PM Element 3. Equipment Maintenance Strategy

How to start the Time Based Maintenance System?
The best way to start is to put more resources into the critical equipment or the most important equipment.
How do you define the critical equipment?
A way to do that is to establish criteria to sort the equipment into A, B, and C categories.
For that, it is necessary to develop some criteria related, for instance, to SHE (Safety, Health, and Environment), Quality, key brands volume production, and what impact an equipment breakdown could cause in each criterion.
Then start developing your program first for A equipment, second for B equipment, and finally for C equipment.
Also, this prioritization can help the maintenance cost reduction because it is possible to focus more resources on critical equipment, reduce work on non-critical equipment, and in the end, keep the same result, spending less money.
Criticality Flow Chart

Legend:
- SHE – Safety Health & Environment
- I – Influence
- EX – Product Expiration Time
- UR – Utilization of Equipment
- KB – Key Brands
- DF – Defects
- MS/AD – Minor Stoppages / Adjustments.
- Q – Quality
- MT – Maintainability
Criteria for Equipment Criticality

Additional reading – Machine Ledger
Maintenance Strategy Applied

Step 1
Divide the equipment by component level
- Equipment
- System
- Subsystem
- Component
Step 2
Determine who is responsible for performing the inspection. The idea is to identify the necessary skill, for instance, operator, mechanic, electrician, contractor, supplier, etc.
Step 3
Determine what the person is looking for during the inspection:
- Wearing, Vibration, Leak, Noise
Step 4
How are the tradesmen or the operator going to do that?
- Visual Inspection, Touching the machine, Measuring the wearing, Functional Inspection.
Also, this is the time to study if an Inspection Standard is required. An Inspection Standard is applied for critical jobs or when a certain level of expertise is needed. This standard explains the inspection step by step.
Step 5
When is it necessary to do this inspection?
Determine the best interval weekly, monthly, quarterly, semi-annually, and annually.

Preventive Maintenance
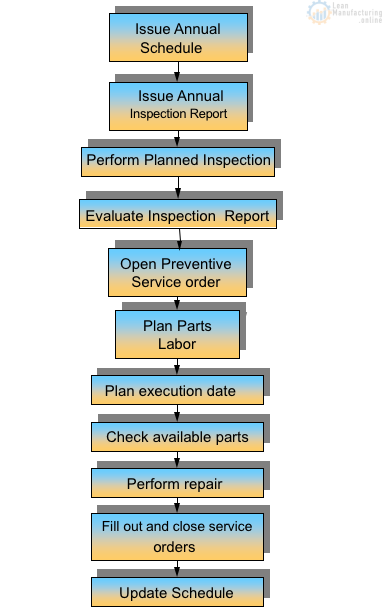
After developing the inspection for the equipment, it is time to establish an annual schedule for the factory. It allows you to visualize the inspections and adherence to this activity.
The Flowchart below describes a preventive system.
MTBF Control
After applying the time-based maintenance for some time, identify the Mean Time Between Failures for each component.
To identify the MTBF for a component, you will need to determine how many times the component has been changed due to breakdown or preventive maintenance.
After identifying the components with the lowest MTBF, these components need to increase their life cycle; then, you will spend fewer hours replacing them and spend less money on spare parts.
Use the MTBF information to improve the inspection plan. If a component has an MTBF of 180 days and it has been inspected every week, you are looking 26 times for this component to find a problem. Is it possible to increase the time between inspections? Using this information, it is possible to identify the equipment that has been over inspected.
Summarizing:
First: Establish a Time-Based Maintenance system to reduce the number of breakdowns.
Second: Use the MTBF by component to improve the system and reduce the cost.
Identify Low MTBF Component
MTBF Control by Component Matrix


MTBF Control
After improving the useful life of critical components, update the inspection schedule.