An Internal Process SOP is a crucial tool for businesses of all sizes. It provides a set of guidelines and steps to follow for specific tasks or processes within an organization. A well-documented SOP ensures that team members know the procedures and can complete tasks efficiently and effectively. This article will discuss the essential elements of creating an effective internal process SOP.
Step 1: Identify the Process or Task
The first step in creating an internal process SOP is to identify the process or task that needs to be documented. This could include anything from managing customer inquiries to managing inventory. The key is to select a process critical to the business’s success.
This step is critical because it sets the foundation for the entire SOP. Identifying the process or task involves understanding the scope of the process, why it is essential, and what outcome or deliverable is expected.
To begin, it’s essential to determine the scope of the process. This involves identifying the starting point and the endpoint of the process. For example, if the process manages customer inquiries, the starting point could be when the customer submits an inquiry, and the endpoint could be when the customer’s issue is resolved.
Next, it’s important to understand why the process is essential. This involves identifying the business objectives that the process supports. For example, managing customer inquiries effectively can help improve customer satisfaction, reduce customer churn, and increase revenue.
Finally, it’s crucial to identify the expected outcome or deliverable of the process. This involves understanding the result that is expected when the process is complete. For example, if the process is to manage inventory, the expected outcome could be to ensure that the right products are available at the right time to meet customer demand.
Once the process or task has been identified, it’s important to document it clearly and concisely. This includes defining any key terms or concepts, outlining the purpose of the process, and providing context around why it is important. By doing this, team members will clearly understand what the process involves and why it is essential to the business’s success.
Step 2: Define the Steps
The second step of creating an Internal Process Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) is to define the steps required to complete the process or task identified in Step 1. This step involves breaking down the process into its components and outlining each step in detail.
To begin, it’s vital to identify all of the actions that need to be taken to complete the process or task. This involves breaking down the process into its components and identifying each step needed to complete the process successfully. For example, if the process is to manage customer inquiries, the steps could include the following:
- Receiving the inquiry from the customer
- Recording the inquiry in a customer service system
- Assigning the inquiry to a customer service representative
- Investigating the inquiry and providing a resolution to the customer
- Closing the inquiry in the customer service system
Once the individual steps have been identified, it’s important to define each step in detail. This involves outlining the specific actions that need to be taken, the materials and equipment required, and any potential issues that may arise. Additionally, it’s essential to guide how to resolve any issues arising during the process.
It’s also important to consider the order in which the steps need to be taken. The steps should be organized logically that make sense to team members following the SOP. Consider using bullet points, numbered lists, or flowcharts to help team members navigate through the SOP.
Step 3: Organize the Steps
This step organizes the steps defined in Step 2 into a logical order. This step involves reviewing the steps that were defined and identifying the most effective way to arrange them for maximum efficiency and clarity.
To begin, it’s important to review the steps defined in Step 2 and consider how they relate to each other. This involves analyzing the workflow and identifying any dependencies or interdependencies between steps. For example, if Step 1 must be completed before Step 2 can begin, it’s essential to ensure the steps are organized correctly.
Once the dependencies and interdependencies have been identified, it’s important to organize the steps into a logical order that makes sense to team members following the SOP. This may involve grouping related steps or arranging the steps in a specific sequence that maximizes efficiency.
Consider using headings, subheadings, and numbering to help organize the steps and make them easier to follow. Additionally, it may be helpful to include diagrams or flowcharts that illustrate the workflow and the relationships between the steps.
It’s also important to consider how the SOP will be used in practice. For example, if multiple team members use the SOP in different locations, it may be helpful to organize the steps in a way that is easily accessible and navigable.
Step 4: Assign Roles and Responsibilities
Step 4 of creating an Internal Process Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) is to assign roles and responsibilities for each step of the process defined in Step 2. This step involves identifying who is responsible for each step and what their specific role is in the process.
To begin, it’s essential to review the steps defined in Step 2 and consider who is best suited to perform each step. This involves analyzing the skills and expertise required for each step and identifying team members with those skills and expertise.
Once the team members have been identified, assigning specific roles and responsibilities for each step is important. This may involve designating a team member as the primary person responsible for a particular step or assigning multiple team members to share responsibilities.
In addition to assigning roles and responsibilities, it’s important to define the expectations for each role. This includes outlining the specific tasks that need to be performed, the expected timeline for completing those tasks, and any quality standards that need to be met.
Consider using a table or chart to outline the roles and responsibilities for each step. This can help make the information clear and easy to understand for team members following the SOP.
Finally, to communicate the roles and responsibilities to the team members following the SOP. This may involve conducting training sessions, providing written instructions, or holding team meetings to discuss the SOP and answer any questions.
Step 4 of creating an internal process SOP involves assigning roles and responsibilities for each process step. By identifying team members with the necessary skills and expertise and defining the expectations for each role, businesses can create a well-defined SOP that supports efficiency, reduces errors, and achieves business objectives.
Step 5: Include Supporting Documents
Step 5 of creating an Internal Process Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) includes supporting documents that provide additional information and guidance for team members following the SOP. This step involves identifying any necessary documents, templates, or resources to help team members understand and follow the process defined in the SOP.
To begin, it’s important to review the steps in Step 2 and consider what types of supporting documents would be helpful for team members. This may include documents such as checklists, forms, templates, guidelines, or reference materials.
Once the supporting documents have been identified, organize them easily for team members to access and use. This may involve creating a separate section within the SOP for supporting documents or providing links to external resources.
In addition to including supporting documents, ensure that the documents are up-to-date and relevant. This may involve regularly reviewing and updating the documents to reflect the current process and any changes made accurately.
Consider using headings or subheadings to organize the supporting documents within the SOP. This can help make the information clear and easy to understand for team members following the SOP.
Step 6: Review and Test the SOP
We will review and test the SOP before implementing it during this step. This step ensures that the SOP is complete, accurate, and effective in achieving the intended objectives.
To begin, it’s necessary to review the entire SOP to ensure that all steps have been defined clearly and accurately, roles and responsibilities have been assigned appropriately, and all necessary supporting documents have been included. This review should be done by a team member who has not been involved in creating the SOP to ensure an objective perspective.
Once the SOP has been reviewed, it’s important to test it in a real-world setting to ensure that it effectively achieves its intended objectives. This may involve conducting a trial run of the process defined in the SOP with a small team of team members. The trial run should be conducted in a controlled environment and should involve team members who have not been involved in creating the SOP.
During the trial run, it’s crucial to observe and gather feedback from team members on the effectiveness of the SOP. This feedback can be used to make any necessary adjustments or improvements to the SOP before it is widely implemented.
After the trial run, it’s important to review the feedback received and make any necessary adjustments or improvements to the SOP. This may involve revising the steps, adjusting the roles and responsibilities, or adding or removing supporting documents.
Once the adjustments or improvements have been made, it’s important to review and test the SOP again before implementing it more widely. This may involve conducting additional trial runs with different team members or in different settings to ensure that the SOP is effective in various situations.
Step 7: Continuously Update the SOP
The final step’s goal is to update the SOP as needed continuously. This step involves reviewing and updating the SOP regularly to ensure it remains accurate and effective in achieving the intended objectives.
To begin, establish a regular review schedule for the SOP. This may involve reviewing the SOP quarterly, annually, or more frequently if the process or task defined in the SOP is subject to frequent changes.
During the review process, it’s important to gather feedback from team members using the SOP. This feedback can be used to identify any issues or areas for improvement and make necessary adjustments or updates to the SOP.
In addition to gathering feedback, review the process or task defined in the SOP to ensure that it remains accurate and effective in achieving the intended objectives. This may involve reviewing the process with subject matter experts, conducting research, or analyzing performance data.
Once any necessary adjustments or updates have been made to the SOP, it’s essential to communicate the changes to the team members who will be using the SOP. This may involve conducting training sessions, providing written instructions, or holding team meetings to discuss the updates and answer questions.
Finally, ensuring team members know the SOP and how to use it is vital. This may involve providing access to the SOP through a central document management system, links to external resources, or conducting training sessions.
Optimizing the Internal Process
Optimizing the internal process SOP can help ensure it is visible and accessible to team members who need it. Here are some tips for optimizing the SOP:
- Use clear and concise language that is easy to understand
- Include relevant keywords in the title and throughout the content
- Use headings and subheadings to break up the content and improve readability
- Link to relevant internal and external resources to provide additional information
- Use alt tags for images and optimize file names
Conclusion
An internal process SOP is vital for businesses of all sizes. By following the essential elements outlined in this article and optimizing the SOP, businesses can ensure that team members have the necessary guidance to complete tasks efficiently and effectively. Additionally, regularly reviewing and updating the SOP can help businesses stay relevant and competitive in an ever-changing business landscape.







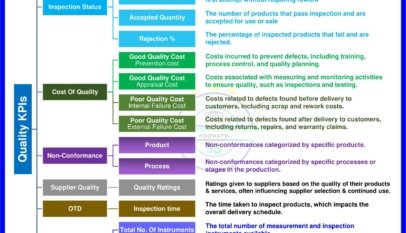








Please You will sharing trend analysis data examples
I need to create a new SOP related Trend Analysis
Title: Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) for Trend Analysis
Objective: To establish a systematic process for conducting trend analysis to identify patterns, changes, and potential opportunities or risks within a specific industry, market, or business environment.
Scope: This SOP applies to all team members analyzing trends, including market researchers, data analysts, and business strategists.
Preparation
1.1 Define the objective: Clearly outline the purpose and goals of the trend analysis, such as identifying emerging markets, analyzing competitor performance, or understanding customer preferences.
1.2 Identify data sources: Determine the relevant data sources, such as internal records, industry reports, market research, or social media platforms.
1.3 Assemble a team: Form a multidisciplinary team with the necessary skills and expertise, including data analysts, market researchers, and industry experts.
Data Collection
2.1 Collect historical data: Gather data from the identified sources, focusing on the period relevant to the analysis.
2.2 Ensure data accuracy: Verify the accuracy and reliability of the collected data, making sure it is up-to-date, relevant, and from credible sources.
2.3 Organize data: Clean and organize the data to ensure consistency and compatibility for analysis.
Data Analysis
3.1 Identify trends: Using data visualization tools, such as charts and graphs, examine the data for patterns, changes, or anomalies over time.
3.2 Analyze trends: Investigate the identified trends, determining their significance, causes, and potential impact on the business or industry.
3.3 Compare trends: Evaluate trends concerning the overall market, industry, or competitors to gain insights and context.
Interpretation and Reporting
4.1 Interpret findings: Assess the implications of the identified trends, considering both opportunities and risks they may present.
4.2 Develop recommendations: Based on the findings, create actionable recommendations to capitalize on opportunities or mitigate risks.
4.3 Prepare a report: Compile a comprehensive report, including data visualizations, interpretations, and recommendations, to present to stakeholders.
Implementation and Monitoring
5.1 Implement recommendations: Execute the recommended actions, such as adjusting marketing strategies, developing new products, or entering emerging markets.
5.2 Monitor progress: Continuously track the performance of implemented recommendations and the ongoing development of identified trends.
5.3 Update trend analysis: Periodically repeat the trend analysis process to stay informed about market, industry, or business environment changes.
Review and Improvement
6.1 Evaluate the effectiveness: Assess the effectiveness of the trend analysis process, considering the accuracy of predictions, the value of insights, and the success of implemented recommendations.
6.2 Identify areas for improvement: Determine any weaknesses in the process and identify opportunities for improvement.
6.3 Update the SOP: Incorporate improvements and update the SOP as needed to ensure its ongoing effectiveness and relevance.
By following this SOP, organizations can systematically conduct trend analysis to stay ahead of the curve, make informed decisions, and capitalize on emerging opportunities or mitigate potential risks.