Considerations
- Steps act as guidelines for the activities to be done;
- They are located in the correct moment of the project;
- However, you don’t need to reshape all your Early Management in place;
- The idea is to:
- Add good ideas to your Early Management process;
- Review some activities importance;
- Review timeline.
- Take this time to reflect about your early management process and think about improvements.
Early Product Management and Early Equipment Management
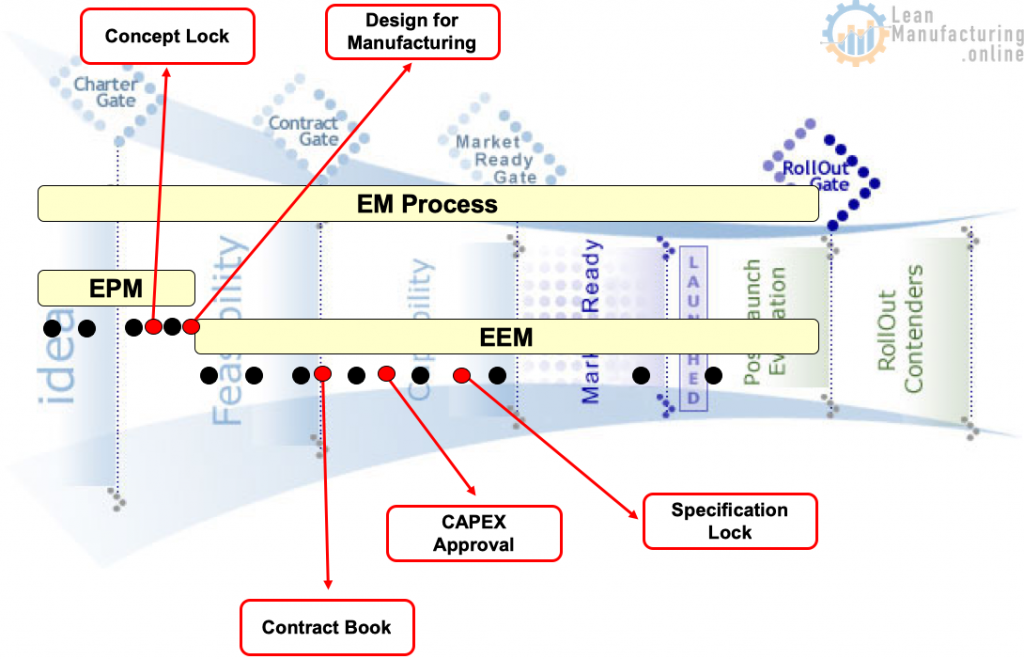
Early Product Management

Early Equipment Management

EPM Objective and Importance
- Step 1 – Project Scoping

- Deployment Exercise
- Step 2 – Design Brief
- Correlation Tool
- Step 3 – Concept Lock
- Final Concept
- Step 4 – Project Optimization
- Design for Manufacturing (Design able to be manufactured)
EEM Objective and Importance
- Step 1 – Project Definition

- Project Kick Off
- Project Deliverables
- Team Selection
- Project Capabilities
- Project Brief and Sign Off
- Step 2 – Conceptual Engineering
- Losses Study
- MP Information
- Internal and External Examples
Workshop 1 – Losses Workshop
- Step 3 – Preliminary Engineering
- Utilities Study
- Lay Out Study
- Risk Management Tools
- Concept Selection
- Step 4 – Detailed Engineering
- First Draft Detailed Design
- MP Tools
- Update Risk Management Tool
- Final Specification
Workshop 2 – Engineering Workshop
- Step 5 – Procurement & Construction
- Order
- Build & Construct
- Continuous Monitoring
- FAT – Factory Acceptance Test
- Initial Flow Planning
Workshop 3 – Installation Workshop
- Step 6 – Installation & Commissioning

- Construction and Installation
- SAT – Site Acceptance Test
- Dry Commissioning
- Wet Commissioning
- Embed New Process in Organization
Workshop 4 – Start Up Workshop
- Step 7 – Start Up & Hand Over
- Ramp Up
- Intensive Care
- Hand Over Documentation
- Hand Over
- Step 8 – Operations & Review
- Set Up Review
- KPI Review
- Project Flow Review
- Project Learning and Follow Up
Workshop 5 – Post Mortem Workshop