This post examines the role of Business Process Management (BPM) as an agile business model in a rapidly changing global economy. We discuss how BPM enhances productivity, speed to market, global market reach, compliance, and innovation. By implementing BPM principles, organizations can streamline their operations, respond quickly to market changes, and create an environment where innovation is encouraged and an integral part of daily operations.
Introduction
Organizations seek innovative ways to improve their operations, maintain a competitive edge, and ensure sustainable growth in an increasingly competitive global business environment. One such approach is adopting Business Process Management (BPM), a systematic approach to managing, optimizing, and streamlining an organization’s processes. This paper examines how BPM serves as a new, agile business model, addressing critical challenges faced by organizations in today’s economy.
Increased Productivity
The need to accomplish more with fewer resources is a pressing concern for modern businesses. By applying BPM principles, organizations can optimize their processes and eliminate redundancies, increasing productivity. BPM facilitates continuous process improvement, allowing companies to adapt to changing market conditions and maintain a competitive edge.
Speed to Market
In the fast-paced business landscape, the ability to quickly bring new ideas and products to market is critical. Effective BPM enables organizations to streamline their operations, identify and remove bottlenecks, and expedite the development and launching of new products or services. As a result, businesses can capitalize on emerging opportunities and maintain a leading position in their respective markets.
Reaching the Global Market
With the growth of the global economy, organizations must adapt to compete in an international marketplace effectively. BPM is crucial in streamlining supply chain operations and ensuring seamless integration across various geographies. By implementing BPM principles, businesses can optimize their processes, reduce lead times, and quickly respond to global market demands, enabling them to take advantage of opportunities wherever they may exist.
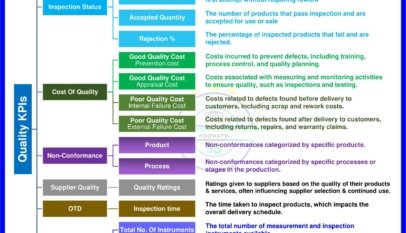
Achieving Compliance
Maintaining complex compliance, regulatory, and corporate governance requirements can be costly and time-consuming for organizations. BPM helps businesses systematically manage these requirements by standardizing processes, maintaining proper documentation, and ensuring transparency. As a result, organizations can efficiently achieve compliance while keeping costs under control and minimizing risks associated with non-compliance.
Accelerating Innovation
Innovation is essential for the long-term success and growth of any organization. BPM fosters an environment where innovation is encouraged and a normal part of daily operations. By implementing BPM principles, organizations can systematically identify and prioritize opportunities for improvement, rapidly test new ideas, and seamlessly integrate successful innovations into their processes. This agile approach to innovation enables businesses to adapt quickly to market changes and maintain a competitive advantage.
Conclusion
Business Process Management, as a new agile business model, provides organizations with the tools and methodologies necessary to navigate the challenges of the modern global economy. By adopting BPM principles, businesses can increase productivity, speed up time-to-market, expand their global reach, achieve compliance, and accelerate innovation. Organizations that leverage BPM to create agile and adaptable operations are better positioned to capitalize on emerging opportunities and ensure sustainable growth in a rapidly changing world.