Introduction
Gap analysis is a valuable tool in the preventive maintenance (PM) industry, as it aids in identifying areas where improvement is required. A comprehensive gap analysis can enhance equipment efficiency, reduce downtime, and increase cost savings. The following article discusses the recent gap analysis performed by our team using the spreadsheet provided: Gap Analysis PM. We will outline the methodology employed, key findings, and suggested solutions for optimizing PM practices.
Methodology
Our team employed a systematic approach to conducting the gap analysis by focusing on the following areas:
- Equipment Inventory: A complete list of assets, including equipment specifications, age, and maintenance history.
- Maintenance Schedule: Review the current PM schedule, including frequency and task lists.
- Maintenance Procedures: Examining maintenance protocols, such as inspection methods, cleaning, and lubrication practices.
- Maintenance Resources: An assessment of available resources, such as personnel, tools, and spare parts inventory.
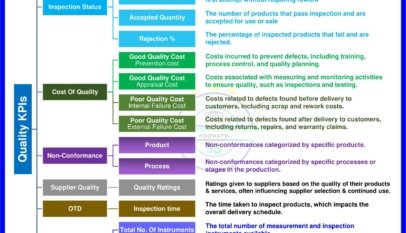
- Maintenance Metrics: A review of performance indicators, including mean time between failures (MTBF), mean time to repair (MTTR), and overall equipment effectiveness (OEE).
Key Findings
The gap analysis revealed the following areas for improvement:
- Inconsistent PM schedules: Some equipment had infrequent maintenance schedules, resulting in an increased risk of failures and downtime.
- Outdated maintenance procedures: Certain procedures did not conform to the latest industry best practices or manufacturers’ recommendations, leading to potential inefficiencies and safety hazards.
- Insufficient maintenance resources: A lack of skilled personnel, tools, and spare parts could negatively impact the PM process.
- Inadequate performance tracking: The absence of a robust system for tracking and analyzing maintenance metrics hindered continuous improvement efforts.
Suggested Solutions
Based on the gap analysis, we recommend implementing the following actions to optimize PM practices:
- Standardize PM schedules: Develop and implement consistent PM schedules based on equipment type, age, and usage. Regularly review and adjust schedules as needed to account for changes in operational conditions.
- Update maintenance procedures: Review and update maintenance procedures to align with industry best practices and manufacturers’ recommendations. Ensure all personnel are adequately trained in the latest techniques and safety protocols.
- Optimize maintenance resources: Evaluate the current allocation of resources and invest in additional personnel, tools, and spare parts as needed to support an effective PM program.
- Implement performance tracking: Establish a system for tracking and analyzing maintenance metrics, such as MTBF, MTTR, and OEE. Regularly review these metrics to identify trends and areas for improvement.
Conclusion
A well-executed gap analysis can significantly enhance PM practices, reducing downtime, extending equipment life, and overall cost savings. Organizations can achieve optimal preventive maintenance performance and ensure long-term success by addressing the identified gaps and implementing the suggested solutions.
To learn more about this assessment, please visit our expanded post