P dash M Analysis is a systematic Problem-Solving Philosophy for Chronic Losses. The term P-M Analysis comes from the following origin: P – Phenomena(non), Physical; M – Mechanism, Relationship (Machine, Man/Woman, Material, Method)
When To Use P-M Analysis?
Root Cause Analysis
Two Types of Problem Solving Techniques
Why is the 5-why Analysis effective?
Example
Problem: No.1 conveyor stopped.
What is Actually happening (Phenomenon):
Overload and the fuse blew.
Why-1 Why was there an overload?
The bearing was not sufficiently lubricated.
Why-2 Why was it not lubricated sufficiently?
The lubricating pump was not pumping.
Why-3 Why was it not pumping sufficiently?
The shaft of the pump was worn and rattling.
Why-4 Why was the shaft of the pump was worn and rattling.
There was no strainer attached and metal scrap got in.
Why-5 Why was no strainer attached?
There are no checking rules.
Action is taken for Root-Cause
|
Why |
Answer (Observation) |
Action |
|
Why was there an overload? |
The bearing was not sufficiently lubricated. Logical linkage is required |
the bearing was replaced. |
|
Why was it not lubricated sufficiently? |
The lubricating pump was not pumping. Logical linkage is required |
The lubrication pump was checked. |
|
Why was it not pumping sufficiently? |
The shaft of the pump was worn and rattling. |
The shaft of the pump was replaced. |
|
Why was the shaft of the pump was worn and rattling? |
There was no strainer attached and metal scrap got in. |
The strainer was attached and cleaned up the lubrication tank. |
|
Why was no strainer attached? |
There are no checking rules. |
An Autonomous Maintenance standard has been developed. |
How can we identify what is actually happening?
Problem
Do’s
- Identify specific problems, which is the deviation between our expectations and actually happening.
Don’ts
- Before identifying specific problems, jump to action.
- Talking with just feeling.
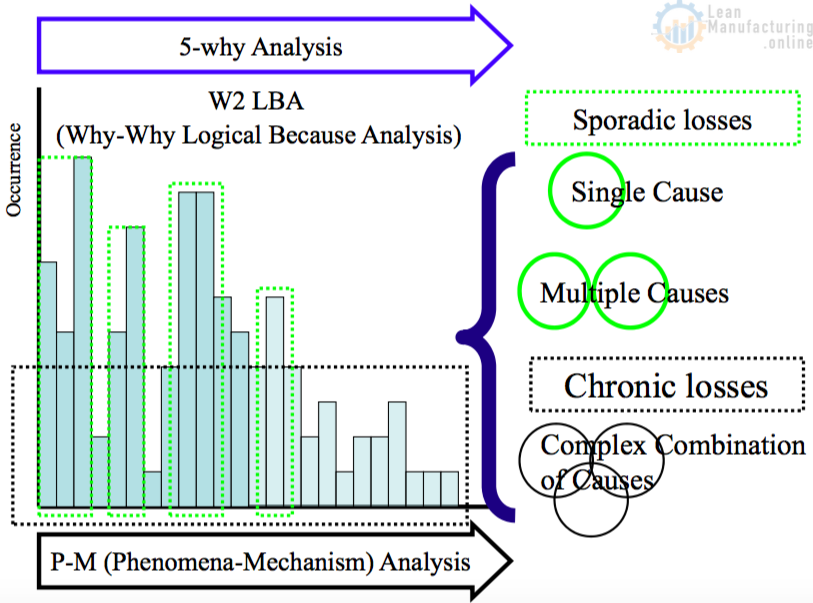
The 5-why analysis must be used when to identify “ Phenomenon” What is “Phenomenon”.
Phenomenon
Is (What is actually happening)
- The fact you observed with your eyes and numeric data.
- The fact without presumption
Is Not
- Your own opinion, feeling.
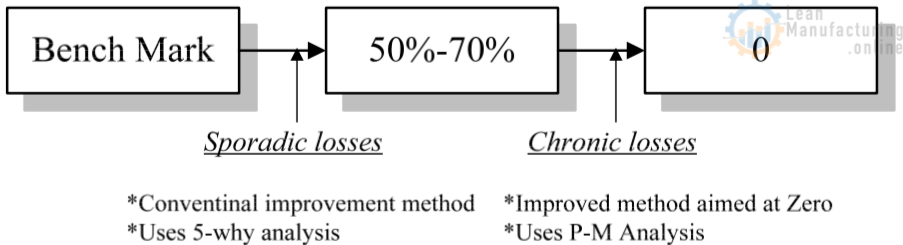
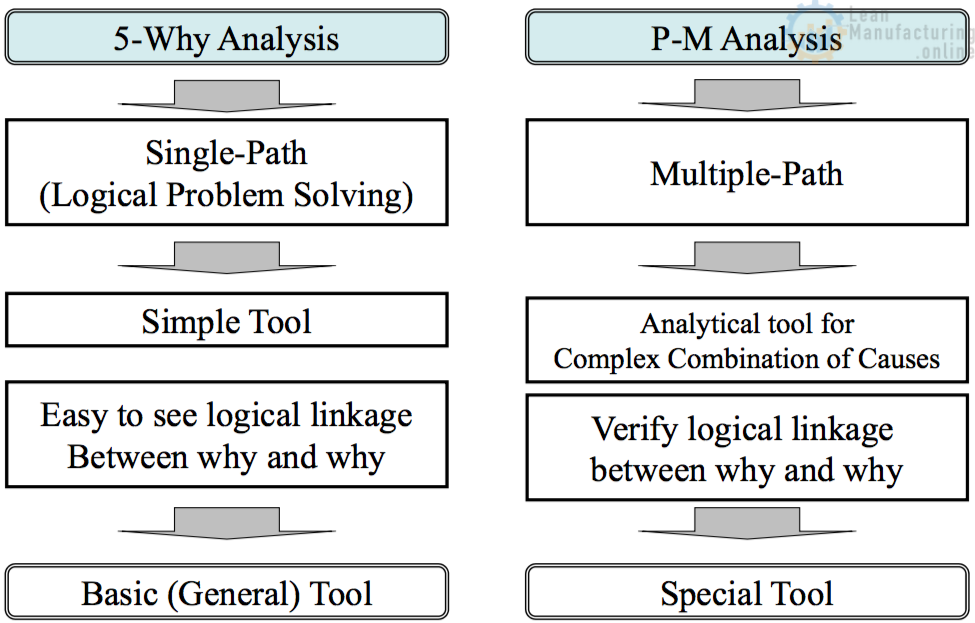
5-Why Analysis vs. P-M Analysis

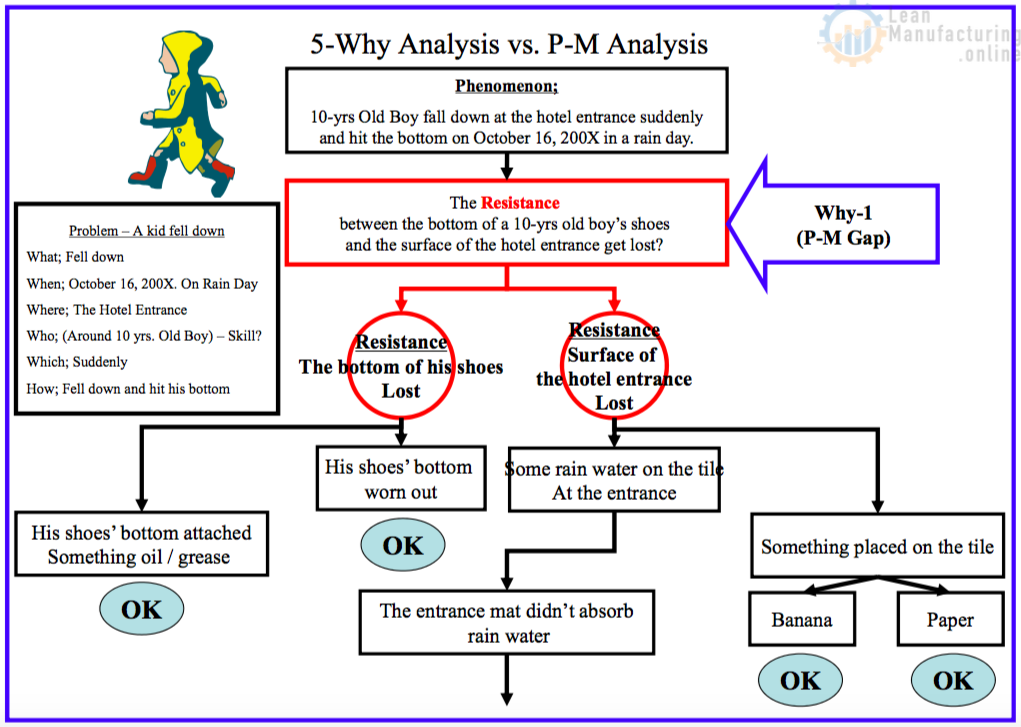
Features in P-M Analysis
|
P-M Analysis (Multiple-Path) |
5-Why Analysis (Single-Path) |
|
|
Phenomenon Statement (Analysis Start-Point) |
– The same step requires identifying the “Phenomenon”. |
|
|
Logical Linkage |
– Describe All Possible factors. – In order to describe all possible factors, Recommend setting up the “P-M Gap” Statement. |
– Describe clearly Why & Answer (because). |
|
Verification Process |
– Identify and describe All Possibilities first, and then verify which factors can contribute to the above possibility (“Gap from Principle of Operation”) -Identify “Gap” instead of “Why” |
– Before moving the next why require to verify (capture) the evidence. – You say “Why”, capture the “evidence”. -You can say “Because …” |
|
Key Points for Use |
– Understand the differences between “Fish-Bone Analysis” and/or “Why-Why Analysis” |
– Show the “evidence” before moving to the next why. |
|
Who should use |
– The higher Team Leaders’ Level. – Since AM Step-4 |
– All Employee |
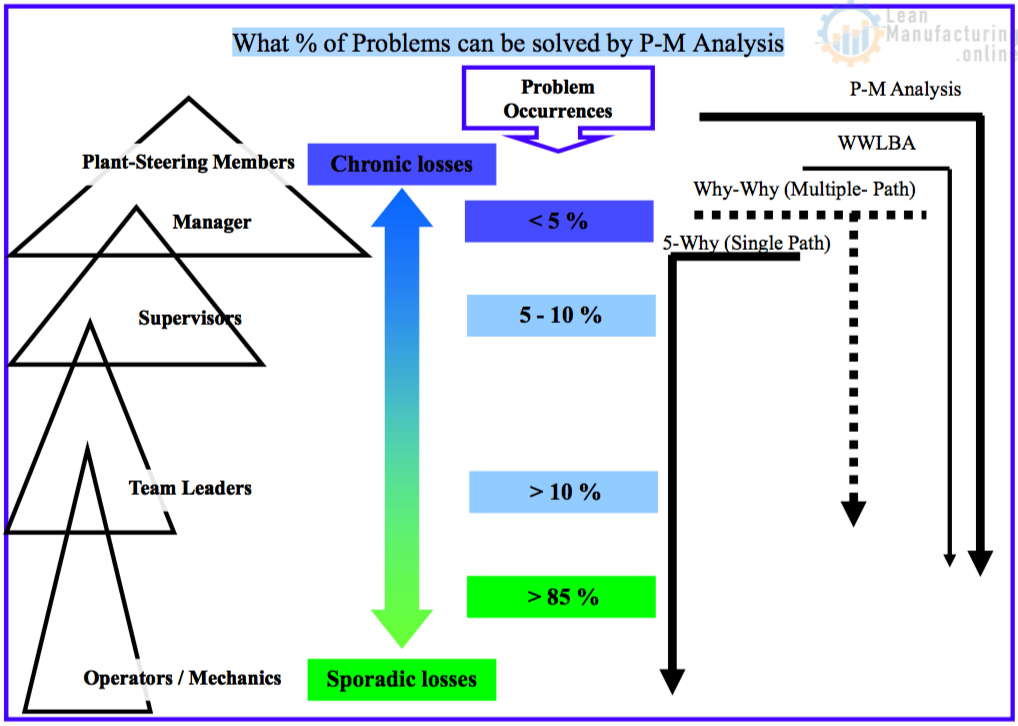
P-M Analysis
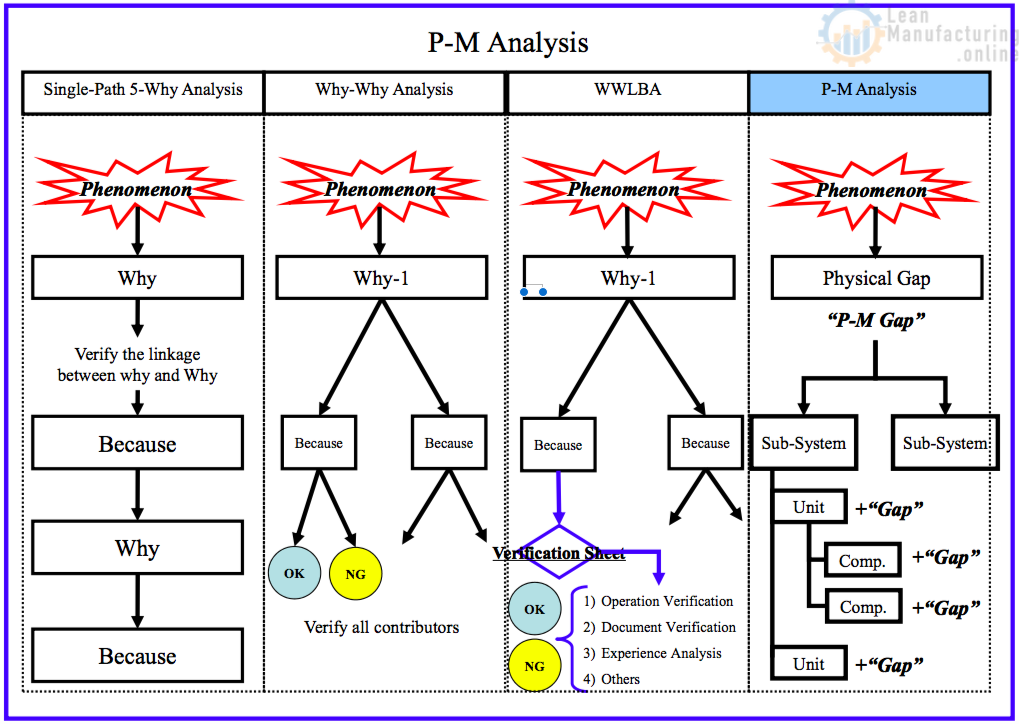
What % of Problems can be solved by P-M Analysis
Steps of P-M Analysis
|
P-M Analysis Step |
Activity |
Key Learning |
|
Step-1 |
Clarify the Phenomenon |
Phenomenon Statement |
|
Step-2 |
Examine-in terms of Physical Principle Involved |
P-M Gap |
|
Step-3 |
Analyze Contributing Conditions |
Principle of Operation |
|
Step-4 |
Study the relationship between 4M’s |
Machine Structure & Function Diagram |
|
Step-5 |
Study of what the conditions must be |
Optimal Conditions |
|
Step-6 |
Study of investigation methods |
Machine Diagnosis Technique & Measurements |
|
Step-7 |
Find out All Potential Abnormalities |
|
|
Step-8 |
Implement & Plan Countermeasures |
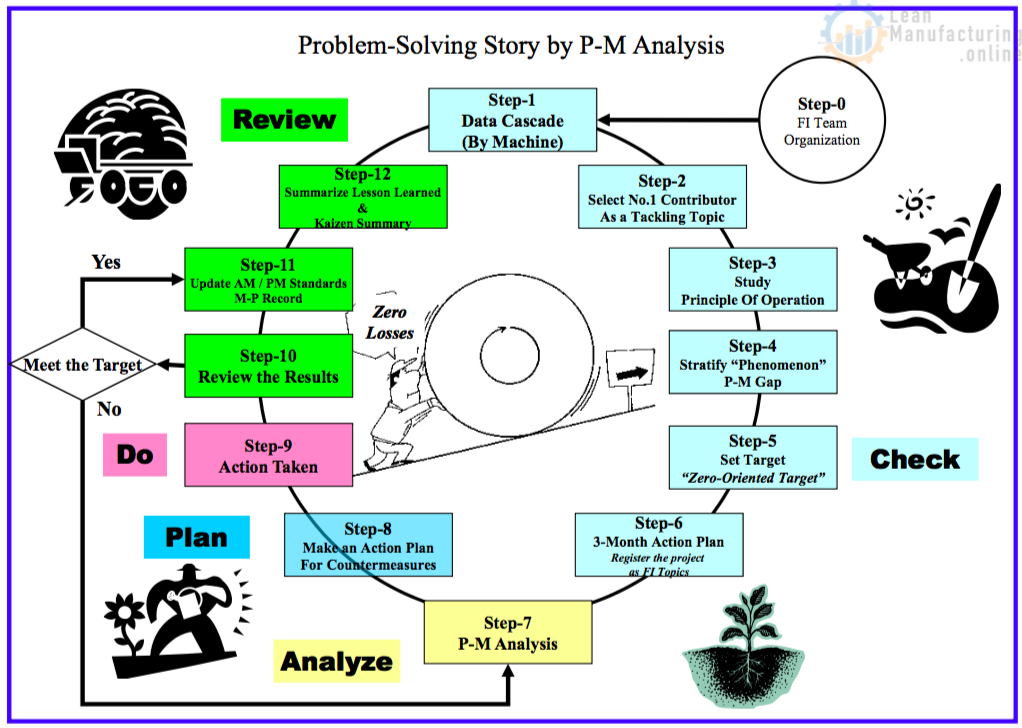
P-M Analysis Story Board Layout
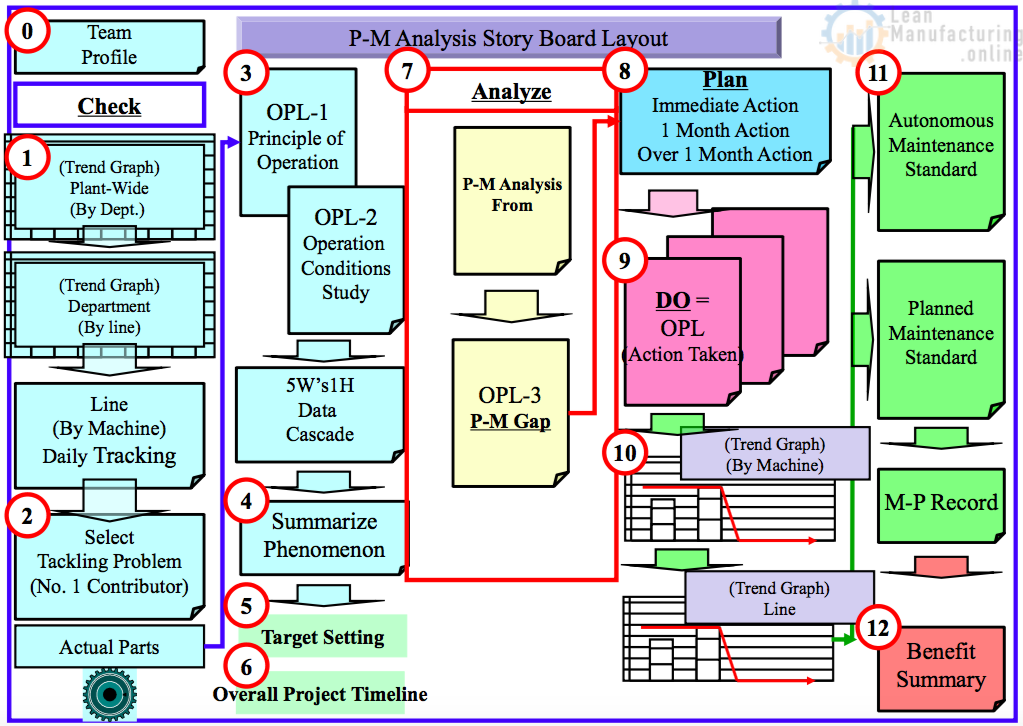
Problem-Solving Story by P-M Analysis
CAP-Do Cycle & P-M Analysis
|
CAP-Do Cycle Process |
P-M Analysis Step |
||
|
Check |
1-1 Analyze the “Gap” between Target and Actual situation. 1-2 Prioritize No.1 Contributor as FI Theme (Topics) 1-3 Stratify Problem into Phenomenon |
Step-1 |
Clarify the Phenomenon |
|
Step-2 |
Examine-in terms of the Physical Principle involved. (P-M Gap) |
||
|
Analyze |
2-1 Principle of Movement (Processing) -Identify the “Gap” between the Principle of Processing and Actual Conditions. -Step-1 to Step-7 |
Step-3 |
Contribute Conditions |
|
Step-4 |
Study the relationship between 4M’s |
||
|
Step-5 |
Study of what the condition must be (Optimal Condition) |
||
|
Step-6 |
Study of investigation method |
||
|
Step-7 |
Point out Abnormal Conditions |
||
|
Plan |
3-1 Develop an Action Plan |
Step-8 |
Implementation and plan of improvement |
|
Do Review |
4-1 Take action for each cause and Root- Cause 4-3 Verify the result in 3 months (90 days) 4-4 Feedback the points of sustaining (maintaining) * Review the Results (Benefit) |
||