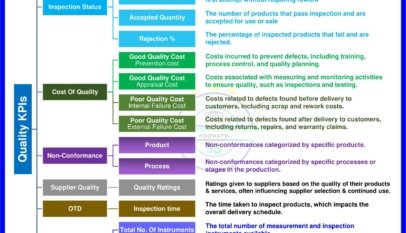
Cpk and Ppk are both measures of process capability, which is a way to evaluate the ability of a manufacturing process to produce parts within specified tolerances. They are used to assess whether a process is capable of consistently producing parts that meet the required specifications and to identify areas for improvement if the process is not capable.
Cpk is a measure of process capability concerning the process’s mean. It is calculated as:
Cpk = min(USL – mean, mean – LSL) / (3 * sigma)
where USL and LSL are the upper and lower specification limits, mean is the process’s mean, and sigma is the standard deviation of the process. Cpk values above 1.0 indicate that the process can produce parts within the specified tolerances, while Cpk values below 1.0 indicate that the process is not capable.
Ppk is similar to Cpk, but it is a measure of process capability with the target value of the process rather than the mean. It is calculated as:
Ppk = min(USL – target, target – LSL) / (3 * sigma)
where the target is the target value for the process. Ppk values above 1.0 indicate that the process can consistently produce parts that meet the target value, while Ppk values below 1.0 indicate that the process is incapable.
In summary, Cpk and Ppk are both measures of process capability used to assess a manufacturing process’s ability to produce parts within specified tolerances. Cpk is a measure of process capability in relation to the process’s mean. At the same time, Ppk is a measure of process capability concerning the target value of the process. Both measures are used to identify areas for improvement in the process and to ensure that the process can consistently produce parts that meet the required specifications.