Term Meaning
3D Tasks Dangerous Difficult Dirty
4M (4M’s) Categorisation of problems and solutions into Man, Method, Machine and Materials
5 Whys Problem solving technique using Why 5 times
5S (Principles) 5 basic activities to establish a foundation for TPM implementation – taken from Japanese words.
5W + 1H 5 Why’s and 1 How analysis to identify the facts only within a problem (the Phenomenon)
Activity Boards Visual display of relevant work
AM Autonomous Maintenance
BM Benchmark
C/O Parts Change over parts
Cascade Pass on an idea through an organization (down)
CBT Computer Based Training
CEDAC Cause and Effect Diagram with the addition of cards
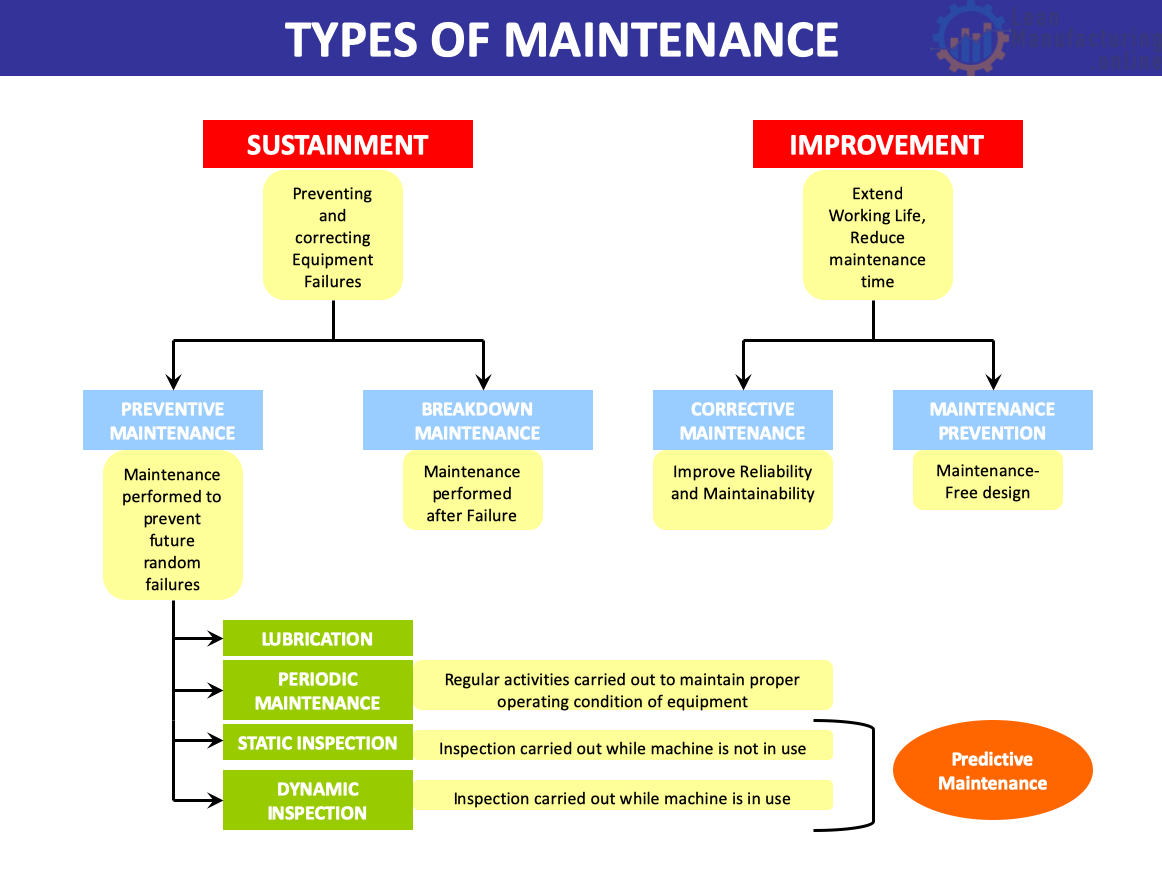
CM Corrective Maintenance
CM Condition Maintenance
CONQ Cost of NON Quality
COSHH Control of Substances Hazardous to Health
DuPont Audits Safe/Unsafe Behavioural Observation/Feedback Technique used by line management/supervision
EC Environmental Care
ECRS Eliminate Combine Replace Simplify
EEM Early Equipment Management
EffM Effective Maintenance
EPM Early Product Management
E-SAP Software for purchasing and stock control
External Stakeholders People with interest in the particular activity who are not actively involved and not part of the business
FAC First Aid Cases
Feet for inspection points Visual example of showing where to stand
FI Focused Improvement activity based on loss data
FMEA Failure Mode and Effect Analysis
Gap analysis Problem solving through working out what difference lies between the current position and the goal
HACCP Approach Hazard Analysis of Critical Control Points
HAZOP Hazard and Operability Study
Horizontal Replication The application of successful/proven improvements to similar activities/equipment
Company Crisis Management SHE Standard Assessment protocol is to guide the member companies in completing their evaluation of crisis management and communications planning
IFC Initial Flow Control – technique to concurrently plan activities within EEM
Initial Clean Step 1 of Autonomous Maintenance
IPM Process Innovation Project Management
ISO International Standards Organisation
JIPM Japanese Institute of Plant Maintenance
Just-in-time Japanese Manufacturing Philosophy for collection and supply of goods
Kaizen is a Japanese word that means small steps but continuous improvement. Used to describe activity and analysis
Kaizen Leader Person running a Kaizen
Kanban Methodology for organizing stocks
KPI Key Performance Indicators
LCC Life-Cycle Costing
LiveLink Database for sharing information within the business that is web-based.
LIRD Local Improvement Record Database
Logical Analysis Problem solving using reasoned thinking
MP Maintenance Prevention
MTBF Mean Time Between Failure
MTBQF Mean Time Between Quality Failure
MTBT Mean Time Between Touch
MTTR Mean Time To Repair
SPC Statistical Process Control
NEBOSH National Examination Board in Occupational Safety and Health (UK)
No Touch Production Machinery runs without any human interaction
OEE Operational Equipment Efficiency
OH&S Occupational Health and Safety
OH&S Control Measures The technical or procedural means by which OH&S risks are reduced.
OPL One point lesson
OSHE Occupational Safety Health and Environment
OTIF On Time In Full
PCDA (R) Plan, Do Check, Act (Review)
PDCA Plan, Do, Check, Act
PDP Personal Development Plan
PHA Preliminary Hazard Assessment
Pillars evolution Continuous improvement and understanding of TPM methodologies as illustrated by the pillars.
PM Planned Maintenance
P-M Analysis Physical – mechanism relationship technique for Problem-solving
Poka-Yoke Fool-Proof or designed to be operated without training
Policy Deployment Pass on an idea down through the organization
PPE Personal Protective Equipment
PQCDSM Productivity Quality Cost Delivery Safety Morale
PQDCSMI PQCDSM + Innovation
PRIAM Project Risk Identification Assessment and Management
Process Mapping Technique used to identify systems used and when they apply
Project Charter Agreement between Customer and Group what, when and how to deliver an objective
Public Drive Area of soft copy storage available to everyone
PY Poka-Yoke
Q (components) Parts with direct influence on Quality
Q-Points Specific parts where Quality is directly influenced
QA Matrix, QM (matrix), Quality Matrix Quality Maintenance Table
QC (stories) Quality Control
QDI Quality Defect Index
QFD Quality Function Deployment
Quality Rate Used to calculate OEE taking into account quality factors
RCM Reliability-Centred Management
Returns Product sent back to SU from customer or consumer-specific
S-Points Parts that directly effect Safety
Safety Lunches An informal management/employee forum for discussing safety issues.
SAP QM Quality Maintenance within purchasing and stock control software
SC Supply Chain
Seiri Sorting Out
Seiton Setting Limits
Seiso Shining Workplace
Seiketsu Systematic Cleaning
Shitsuke Sticking to the Rules
Shadow Board Visual display which indicates by shape what is held on display
SHE Safety Health and Environment
SKU Stock Keeping Unit
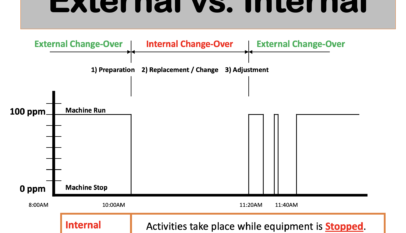
SMED Single Minutes Exchange of Dies
SOP’s Standard Operating Procedures
SPC Techniques Statistical Process Control
SU Sourcing Unit
Synchronous Production Manufacturing goods on-demand with no losses and no stocks
Tagging Activity to indicate work required on physical parts of a machine
Taguchi Method Japanese technique to establish critical part of the machine
TD Training and Development Pillar same as Education and Training Pillar
THA’s Task Hazard Analysis
Toolbox talks Presentation explaining techniques
TPM Total Productive Maintenance
TPM Cell TPM group / team / sub-committee
TPM COP Kaizen Database TPM Community of Practice Kaizen Database: WIRD
TPM Loss Tree Loss deployment methodology to measure losses in groups
TPM Pillar 1 area of activity in a factory of which there are 9
TPM SA TPM Self Assessment Audit
Underpinning knowledge Reinforcing learning through evidence
Value Engineering Technique to ensure that all factors are at the correct level
VIP Value Improvement Plan
Visual Management Use of displays and physical markings to pass on knowledge
WBLA Why Because Logical Analysis problem-solving technique
Why Why Problem solving approach similar to 5 Why, but more extensive
Zero Failure Expertise How to get to a position where zero losses can be made
Zero Losses No losses against particular areas, e.g. Zero loss line
WIRD Worldwide Improvement Record Database