Project management is a discipline that involves planning, organizing, and managing resources to achieve specific goals and objectives. It consists of several key processes and tools, including scope definition, scheduling, budgeting, risk management, quality assurance, communication, resource management, stakeholder management, change management, status reporting, and earned value management.
Project management is used in various contexts, including business, engineering, construction, and technology development. It helps to ensure that projects are completed efficiently and effectively within the defined scope, schedule, and budget. It also helps to identify and mitigate potential risks and monitor and control the project’s progress.
- Scope: The scope of a project refers to the defined boundaries and deliverables of the project. It includes the specific goals, objectives, tasks, and resources needed to complete the project.
- Schedule: The schedule is a timeline that outlines the planned start and end dates for each task or activity within a project. It helps to organize and track the progress of the project.
- Budget: The budget is a financial plan for the project, including the estimated costs of all resources and activities. It helps to ensure that the project stays on track financially.
- Risk: Risk refers to potential threats or challenges that could impact the success of a project. Project managers identify and assess risks to determine their likelihood and potential impact and develop mitigation strategies.
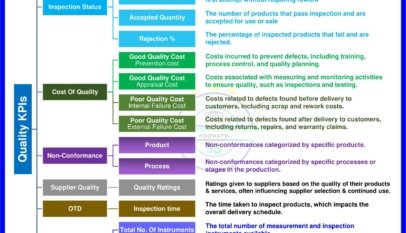
- Quality: Quality refers to the degree to which a product or service meets the specified requirements or expectations. In project management, quality assurance evaluates and verifies that the project meets the required quality standards.
- Communication: Communication is a critical aspect of project management, involving exchanging information, ideas, and feedback among team members and stakeholders.
- Resource: A resource is any item or person that is needed to complete a task or activity within a project. Resources can include materials, equipment, and human resources.
- Stakeholder: A stakeholder is any person or group with a vested interest in the project, including the project team, customers, and sponsors.
- Change management: Change management is the process of planning, implementing, and controlling changes to a project. It helps to ensure that changes are controlled and coordinated without disrupting the project’s progress.
- Status report: A status report is a document that provides updates on the progress of a project. It includes information on the project’s current status, any issues or challenges that have arisen, and the following steps to be taken.
- Work breakdown structure (WBS): A work breakdown structure is a visual representation of the work required to complete a project. It is a hierarchical breakdown of the project into smaller, more manageable tasks and activities.
- Gantt chart: A Gantt chart is a graphical representation of the schedule for a project. It shows the tasks, duration, and dependencies for each activity within the project.
- Earned value management (EVM): Earned value management is a project management technique that compares the planned value of the project with the actual value of the work completed. It helps track the project’s progress and identify potential issues or deviations from the plan.
Overall, the goal of project management is to deliver a successful project that meets the needs and expectations of the stakeholders and contributes to the organization’s overall success.