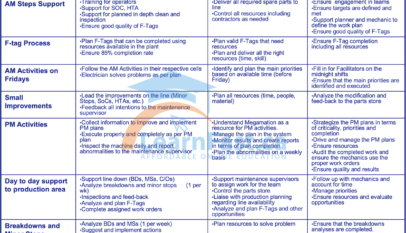
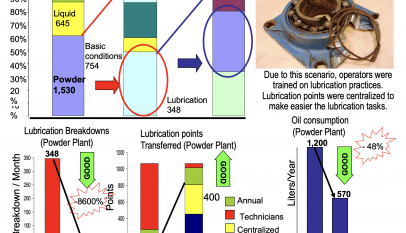
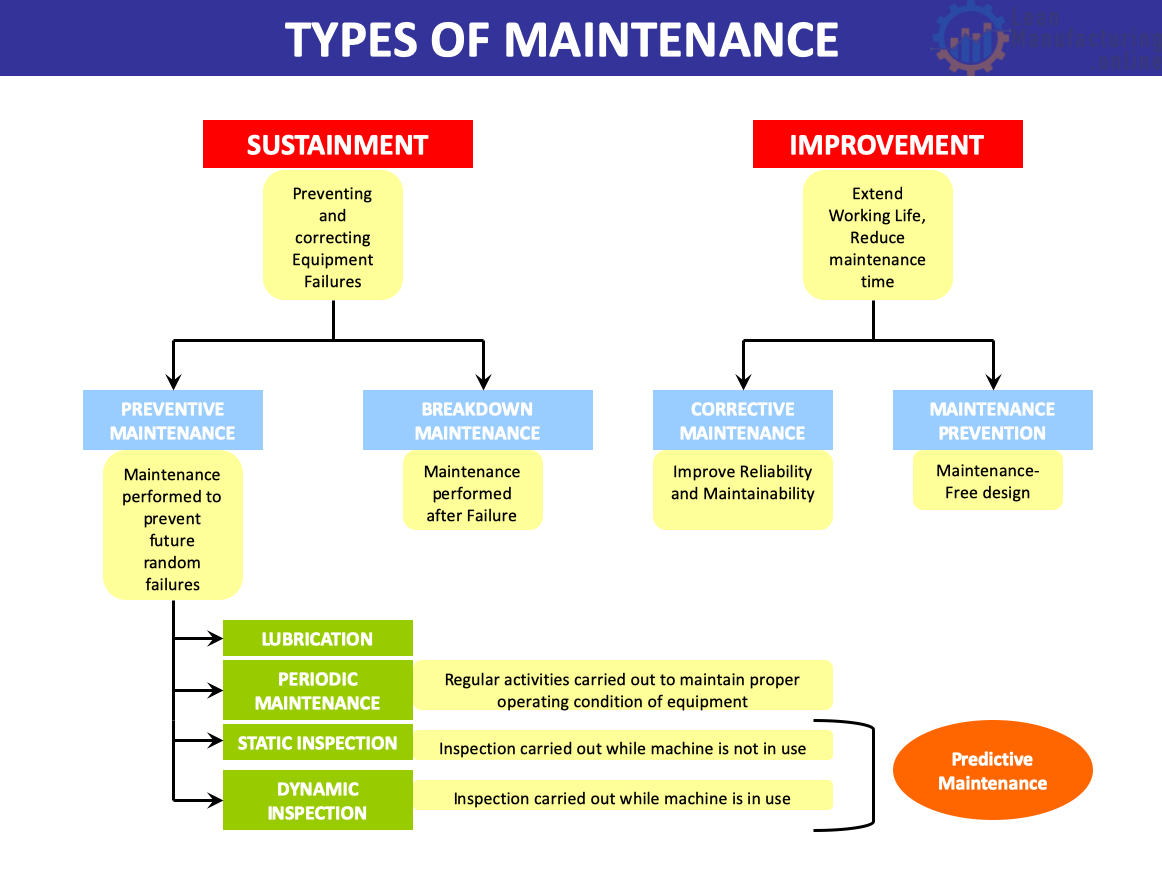
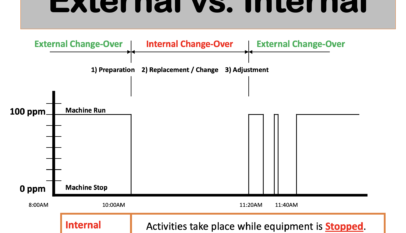
The manufacturing industry is evolving rapidly as companies strive to remain competitive in an increasingly challenging business environment. Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) is a lean manufacturing methodology designed to improve productivity, quality, and efficiency by eliminating waste and optimizing equipment performance. Implementing TPM requires an integrated approach, and the roles of mechanics, electricians, planners, and supervisors are crucial to its success. This article will discuss how these professionals can contribute to implementing TPM in a manufacturing facility.
Section 1: The Role of Mechanics and Electricians in TPM
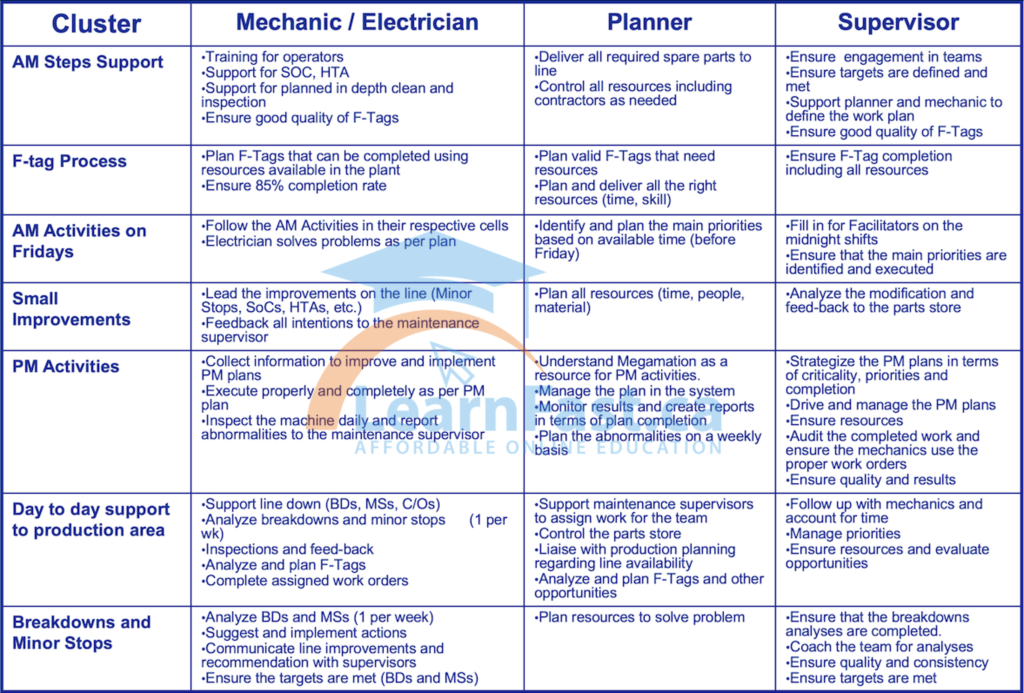
1.1 Equipment Maintenance and Reliability
Mechanics and electricians play a pivotal role in ensuring the reliability and efficiency of equipment by performing preventive maintenance and swiftly addressing any arising issues. In a TPM framework, they are responsible for the following:
a. Conducting regular inspections to detect signs of wear and tear helps prevent sudden breakdowns and minimize downtime.
b. Implementing a proactive approach to equipment maintenance, replacing parts before they fail, and taking corrective actions to address the root causes of issues.
c. Collaborating with operators to train them in basic maintenance tasks, enabling faster response times to minor issues and fostering a sense of ownership among operators.
1.2 Continuous Improvement
Mechanics and electricians also contribute to the continuous improvement aspect of TPM by:
a. Identifying opportunities to optimize equipment performance and reduce energy consumption.
b. Collaborating with other departments to implement best practices and standardize equipment maintenance and operation procedures.
c. Participating in regular reviews to analyze equipment performance data and identify areas for improvement.
Section 2: The Role of Planners in TPM
2.1 Production Planning and Scheduling
Planners are responsible for developing production plans and schedules considering equipment availability and maintenance requirements. In a TPM framework, their responsibilities include:
a. Coordinating with other departments to ensure that maintenance activities are aligned with production schedules, minimizing the impact on productivity.
b. Incorporating preventive maintenance tasks into the production plan, ensuring that equipment is maintained in optimal condition and reducing the likelihood of unplanned downtime.
c. Continuously monitor production performance to identify potential bottlenecks and adjust schedules accordingly.
2.2 Resource Allocation
Planners are also crucial in allocating resources effectively to support TPM initiatives. This includes:
a. Allocating manpower for maintenance tasks, ensuring that mechanics, electricians, and operators have the required skills and competencies to perform their duties.
b. Ensuring that spare parts and consumables are available when needed, reducing the risk of extended downtime due to lack of necessary resources.
c. Collaborating with procurement to source high-quality components, contributing to the overall reliability and efficiency of the equipment.
Section 3: The Role of Supervisors in TPM
3.1 Leadership and Employee Engagement
Supervisors drive TPM initiatives by providing leadership and promoting employee engagement. They are responsible for the following:
a. Communicating the importance of TPM to their teams, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and proactive maintenance.
b. Encouraging cross-functional collaboration to identify and resolve equipment-related issues. c. Recognizing and rewarding employees for their contributions to TPM initiatives, further motivating them to continue their efforts.
3.2 Monitoring and Performance Evaluation
Supervisors are also responsible for monitoring the implementation of TPM and evaluating its impact on production performance. This includes:
a. Establishing performance metrics to track the effectiveness of TPM initiatives, such as equipment availability, mean time between failures, and overall equipment effectiveness.
b. Conduct regular reviews to analyze performance data and identify areas for improvement.
c. Implementing corrective actions to address performance gaps and ensure continuous improvement.
Conclusion
To successfully implement Total Productive Maintenance (TPM) in a manufacturing facility, collaboration among professionals such as mechanics, electricians, planners, and supervisors is essential. Each individual must understand and fulfill their respective roles in the TPM process to ensure the initiative’s success.
Mechanics and electricians ensure equipment reliability through proactive maintenance and continuous improvement efforts. Planners optimize production planning and resource allocation, while supervisors provide leadership and drive employee engagement in TPM initiatives. Together, these professionals form a strong foundation for the successful implementation of TPM, resulting in increased productivity, reduced downtime, and improved equipment performance in the manufacturing facility.
By leveraging the skills and expertise of these crucial team members, manufacturing facilities can unlock the full potential of Total Productive Maintenance, ensuring long-term sustainability and competitiveness in an ever-changing business landscape.