Quality management is a crucial aspect of any organization’s success, and one of the most important components of this process is the implementation of effective Corrective and Preventive Actions (CAPA). CAPA is a systematic approach to identifying, documenting, and addressing problems within a business to ensure that they do not recur. In this blog post, we will dive into the various elements of CAPA and provide a comprehensive guide to help you better understand and implement this vital quality management process.
- Importance of CAPA in Quality Management
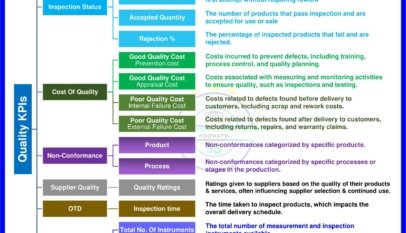
CAPA is the cornerstone of an organization’s Quality Management System (QMS). It plays a significant role in maintaining and improving product quality, ensuring regulatory compliance, and enhancing customer satisfaction. Implementing CAPA is a good business practice and a regulatory requirement in pharmaceuticals, medical devices, and food and beverage industries.
- Identifying and Investigating Problems
The first step in CAPA is identifying and investigating problems or non-conformities within the organization. This can involve analyzing data from internal audits, customer complaints, process monitoring, or product returns. Organizations should develop a systematic approach to identifying and documenting problems using standardized forms or a centralized database.
- Root Cause Analysis
Once a problem has been identified, the next step is to perform a root cause analysis. This is a systematic method for determining the underlying cause(s) of a problem or nonconformity. Various tools and techniques can be used to analyze root causes, including the 5 Whys, Ishikawa (fishbone) diagrams, and Failure Modes and Effects Analysis (FMEA).
- Implementing Corrective Actions
Corrective actions are the steps taken to eliminate the root cause(s) of a problem and prevent its recurrence. These actions should be based on the root cause analysis findings and may include changes to procedures, training, or equipment. Developing a plan for implementing corrective actions, including assigning responsibility, setting deadlines, and allocating resources, is important.
- Implementing Preventive Actions
Preventive actions are proactive measures taken to identify potential problems before they occur and implement changes to prevent them. Examples of preventive actions include conducting risk assessments, updating procedures, and implementing process controls. As with corrective actions, developing a plan for implementing preventive actions is essential, including assigning responsibility, setting deadlines, and allocating resources.
- Verification of Effectiveness
After implementing corrective and preventive actions, verifying their effectiveness in addressing the identified problem(s) is crucial. This can involve monitoring relevant data, conducting follow-up audits, or testing product samples. If the actions are ineffective, further investigation may be needed to identify additional root causes and implement new corrective and preventive actions.
- Documentation and Record Keeping
Proper documentation and record-keeping are essential components of CAPA. This includes maintaining records of identified problems, root cause analysis findings, corrective and preventive actions, and verification results. Accurate documentation ensures that organizations can demonstrate compliance with regulatory requirements and enables continuous improvement through the analysis of historical data.
- Continuous Improvement
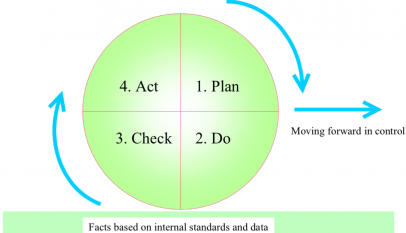
CAPA should be viewed as an ongoing process integrated into the organization’s overall QMS. This means regularly reviewing and updating procedures, conducting training, and monitoring performance to identify opportunities for improvement. By continually refining and enhancing CAPA processes, organizations can achieve higher product quality and customer satisfaction levels.
Implementing an effective CAPA system is crucial for any organization that aims to maintain high quality and compliance standards. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can establish and maintain a strong CAPA process that helps meet regulatory requirements, promotes continuous improvement, and drives long-term success. It’s important to remember that quality management is not a one-time task but an ongoing journey that demands constant vigilance, dedication, and commitment. By embracing and integrating the CAPA process into your organization’s culture, you can proactively address potential issues and consistently provide top-notch products and services to your customers. So, begin constructing your CAPA system today and pave the road to your organization’s more prosperous future.