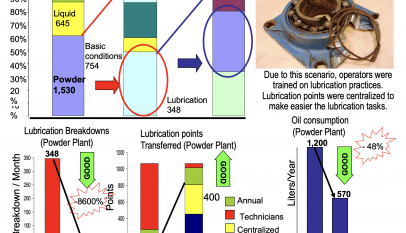
In our previous posts, we discussed a couple of essential maintenance KPIs, such as MTBF and MTTR.
During our recent interactions with the client, they asked me: “How do you ensure the maintenance department delivers?” After explaining, I asked the operations manager if they tracked MTBF and MTTR. Do you have a maintenance planner and CMMS? The answer was a “shocking” NO.
So today, I would like to take a step back and talk about the situation “before” when your maintenance team equals 🔥🚒🧯.
To focus on the maintenance issues only, let’s assume that the maintenance department gets enough downtime from production planning to perform preventive maintenance work orders.
The traditional “wait until it breaks” mentality has long been a general approach to equipment maintenance in various industries. This post analyzes the advantages of planned maintenance strategies compared to reactive “firefighting mode” practices. Through a comprehensive examination of existing literature, the post highlights the benefits of planned maintenance, including cost savings, improved equipment efficiency, increased operational reliability, and enhanced safety. The post also presents strategies for convincing stakeholders to adopt proactive maintenance practices and discusses the barriers to change. Ultimately, it is argued that embracing planned maintenance is essential for organizations seeking to optimize their operations and thrive in competitive markets.
Introduction
Equipment maintenance is critical to any organization’s operations, directly impacting productivity, efficiency, and profitability. Traditionally, many organizations have adopted a reactive “firefighting mode” approach, addressing equipment issues only when they break down or malfunction. This mindset has contributed to substantial financial and operational costs and increased safety risks. In contrast, planned maintenance strategies offer numerous benefits, including cost savings, improved equipment performance, and enhanced safety. This post aims to analyze the advantages of planned maintenance over reactive approaches and explore strategies for convincing stakeholders to adopt a proactive mindset in maintenance management.
Benefits of Planned Maintenance:
- Cost Savings: Planned maintenance schedules allow organizations to accurately predict and budget for maintenance expenses, reducing the likelihood of unexpected costs resulting from equipment failures. Furthermore, proactive maintenance can extend equipment life, reducing the need for costly replacements.
- Improved Equipment Efficiency: Regularly maintained equipment operates more efficiently, consuming less energy and minimizing wear and tear. This, in turn, can lead to reduced operational expenses and a lower environmental impact.
- Increased Operational Reliability: A planned maintenance approach ensures that equipment is consistently maintained at optimal performance levels, reducing the likelihood of unexpected breakdowns and minimizing downtime. It increases operational reliability, ensuring organizations meet their production goals and maintain a competitive edge.
- Enhanced Safety: Proactively addressing potential equipment issues reduces the risk of accidents and injuries, promoting a safer work environment. Furthermore, a planned maintenance approach allows organizations to remain compliant with industry regulations and standards, reducing the risk of fines and penalties.
Barriers to Change and Strategies for Convincing Stakeholders
Despite the clear benefits of planned maintenance, organizations often face resistance when shifting from a reactive “firefighting mode” to a proactive approach. Critical barriers to change include:
- Entrenched cultural norms.
- Limited understanding of the benefits of planned maintenance.
- Concerns about the costs associated with implementing new strategies.
To overcome these barriers and convince stakeholders of the value of planned maintenance, the following strategies may be employed:
- Educate: Provide stakeholders with clear, evidence-based information on the benefits of planned maintenance, emphasizing the potential cost savings, improved efficiency, and enhanced safety associated with proactive strategies.
- Communicate Success Stories: Share examples of organizations that have successfully transitioned to planned maintenance, highlighting the positive outcomes they have experienced.
- Develop a Compelling Business Case: Clearly outline planned maintenance’s financial and operational benefits, demonstrating how adopting a proactive approach can lead to increased profitability and competitive advantage.
- Engage Champions: Identify and engage individuals within the organization who are passionate about the benefits of planned maintenance and can help drive the necessary cultural shift.
Conclusion
The “wait until it breaks” mindset has long been an accepted approach to equipment maintenance, resulting in substantial costs, inefficiencies, and safety risks. In contrast, adopting a planned maintenance strategy offers numerous benefits, including cost savings, improved equipment performance, increased operational reliability, and enhanced safety. Convincing stakeholders to embrace planned maintenance requires overcoming cultural barriers and providing clear evidence of the value of proactive strategies.