EFFECTIVE TEAM MEETINGS – Step 1 Establish Meeting Guidelines
- The first step for effective meetings
- Defines how teams will work together
- Provides team with a set of expectations
- Helps prevent misunderstandings and disagreements
At the first meeting, set up RULES for yourselves that everyone agrees to follow.
They set the OBJECTIVE of HOW you all want to work together.
Later, you can point to them in a more objective, less personal way – to say “we agreed” to do this.
EFFECTIVE TEAM MEETINGS – Step 1 Meeting Guidelines – Example
DECISIONS – decide how you will make decisions.
What is Consensus?
It doesn’t mean that everyone is in total agreement with the decision, it means that everyone agrees to ACCEPT AND SUPPORT the decision of the team.
There is a good short module on the Decisions that discusses different methods of making decisions – and what to consider when selecting which method to use.
Be careful not to call Majority Rule a Consensus – it is not unless the people who voted against the decision understand and support it in the end.
When setting your guidelines, consider things you think might not go well – set a ground-rule to help keep you on the right track for that behavior or issue. Consider your history and experience.
EFFECTIVE TEAM MEETINGS – Step 2 Plan the Meeting
- Set objectives
- Handle logistics
- Prepare the agenda
The next step is PLANNING the meeting.
You may think LOGISTICS are obvious – but it is often overlooked – handouts, location, audiovisual…
What kinds of things have gone wrong re. Planning in your experience?
Here’s an example agenda that has worked well in manufacturing sites.
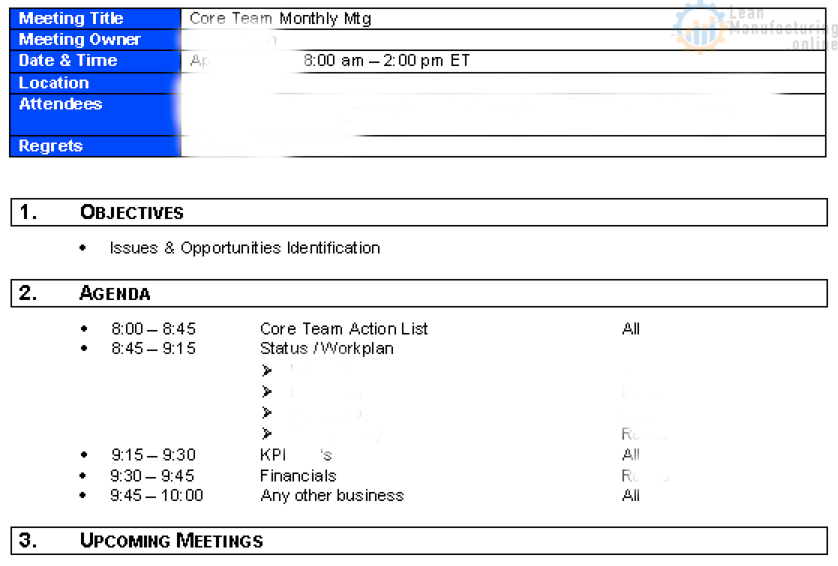
Note the detail of the TIME included on the agenda. This is a good tool to use to keep the meeting from getting off track. Often conversations that go on in meetings between 2 or 3 people could more effectively use limited resources by taking them off-line. We tend to want to solve all the issues/problems at the meeting, which is not always practical – TIMES keep that in check.
Also, use a PARKING LOT flip chart – decide WHO will address an issue and WHEN outside the meeting.
EFFECTIVE TEAM MEETINGS – Step 3 Conduct the Meeting (Site Steering Committee)
- Open the Meeting
- Review minutes and status of actions from the last meeting
- Review, Identify & Prioritize Issues & Activities against the Plan for each key area:
- Safety, Health, Environment
- Quality
- Improvement Teams
- Production
- Maintenance
- Human Relations
- Any Capital Project Activities
- KPI’s (PQCDSM)
- Record/review new actions; assign timing and responsibility.
- Any other business & set date for next meeting.
Now the step of actually CONDUCTING the meeting.
This is in the context of TPM. The meeting flow is aligned with the pillars. MASTER PLAN defines the ACTIVITIES, RESOURCES & TIMELINES.
Steering Committee reviews the progress/status against the site Master Plan. The meeting revolves around the status of that plan.
One main role of the Steering Committee is to REMOVE OBSTACLES to progress on the Plan.
EFFECTIVE TEAM MEETINGS -Step 4 Issue Team Documents
- Distribute minutes immediately or within 2 days
- Documentation helps leverage learning among teams
- Paper trail provides a communication vehicle
DOCUMENTATION is a good communication tool regarding what everyone agreed and committed to!!
EFFECTIVE TEAM MEETINGS – Step 4 Issue Team Documents – Meeting Minutes
- Minutes for each meeting may contain:
- Date and time of the meeting
- Names of those attending
- Topics discussed
- Decisions made and actions taken
- Assignments made
- Long- and short-term action plans
- Meeting evaluation
- Date, time, and location of next meeting
The bolded points are KEY to Success
If you do nothing else, at least document ACTIONS for your meetings!!
EFFECTIVE TEAM MEETINGS – Step 4 Issue Team Documents – Action List
This format has proven easiest
Sequential numbers
Action items stay on the list until complete, then move to the Complete list for the historical record.
Every meeting, review the status and put a comment on progress/report
EFFECTIVE TEAM MEETINGS – Step 5 Evaluate the Meeting
- Provides teams with the opportunity to critique the effectiveness of teams
- Helps team resolve problems
- Usually takes place at the end of the meeting
- Evaluate formally and informally
- Define what worked well and what to improve
The last step is EVALUATING the meeting.
Don’t have to do every meeting – but set a time frame for how often to assess.
Talk briefly about how you are doing.
You can use a form with scores – or just discussion, or flip chart.
(Discussion on FACILITATORS – what that role provides – can a member be a facilitator? Rotate the role of facilitator. The facilitator focuses on the PROCESS/HOW of the meeting vs. the CONTENT/WHAT) Timekeeper, agenda…
There is Facilitator training material available if wanted.
ROLES & RESPONSIBILITIES OF A PLANT STEERING COMMITTEE

The Red section, step 0 – It will take more than just this meeting to sort out the FOUNDATION – these steps are important GROUNDWORK for the rest of the process.
SUPPORT ORGANIZATION = PILLAR CHAMPS
Once the Steering Committee is in place and understands their roles – then you do the 6 steps.
- The VISION is where you want to go
- The MISSION defines HOW you will get to your destination.
- The MUST WIN BATTLES are like the “Interstates” you will use. The STRATEGIC THRUSTS are how you will win the MWB’s
- PLAN for the next 12 – 18 months. ACTIONABLE plan to get to the Vision. The plan is the DETAIL on achieving the vision.
- MOST of what you are charged with as a Steering Committee – and the hardest part – is GETTING PEOPLE TO IMPLEMENT THE PLAN. Generate enthusiasm!!
- Loopback – are you getting to the Vision? Revisit the Vision – is it still valid?
Site Steering Committee – How are you going to ENERGIZE RESOURCES – and are you ON TRACK to the GOALS??
Responsibilities of the Plant Steering Committee
- Develop the Vision
- Provide sound Leadership
- Articulate a common, shared vision for the site consistent with the company Vision.
- Create the Mission
- Provide clear direction
- Establish the Must Win Battles, Strategic Thrusts, Key Strategies
- Determine the most fundamental changes (2 – 5 yrs out) which must occur to accomplish the Vision in 5 yrs.
- Establish Plan
- Develop an implementable site Master Plan (12 – 18 months) to achieve Key Strategies, Must Win Battles and Vision
- VISION will be POSTED – people need to RELATE to it.
- Mission – “we will achieve the Vision BY…..”
Drilling down from the vision to the action plans is sort of like the “5 Why” analysis – except it’s the 5 HOWs. Keep asking “how will you do that” – to lower levels of detail.
- Energize Resources
- Champion change and lead by example
- Nominate, select, prioritize improvement activities and teams
- Provide education & training where needed
- Ensure appropriate resource is made available to sustain Continuous Improvement
- Anticipate, avoid and/or remove obstacles to progress at the plant level
- Promote pride and fun in the workplace
- Review Results and Assign Actions
- Report plant performance same way, one way
- Follow up / implement team recommendations
- Elevate relevant issues outside of plant control to the appropriate Leadership contact
- Publicly recognize worker/Team contributions
- Replicate positive results throughout the site and learn from mistakes
Remember we said most of your efforts will be to ENERGIZE RESOURCES.
Nominate, select, prioritize – Your role – there are limited resources and many opportunities.
Sustain Continuous Improvement – as laid out in the Plan. The key is to STRETCH – but make it ATTAINABLE.
Not just REMOVE OBSTACLES, but Anticipate and Avoid fun in the workplace – make it ENJOYABLE!!
Last: Review Results and
the same way one way – Everyone agrees on what measures are and how they affect
follow-up – Remember – The easiest way to demoralize a team is NOT to act on their recommendation / not even respond or recognize.
ELEVATE issues – understand what is in/out of your control and raise the issue for help if needed.
Recognize – goes back to “fun in the workplace” – we always tell people when they are wrong, but seldom when they are right – we just expect it.
Replicate – successes on one line – move to another.
Key Requirements For Success

So – what are the KEY REQUIREMENTS?
To summarize all those Responsibilities, your role is to
PROVIDE these 5 things to the site!
Key Requirements For Success
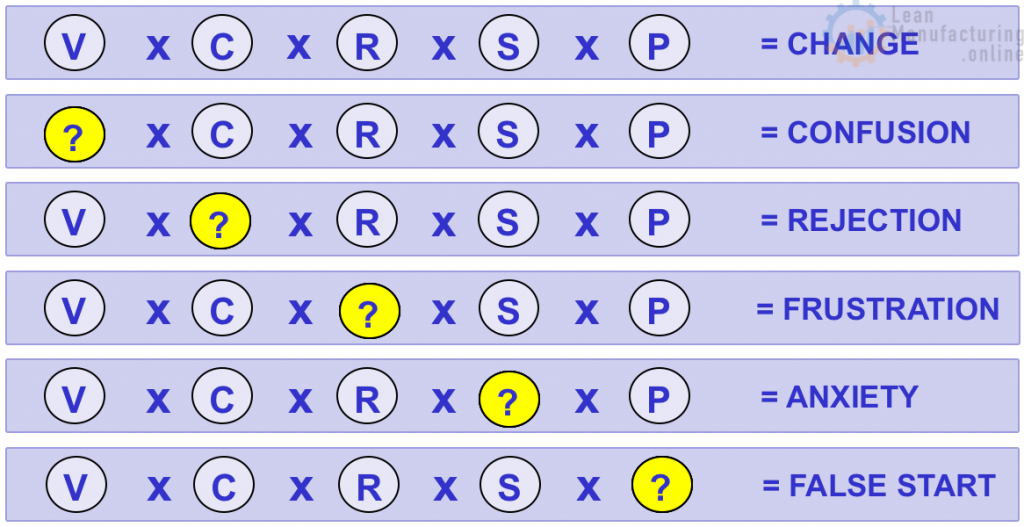
- If you have all these factors – VISION, COMMITMENT, RESOURCES, SKILLS, and a good PLAN, then the result is CHANGE!!
- If you have all but the Vision, there is confusion.
- If Commitment is missing, the change is Rejected
- If Resources are inadequate, people get Frustrated
- If people don’t have the skills they need, Anxiety holds back progress toward the change.
- And if the PLAN is not good, you’ll have False Starts and have to loop back to plan properly.
SITE MANAGEMENT VIA THE PILLAR STRUCTURE
TPM has borrowed the Steering Committee approach to management – with Continuous Improvement as the ultimate goal.
This is not solely TPM – it’s everything about how to manage a site – it should include new equipment installation, Framework Standards gap closure…. Everything that you are doing at the site should be managed by a pillar structure Steering Committee.
- 0. Build Support Infrastructure
- a. Identify Support Organization
- b. Develop Steering Committee
- 1. Develop the Vision –> Sets the Destination
- 2. Create Mission —–> Provides Purpose
- 3. Establish Strategy–> Determines the Path
- a. Define Policies –> Sets Rules of the Road
- b. Set Goals ——> Defines Success
- 4. Establish Plan —–> Provides Focus
- 5. Energize Resources -> Generates Passion
This is the “anchor slide” – we come back to it to show where we are in the steps. The next part is how to manage the site via a Pillar Structure. We are now talking about Building a Support Organization.
To be continued…