If your company manufacture food and sell it in big name stores, such a Walmart, Costco, Loblaws etc., your facility must be certified by one or more programs of Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI). Certification according to a GFSI recognized scheme can be achieved through a successful third party audit against any of the following schemes recognized by the GFSI:
- BRC Global Standard for Food Safety (Seventh Edition)
- BRC-IOP Global Standard for Packaging and Packaging Materials Issue 5
- BRC Global Standard for Storage and Distribution
- CanadaGAP (Canadian Horticultural Council On-Farm Food Safety Program)
- FSSC 22000 Food Products
- Global Aquaculture Alliance Seafood – BAP Seafood Processing Standard
- GLOBALG. A. P. Integrated Farm Assurance Scheme Version 5, Product Safety Standard Version 4 and Harmonized Produce Safety Standard
- Global Red Meat Standard (GRMS) 4th Edition 4.1
- IFS Food Version 6
- IFS Logistics Version 2.1
- IFS PACsecure, Version 1
- PrimusGFS Standard (v.2.1 – December 2011)
- SQF Safe Quality Food Code 7th Edition Level 2
Let’s begin, first step is
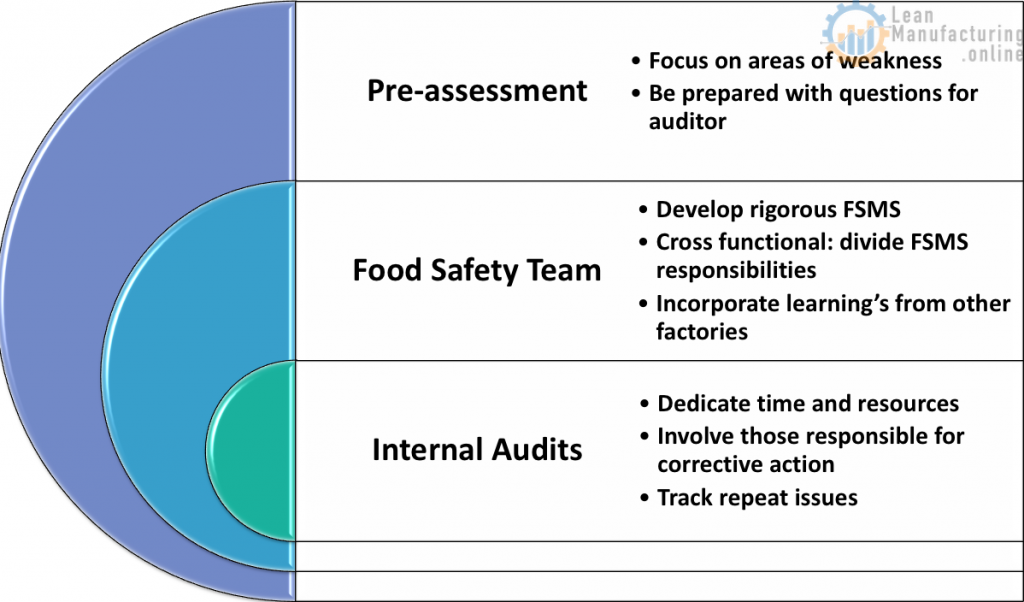
Food safety team
Cross functional
- Collective knowledge of entire process and hazards
- Quality, Operations (including select operators), maintenance/engineering, cleaning/sanitation, procurement, HR, product group/category quality
- Cover all shifts
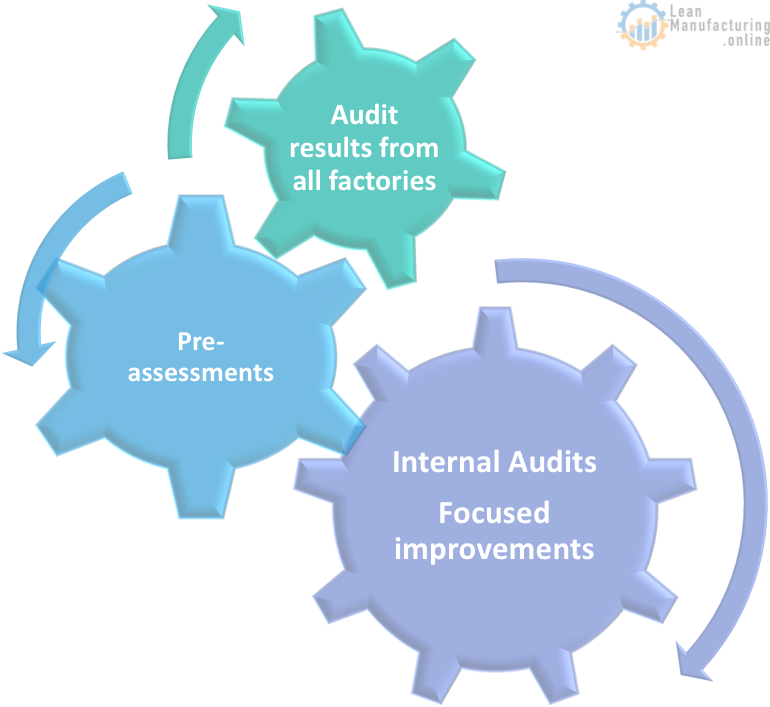
Drives food safety management system continuous improvement
- Internal audits
- Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) team
- Focused improvements
- Regular meetings
- Cascade training/ communication on production floor
Certification responsibilities are divided among food safety team members
Critical for continuous improvement of food safety management systems to protect the consumer.
Critical for implementing GFSI program
Assures food safety management systems protect the consumer
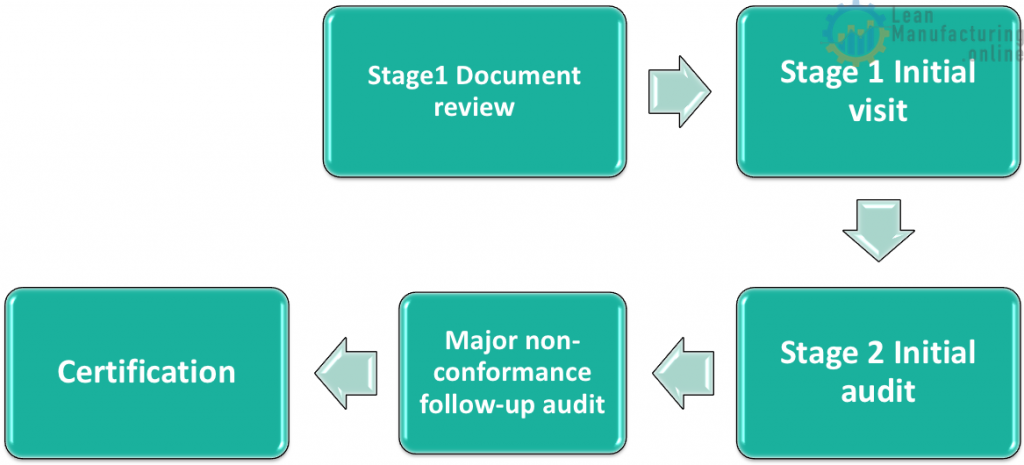
Certification milestones
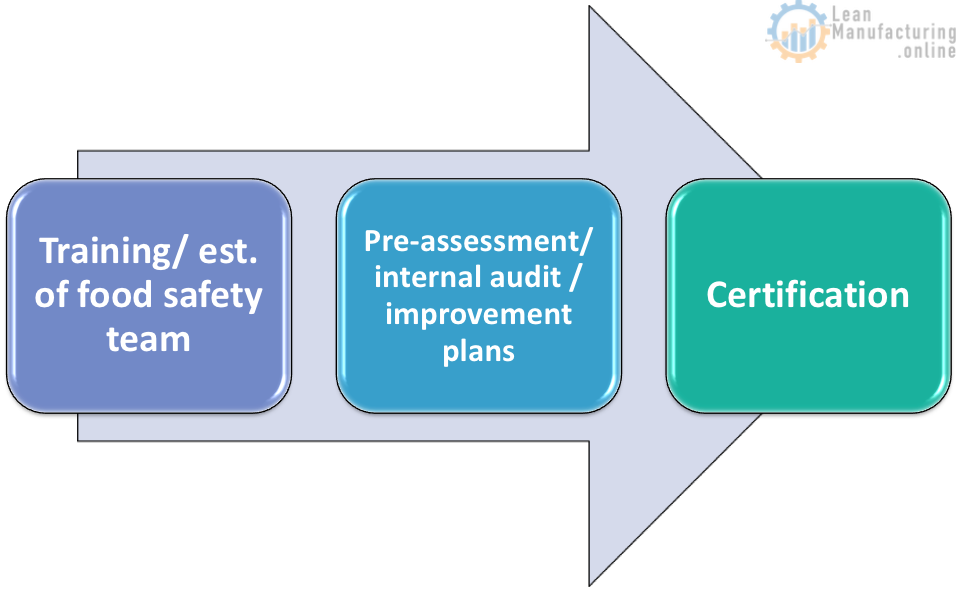
Training/ food safety team establishment

Meetings and food safety team training session are lead by the food safety team leader
Pre-assessment/ internal audit / improvement plans
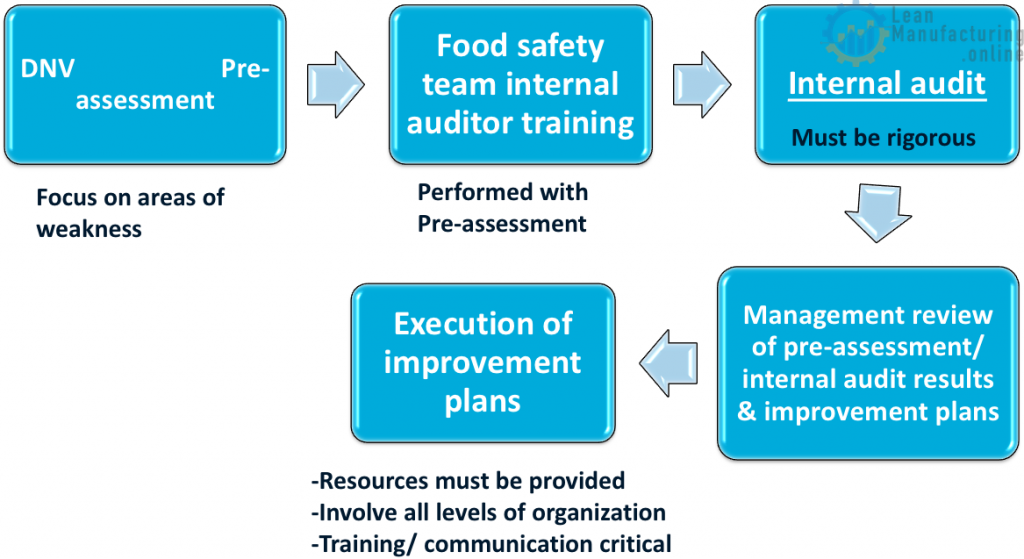
Certification
- There is no certification score
- Factories will either receive certification or not receive certification
- A factory will not receive certification if they have 1 or more major non-conformances which are not corrected within 90 days
- A DNV auditor must perform a follow up audit within 90 days to verify that all major non-conformances have been corrected
Managing nonconformance
Agenda
- Nonconformance definition
- Managing nonconformance
- Reporting nonconformance’s, observations and noteworthy efforts
- Using certification results from other factories to continuously improve Food Safety Management System (FSMS)
Minor nonconformance
Lapse of discipline/ control during implementation of a food safety system
- Does not indicate system breakdown
- Does not raise doubt that products are safe
- Isolated incident
- There are not multiple similar incidents
Managing minor nonconformance
- Must communicate action plan to auditor
- Provide corrective action in writing to auditor as soon as possible (max. 30 days)
- Correct nonconformance immediately or as soon as possible
- Before conclusion of audit if possible
- Review improvement plan with auditor during audit
- Must prevent repeat and similar nonconformance’s
- Report to Corporate Quality to share information with our factories
- Data base of nonconformance’s
Major Nonconformance
Will not receive certification until major nonconformance is corrected
Requires follow up audit to be completed within 90 days
Definition
- Failure to comply with legal requirements
- Serious food safety issue
- Absence of food safety system elements that raises significant doubt regarding safety of products
- Group of minor nonconformities indicating inadequate effectiveness/ implementation of FSMS
Managing major nonconformance
- Develop improvement plan before conclusion of audit and review with auditor
- Schedule follow-up audit before conclusion of audit
- Review and develop corrective action with food safety team
- Verify effectiveness of corrective action before the follow up audit
- Corrective action must be fully implemented
- Corrective action may require training of operators
- Report to Corporate Quality to share information with our factories
Preventing nonconformities
Observations
- Near miss
- Treat internally as a nonconformance
- Implement corrective action before situation escalates
- Prevent recurrence
- Report to Corporate Quality to share information with our factories
FSMS Continuous Improvement
FSSC 22000 certification roles & responsibilities
Agenda
- Supply leader/ factory leadership team
- Food safety team leader
- Food safety team
- Product group quality
- Corporate Quality team
Roles and Responsibilities
Supply Leader/ Factory Leadership Team
- Demonstrated commitment to food safety system continuous improvement
- KPI’s
- Improvement plan completion
- Incident reduction
- Consumer Complaints per Million Units (CCPMU) reduction
- Demonstrated Management Commitment
- Ensure availability of resources
- Conduct management reviews
- Supports food safety team
- Food safety communication
FSSC 22000 certification success depends on participation of everyone at every level of the organization.
Certification can not be successful without support from the supply leader and the factory leadership team.
The leadership team must demonstrate that they support and will provide the resources for food safety management system continuous improvement.
Management commitment can be demonstrated by providing resources to assure that:
- improvement plans from internal audits, Operational Quality Reviews (OQR) etc. are completed.
- Focused improvement projects to reduce incidents and consumer complaints are implemented.
- Regular communication in the factory regarding management commitment to consumer safety.
- Consumer safety/ quality is on the agenda for regularly scheduled factory leadership team meetings.
Food Safety Team leader
- Schedules certification activities with auditor (example DNV)
- Leads FSSC 22000 implementation
- Leads food safety team
- Drives FSMS continuous improvement
- Reports to factory leadership team regarding FSMS effectiveness
- Leads internal audit program
- HACCP team leader?
- Leads food safety & FSSC 22000 training at the factory
Food safety team leader responsible for leading continuous improvement of food safety management systems in the factory.
- Liaison with Corporate Quality team and auditor.
- Liaison with factory leadership team.
- Leads food safety team meetings.
- Responsible for assuring food safety team meeting activities are documented.
- The food safety team leader may also be the HACCP team leader.
Food Safety Team Members
- Operational HACCP
- Drives FSMS continuous improvement
- Internal Audits
- Approve factory SOP’s
- Divide FSMS responsibilities for certification
- Documentation/ records
- Certification audit responsibilities
- Internal audits
- Food safety leaders/ advocates
- On production floor
- Within management team
- Lead factory grass roots food safety activities
Food safety team must be cross functional. It should include supervisors, managers and operators. Certification responsibilities must be divided among the food safety team members. Food safety team members should be motivated to be food safety leaders on the production floor.
Corporate Quality Team
- Drives FSMS continuous improvement within the product group
- Drives closure of improvement plans/open actions (Foreign material risk assessments, HACCP peer reviews, OQR’s etc.)
- Communicates common FSSC 22000 certification learning’s within the product group
- Share non-conformance lessons learned with product group
- Share observations and noteworthy efforts within product group
- Organize shadow audits
- Ingredient hazard analysis coordination for common ingredients
- Develop and communicate specific SOP’s
- Certification planning and prioritization within the product group
- FSMS category specific Good manufacturing practices (GMP) requirements