3: Supplier Approval Request Form is issued
Since all supplier must have an approved audit or be audited, we will no longer need to send a Company self assessment.
Step 4: QA Reviews Supplier Documentation And Determines Risk.
QA Reviews form (including audits and corrective actions if provided).


Step 5: QA Notifies SM Of Supplier Risk Status
QA notifies SM of Supplier Risk status and next steps:
- If an acceptable audit and corrective actions were provided, supplier approval is complete. See Audit Requirements
- Risk analysis determines frequency of recurrent audits
- High Risk every 2 Years
- Medium Risk every 3 Years
- Low Risk every 4 Years
- If no acceptable audit was provided, SM must inform supplier that one must be scheduled. Audit must be completed and supplier approved prior to purchase date.
Audit Requirements: (For audits that supplier has had performed prior to Company business)
- The acceptable protocols assess the overall quality management system. They are Quality and Consumer Safety Protocols. They are not ISO certifications. Company does not require ISO certification, and ISO certification does not provide exemption from Company’s audit requirement.
- NOTE: ISO 9000 is a family of standards and guidelines for quality in the manufacturing and service industries from the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). ISO 9000 defines the criteria for what should be measured. ISO 9001 covers design and development. ISO 9002 covers production, installation and service, and ISO 9003 covers final testing and inspection. While ISO certification is an indication of a supplier’s commitment to Quality principles, Company does not accept ISO certification in lieu of the selected audit protocols .
High Risk: (all audits must be approved and have taken place within the last 12 months)
Medium Risk: (all audits must be approved and have taken place within the last 18 months)
Low Risk: (all audits must be approved and have taken place within the 24 months)
Step 6: SM Provides Protocol To Supplier To Schedule Audit
If no acceptable audit was provided, Supply Management must inform supplier that one must be scheduled. Supply Management and QA will consult with Supplier to schedule audit. Audit must be completed and supplier approved prior to purchase date. Copy of guidelines must be sent to each supplier by Supply Management.
Step 7: Third Party Performs The Audit
- If the supplier does not have an acceptable audit, QA will assign the audit to one of the preferred firms. The Third party will contact the supplier and schedule the audit. Supplier is responsible for payment and sharing of information with Company. This applies to all suppliers in and out of region.
- If supplier is not approved, Company is not authorized to use the supplier
- Supplier must be re-evaluated by the original third party and pass before they will be approved for use by Company
Step 8: Supplier Is Entered Into Company Database
All approved supplier locations will be entered into a supplier database. The database will have current data on supplier status, audit performance and schedule for future audits from the risk based frequency.
Prior to sourcing with any supplier (current or new), QA, should be consulted by using the request for supplier approval form, so that the database can be reviewed and third party can advise on supplier approval status.
Possible Issues and Actions to be Taken
Issue: We have used a supplier location for many years and they are not approved.
Supply Management will explain process to Supplier. Supply Management will contact QA, QA will work with Supply Management to have Supplier Audited.
Issue: New Supplier has an audit from an approved provider, audit is old.
Supply Management will explain process with Supplier. Supply Management will contact QA, QA will work with Supply Management to have Supplier Audited.
Issue: Current Supplier refuses to pay for audit(s).
Supply Management will explain process with Supplier. Supply Management will work with Supplier. If unable to resolve, Company is not approved to use Supplier Manufacturing location. Supply Management must find alternative manufacturing location, or supplier that is approved.
Issue: Current Supplier Manufacturing Location fails audit
Company is not approved to use Supplier Manufacturing location. Supply Management must find alternative manufacturing location, or supplier that is approved.
Issue: New Supplier fails audit
Company is not approved to use Supplier Manufacturing location. Supply Management must find alternative manufacturing location.