Need: To identify PMs and improvement opportunities for our critical systems.
Objective: To create a comprehensive list of improvements and PM requirements to improve the reliability of our equipment.
FMEA: Failure Mode and Effects Analysis
Concept of FMEA
- Identify ways the product or process could fail
- Determine effects resulting from the failure mode
- Then plan how to minimize the occurrence, or to respond to these potential failures
Benefits of FMEA
- Makes process visible
- Documents and tracks actions taken to reduce risks
- Prioritizes deficiencies to focus on improvement efforts
- Reduces the amount of rework, repair, and scrap
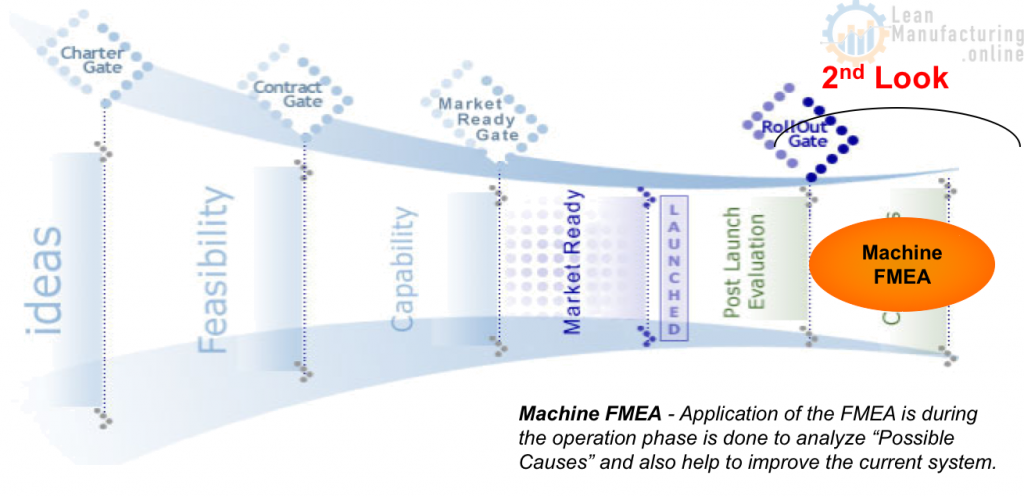
Where is FMEA used?
Five types of FMEA can be applied to different stages of the Product Innovation Funnel:

Why MFMEA?
Using this tool, we can develop corrective action plans that will remove or reduce the impact of the potential failure modes of a machine.
FMEA roadmap
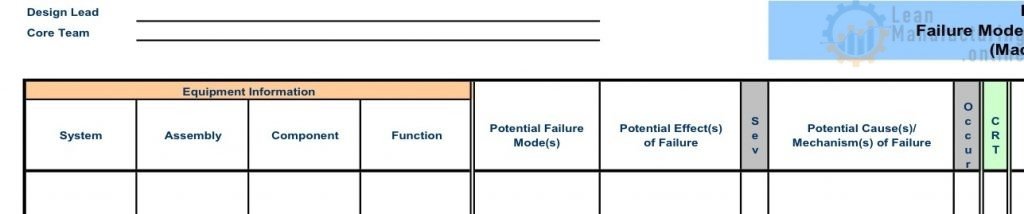
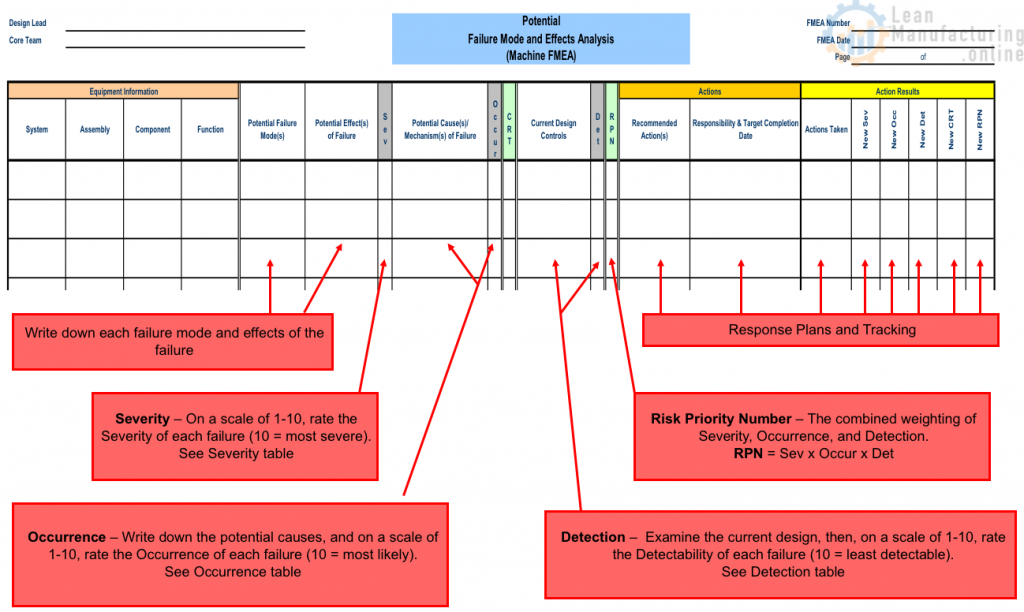
FMEA worksheet
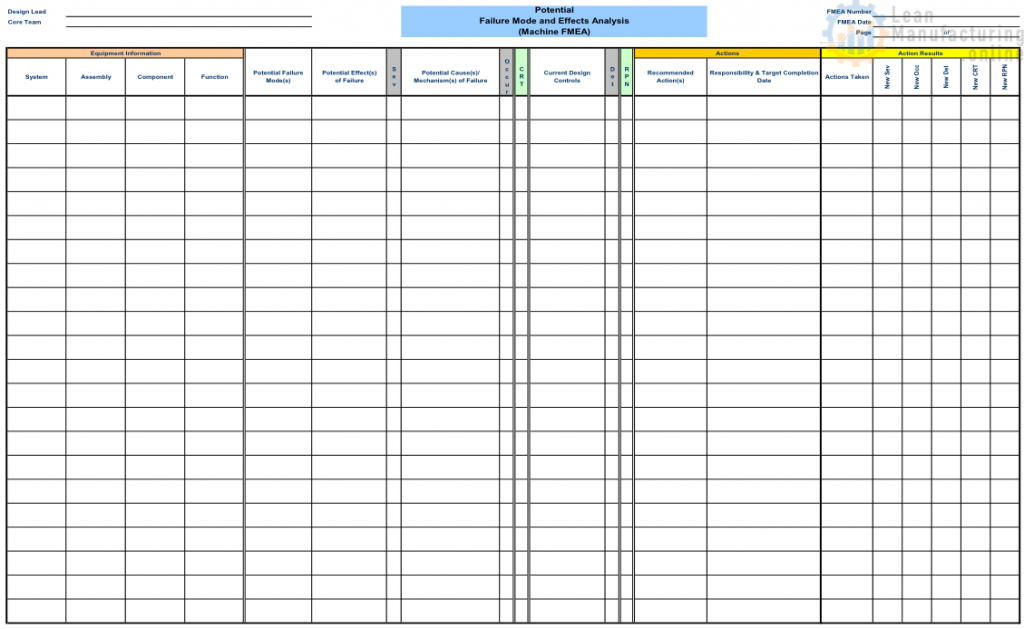
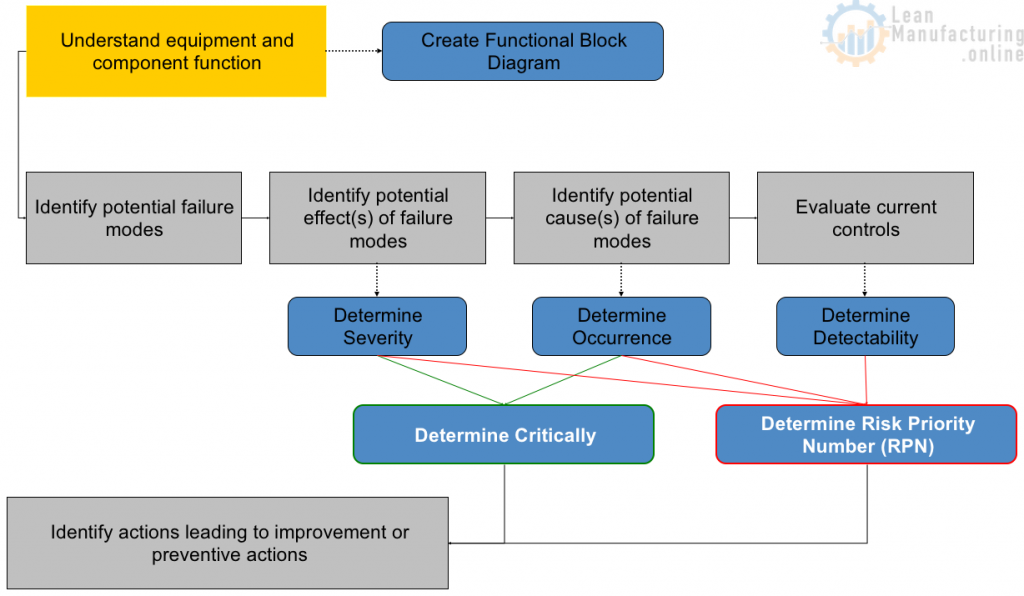
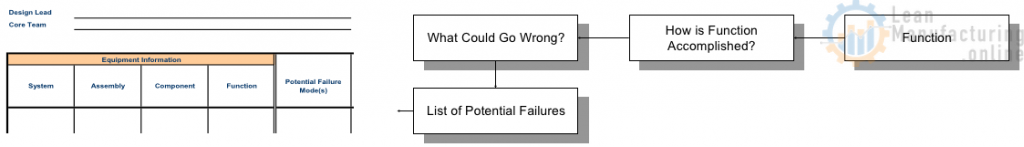
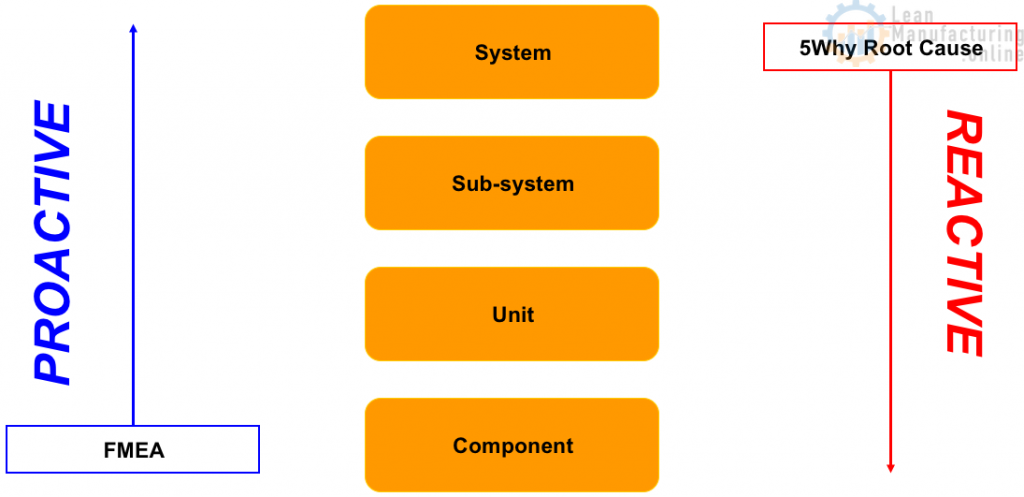
Understand equipment and functions
Understand and breakdown the system into: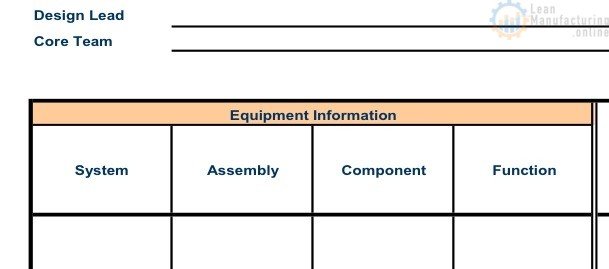
- Sub-system – Can be defined as a sequence of operation of the system in the manufacturing process
- Unit – Can be defined as a functional group of components having a condition of moving
- Component – Can be defined as a basic element of a system
Identify component functions:
The “first step” is CRITICAL to the process
…Use both Manuals, Drawings, and Supplier Information to collect data to understand the equipment and functions.
.Functional Block Diagram Example

Study Case – Palletizer breakdown – Step 1
Hands-on training for teams step 1
Divide into two groups:
- Group 1
- Mechanic #1
- Operator #1
- Supervisor #1
- Group 2
- Mechanic #2
- Operator #2
- Supervisor #2
- Each team will receive a flashlight and an FMEA training package
- Understand the equipment and list all component functions
Identify potential failure modes
Analyze & verify all potential failure modes for each component
- Failure: Ways in which components fail to perform the desired function/operation
- Failure mode: How a failure manifests itself. Typical cases are break, fatigue, bad contact, short circuit, premature stress, leak…
Study Case – Palletizer breakdown – Step 2
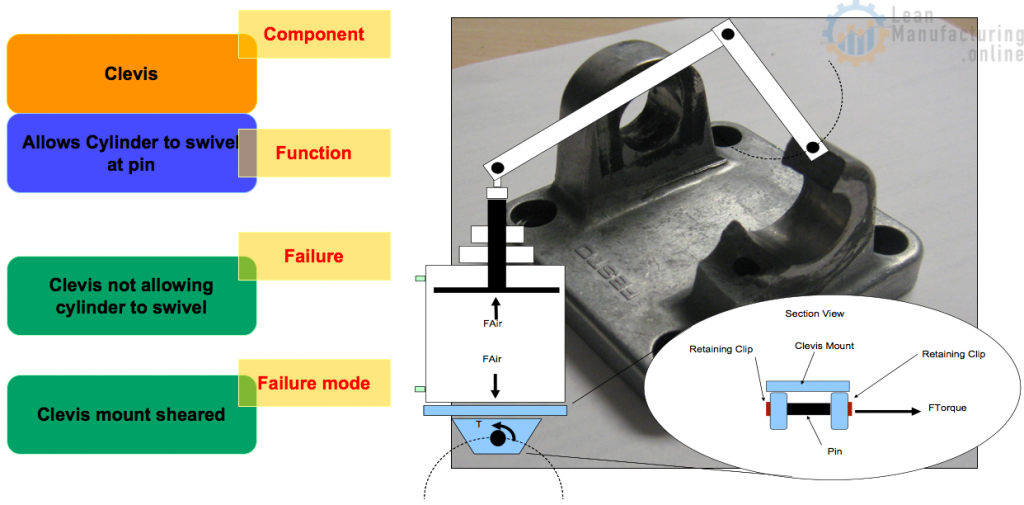
Hands-on training for teams step 2
- Each team will receive a flashlight and FMEA package
- Identify all potential failure modes
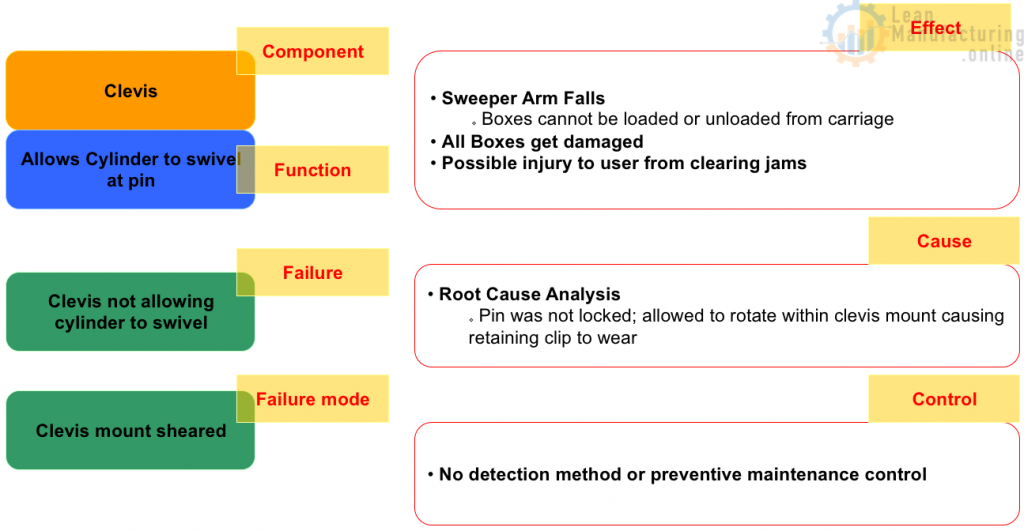
Identify potential effect(s) of failure modes

Analyze the effects of each failure mode. Effects can be described by the following:
- Breakdowns – Machine Downtime
- Minor Stops – Machine Downtime
- Set-up/Adjustments – Machine Downtime
- Start-up Losses – Machine Downtime
- Quality
- Safety
… The above are the categories that effect can be classified in. When identifying the effect be as specific as possible.
- Machine Downtime
- Boxes not turning, Full pallet jam, Degraded performance, etc…
- Quality
- Open flaps, Damaged Cases, etc…
- Safety
- Noise, Injury to the user, Odors, etc…
Determine Severity rating
Evaluate Severity Rating -> (1:10) for each failure mode effect See Severity Table*
Severity is a rating corresponding to the seriousness of the effect(s) of a potential equipment failure mode.
Severity is comprised of three components:
- safety considerations to equipment, operator, or customer
- equipment downtime
- quality
…A reduction of Severity can only be done through an improvement
MACHINE FMEA – Severity

FMEA – Identify the potential cause(s) of failure modes

Analyze immediate causes of each failure mode
- Design deficiency
- Machine process variation
Identification of causes should start with the failure modes with the highest severity rating.
Brainstorm potential cause(s) of each failure mode by asking questions such as:
- What could cause the component to fail in such a manner?
- What circumstances could cause the component to fail to perform its function?
Determine Occurrence rating
Evaluate Occurrence Rating -> (1:10) for each failure mode cause See Occurrence Table*
Occurrence is a rating corresponding to the likelihood that a particular failure mode will occur within a specific time period.

Determine Criticality ranking

Calculate the Criticality ranking
- The Criticality ranking is the product of the Severity and Occurrence rating
CRT = SEV x OCCUR
Remember, rankings like Criticality, in themselves, have no value or meaning
Criticality numbers should only be used to prioritize the potential design weaknesses for consideration of possible improvements and preventive maintenance
Evaluate current controls

Analyze control methods, techniques, devices, or tests used to:
- Detect the cause and lead to corrective design actions
- Detect the failure mode
- Prevent the cause or reduce the occurrence of the failure mode*
Identification of the control should begin with those failure modes with the highest Criticality ranking
*Note: Preventive Maintenance (TBM, predictive, visual controls) schedules, procedures, and in-plant resources are valid design controls to reduce the occurrence rating.
Determine Detection rating
Evaluate Detection Rating -> (1:10) for each failure mode See Detection Table*
Detection is an assessment of the ability of the controls to detect a potential cause or to detect the potential failure mode.

Determine the Risk Priority Number
Calculate the Risk Priority Number (RPN)
- The RPN is the product of the Severity, Occurrence, and Detection rating
RPN = SEV x OCCUR x DET
Remember, RPN, in itself, have no value or meaning
RPN should only be used to prioritize the potential design weaknesses for consideration of possible improvements and preventive maintenance.
Study Case – Palletizer breakdown – Step 3
Hands-on training for teams step 3
Each team will receive a flashlight and FMEA package
- Identify all:
-
- potential failure mode effects
- potential failure mode causes
- evaluate current control method
- identify all ranking – Severity, Occurrence, Detection, Criticality, and RPN
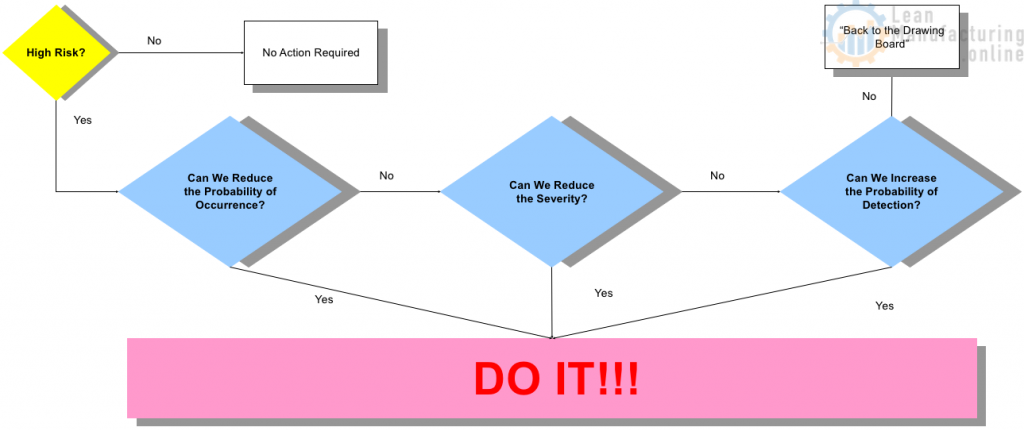
Identify actions leading to improvement or preventive actions
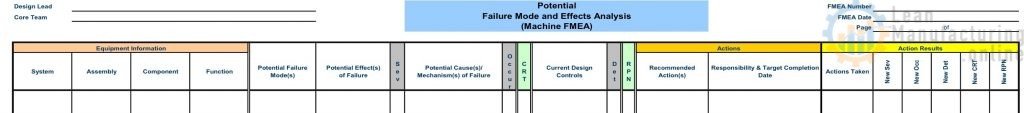
This is one of the most important parts of FMEA. The FMEA will have little value without real effort on this step. Corrective actions must be initiated for the highest priorities.
Actions should be prioritized in the following order:
- A failure mode/cause with a high Criticality
- A failure mode/cause/control with a high-Risk Priority Number (RPN)
…Actions may be Improvements or Preventive Maintenance (TBM, Predictive, CBM)

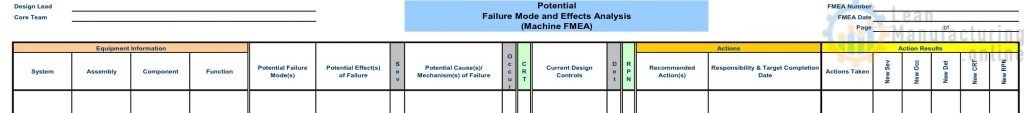
Hands-on training for teams step 4
- Each team will receive a flashlight and FMEA package
- Prioritize failure modes and define countermeasures and responsibilities
Assess Results
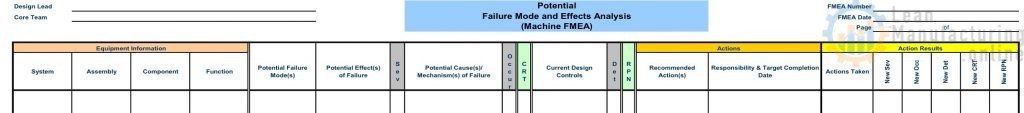
- After the actions have been identified, re-estimate, and record the subsequent Severity, Occurrence, Detection, Criticality, and RPN rating.
- The FMEA leader is responsible for assuring that all recommended actions have been implemented.
Keys To Success
- Build consensus on prioritization
- Encourage creativity…TEAMWORK!
- PLAN!
- ASK QUESTIONS!
Corrective actions implemented effectively.
Limitations / Roadblocks
- Identifying Failure Modes is a team brainstorming activity. If the team forgets to list it, an important failure mode could be left alone, waiting to occur.
- Rating Scales should be modified so that they are meaningful and specific to the machine/equipment into consideration. Make sure the PM actually solves the problem, use proper modes of inspection.
- A superficial look at the equipment will miss many failure modes.