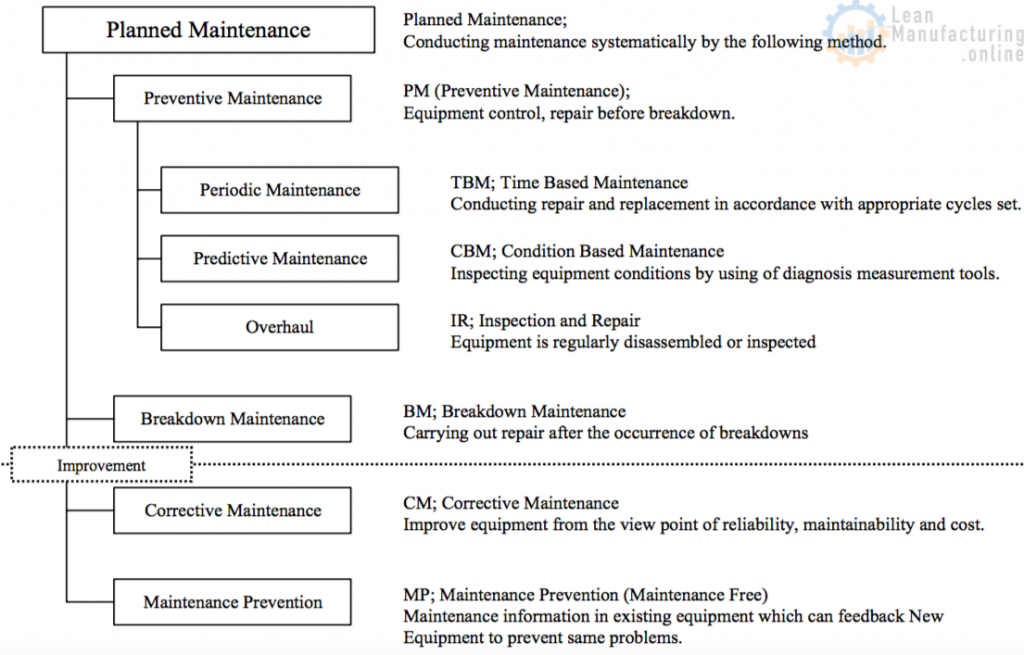
Types of Maintenance
- Preventive Maintenance
- Time Based Maintenance (TBM)
- Advantage: Maintenance tasks such as inspection are avoided. Few failures occur
- Disadvantage: The equipment is over-maintained. Maintenance costs are high
- Predictive (PdM), or Condition Based Maintenance (CBM)
- Advantage: Over-maintenance, the disadvantage of TBM is avoided
- Disadvantage: Costs are incurred for equipment diagnostics and monitoring systems
- Overhaul – Inspection and Repair (IR)
- This is a middle point between CBM & TBM. It requires adjustment of production and provision of spare machines
- Time Based Maintenance (TBM)
- Breakdown Maintenance
- Inspection and periodic replacement is not performed at all
- Advantage: Because the equipment is used to the end of it’s working life, it is highly economical as long as no secondary failures occur
- Disadvantage: The more machines are in use the greater the number of failures, considerably impeding production
- Inspection and periodic replacement is not performed at all
- Corrective Maintenance
- To raise the maintainability and reliability of the equipment, a wide range of improvements are included as part of maintenance, such as upgrading, prevention of recurrence of failures, an extension of the working life of the equipment, reduction of the maintenance time, and improvement of productivity
- Maintenance Prevention
- In this activity, maintainability and ease of Autonomous Maintenance are reflected in the construction of a new machine. Corrective Maintenance data in particular is excellent. Improvement of equipment as well as replacement are taken as opportunities to implement this approach
Total Productive Maintenance

The Objective of Planned Maintenance

Categories of Planned Maintenance
Zero Breakdown Approach

Why do breakdowns occur? Stress-Strength Model

Stress-Strength Model
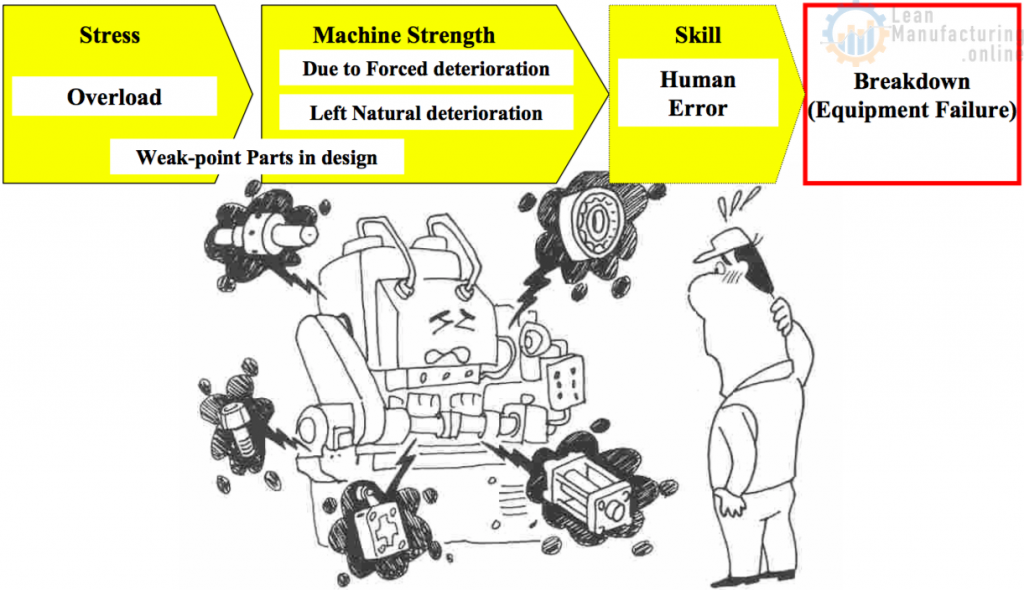
Five Major Causes of Breakdown

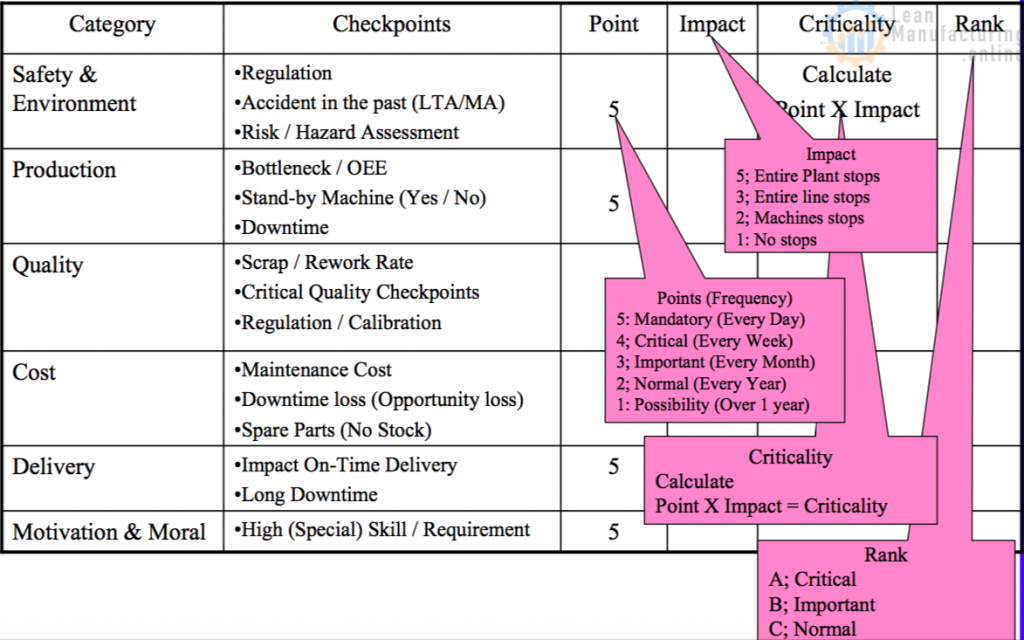
Equipment Criticality
Outlook of Planned Maintenance
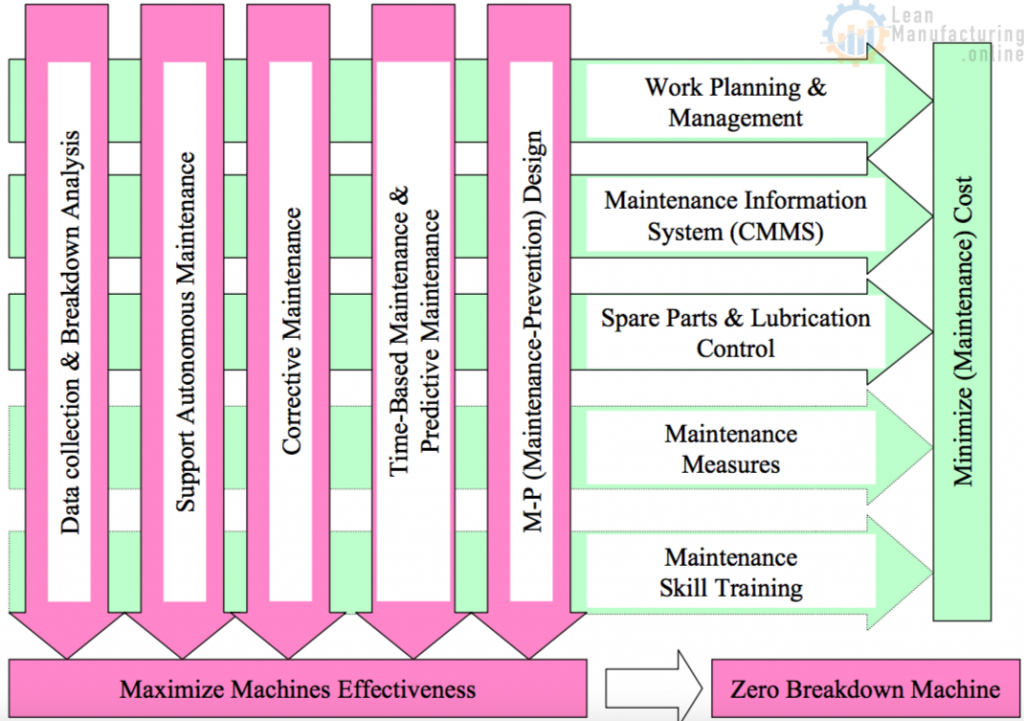
Data collection & Breakdown Analysis -1

Data collection & Breakdown Analysis -2

Data collection & Breakdown Analysis -3

Data collection & Breakdown Analysis -4

Data collection & Breakdown Analysis -5

Support Autonomous Maintenance-1
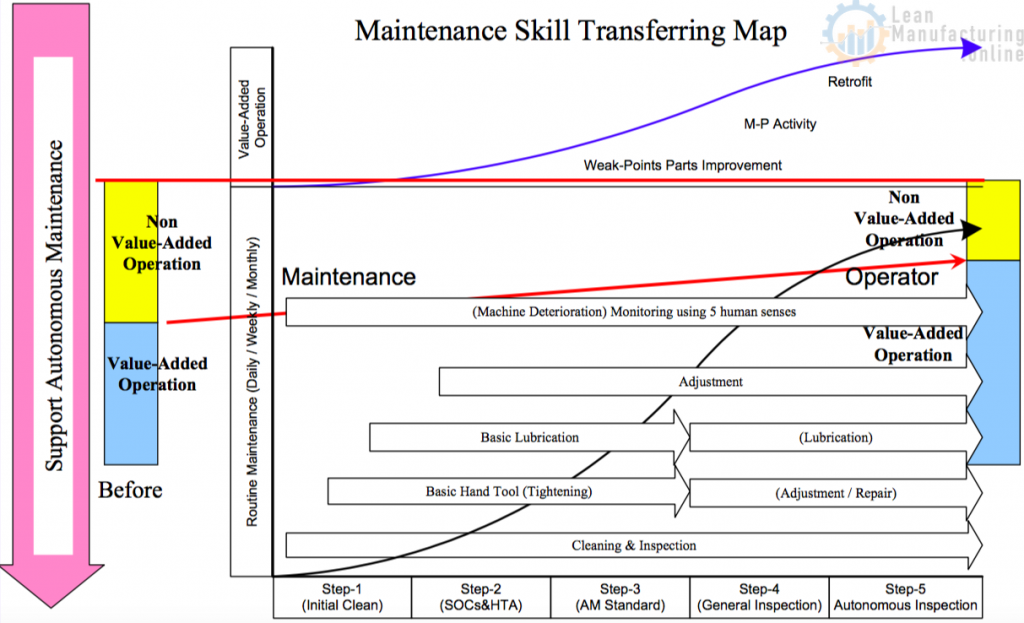
Support Autonomous Maintenance-2
![]()
Relationship between AM and PM