PM-analysis
Safety, Health and Environment Investigation Report and Analysis
5 Why Analysis Blog Cap-Do Lean Six Sigma PM-analysis Root Cause Analysis Safety Safety, Health and Environment TPM
All modern manufacturing facilities use principles that “all accidents are preventable,” but sometimes incidents or accidents can still happen. Gathering as much data as possible and analyzing it to prevent a recurrence is essential. Investigation Report Let’s review the first part – [ Incident Reporting ] A. To be completed…
Read More »P-M Analysis Basics
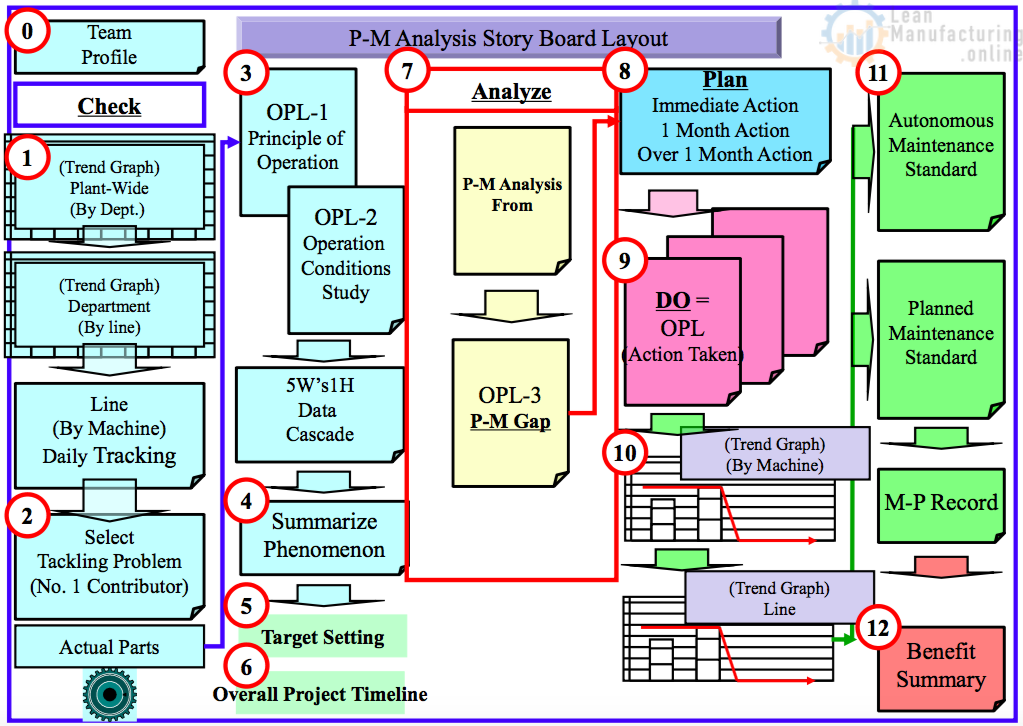
P dash M Analysis is a systematic Problem-Solving Philosophy for Chronic Losses. The term P-M Analysis comes from the following origin: P – Phenomena(non), Physical; M – Mechanism, Relationship (Machine, Man/Woman, Material, Method) When To Use P-M Analysis? Root Cause Analysis Two Types of Problem Solving Techniques Why is the 5-why Analysis effective?…
Read More »Identifying Phenomena for Minor Stops – 6 Gens
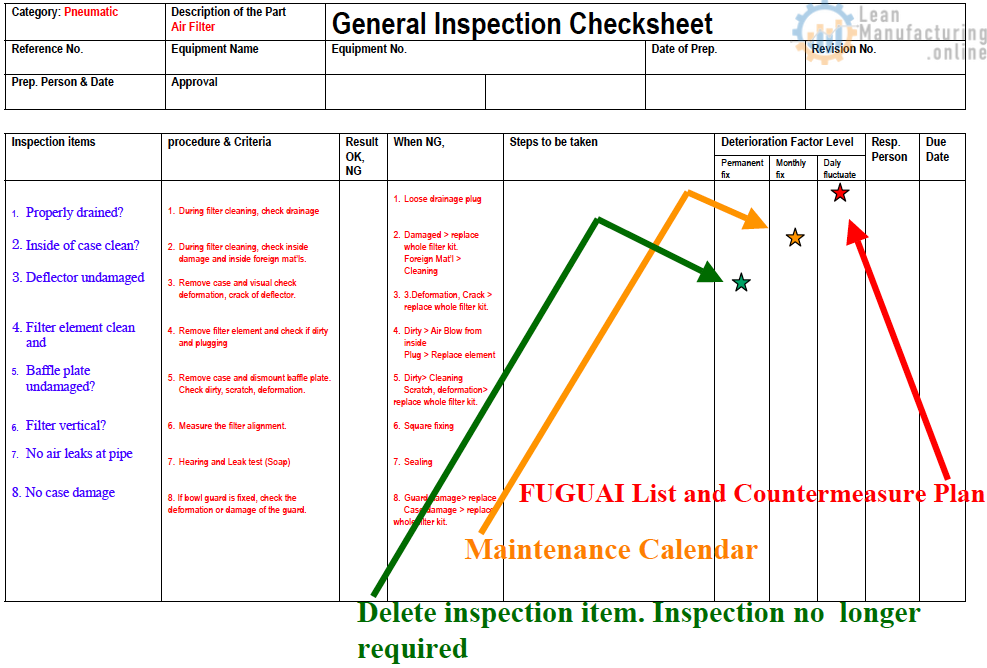
The Deep KAIZEN Approach to Minor Stops (Identifying Phenomena) 1. The 6 ‘Gens’ “Gen ba” 現場 – The Precise Location Go to the actual place where the problem occurs and examine everything carefully. “Gen butsu” 現物 – The Evidence View the actual objects, parts, and materials involved in the problem. “Gen shou”…
Read More »P-M or 4M analysis
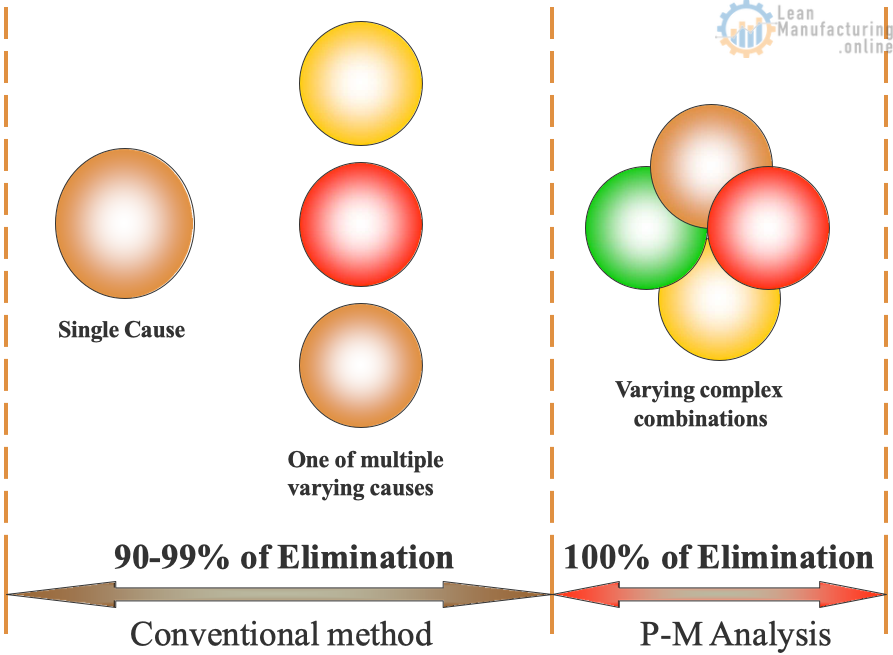
Chronic & Sporadic Losses Sporadic losses occur suddenly and infrequently, they result from a single cause that is relatively easy to identify and solve; Chronic losses, on the other hand, live up to their name by resisting a wide variety of corrective measures. P-M Analysis Single causes that vary constantly…
Read More »