Problem-solving is essential for any organization to improve their processes, products, and services. A3 problem-solving is a structured approach that helps teams identify and analyze the root causes of problems and develop solutions. This paper describes the A3 problem-solving process, its benefits, and how it can be applied in different industries.
Introduction
Problem-solving is a critical activity every organization must undertake to improve its operations and meet its objectives. However, problem-solving can be complex and challenging, especially when dealing with complex issues requiring a systemic approach. A3 problem-solving is a structured problem-solving approach that helps teams identify the root causes of problems, develop solutions, and implement them effectively. This paper provides an overview of the A3 problem-solving process and its benefits.
The A3 Problem-Solving Process The A3 problem-solving process is a structured approach that follows a step-by-step process to identify and solve problems. The process is named after its paper size (A3), a standard paper size used in many countries. The A3 problem-solving process consists of the following steps:
Step 1. Problem Clarification
1.0 Background
- Background information about the situation
- You and your responsibilities
- The scope of the subject/problem
- Why am I tackling this problem, and why is it important?
- Where do the Ideal Situation and Ultimate Goal come from?
- What is the impact on the business?
1.1 Gap Analysis – GAP is visualized
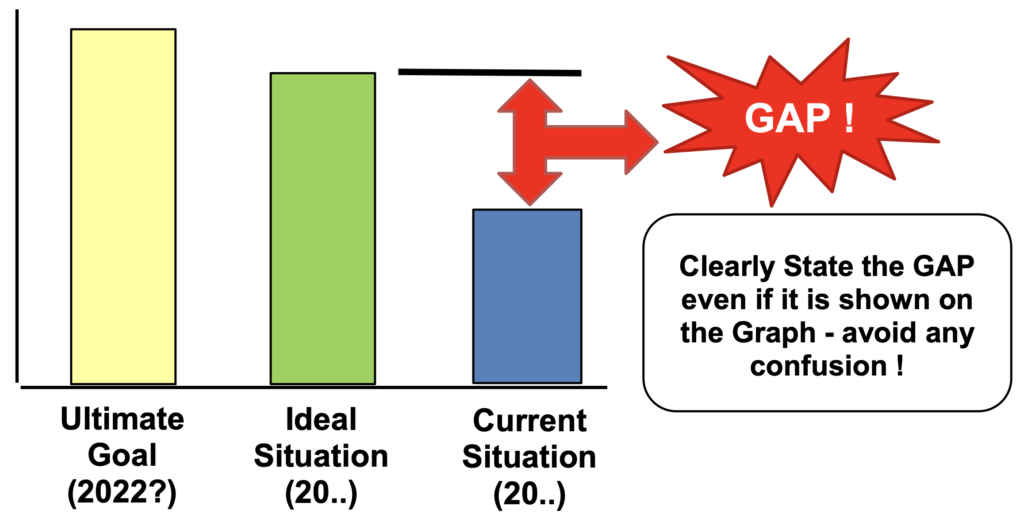
1.2 Problem Statement
Ultimate Goal:
Where do you want to be, e.g. 3-5 yrs? Where does this figure come from?
Ideal Situation:
Where should you be?
Current Situation:
Where are you now?
Problem Statement:
The GAP between the Ideal and Current Situation. How much is this worth?
Step 2. Containment
Containment Activity (5W, 2H):
- What: What is the activity?
- When: When is the start date and timing?
- Where: Where will the activity be done?
- Who: Who will be involved (name, title)?
- Why: What is the purpose of the activity? How: How will it be done?
- How much: What do you expect to achieve?
Ideal Situation
Visualize: Is the Containment working?
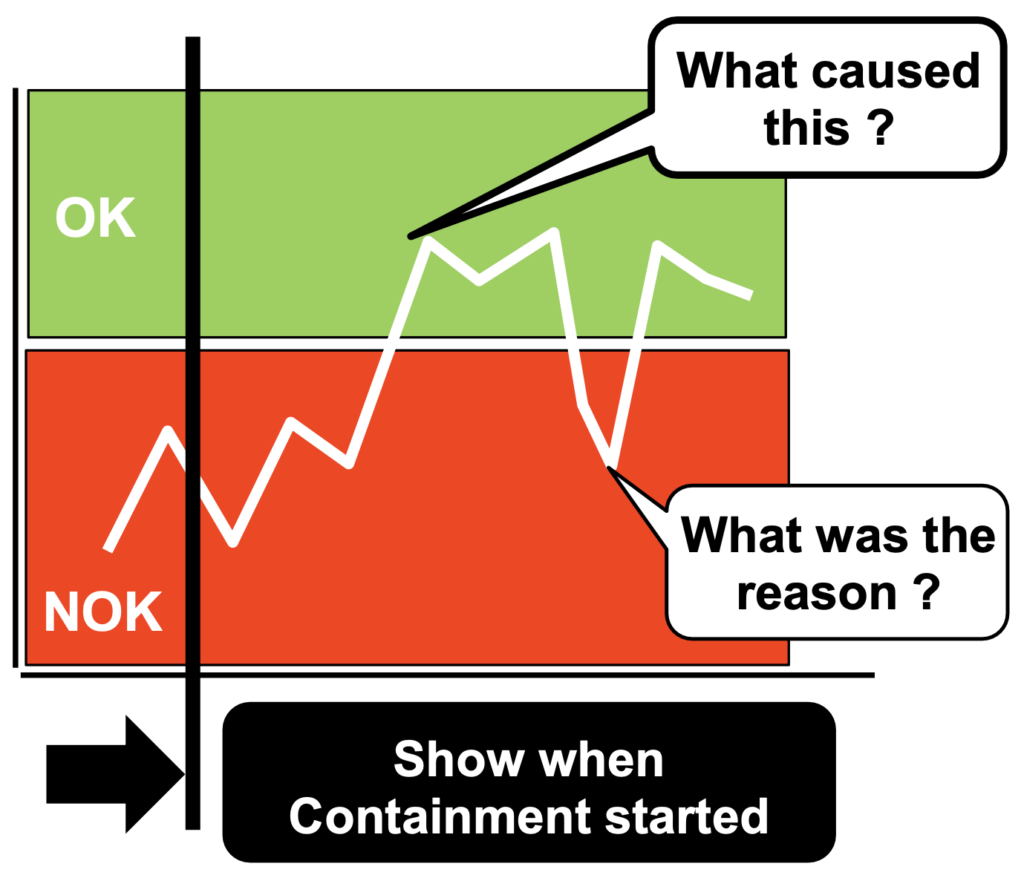
What actions have you taken during Containment?
Show some of the actions taken, and what have you discovered and learnt from the Containment activity?
- Screenshots
- Photos
What is the impact of Containment on the Gap?
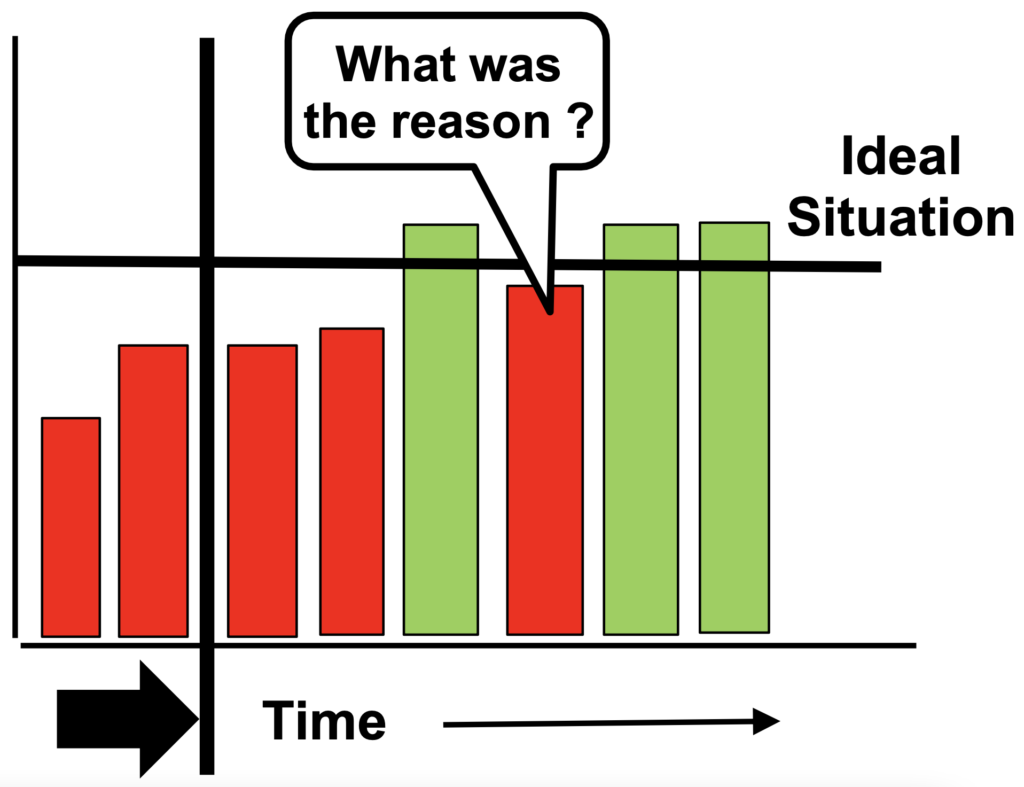
Step 3. Problem Analysis and Breakdown
Breakdown the Current Situation or Gap
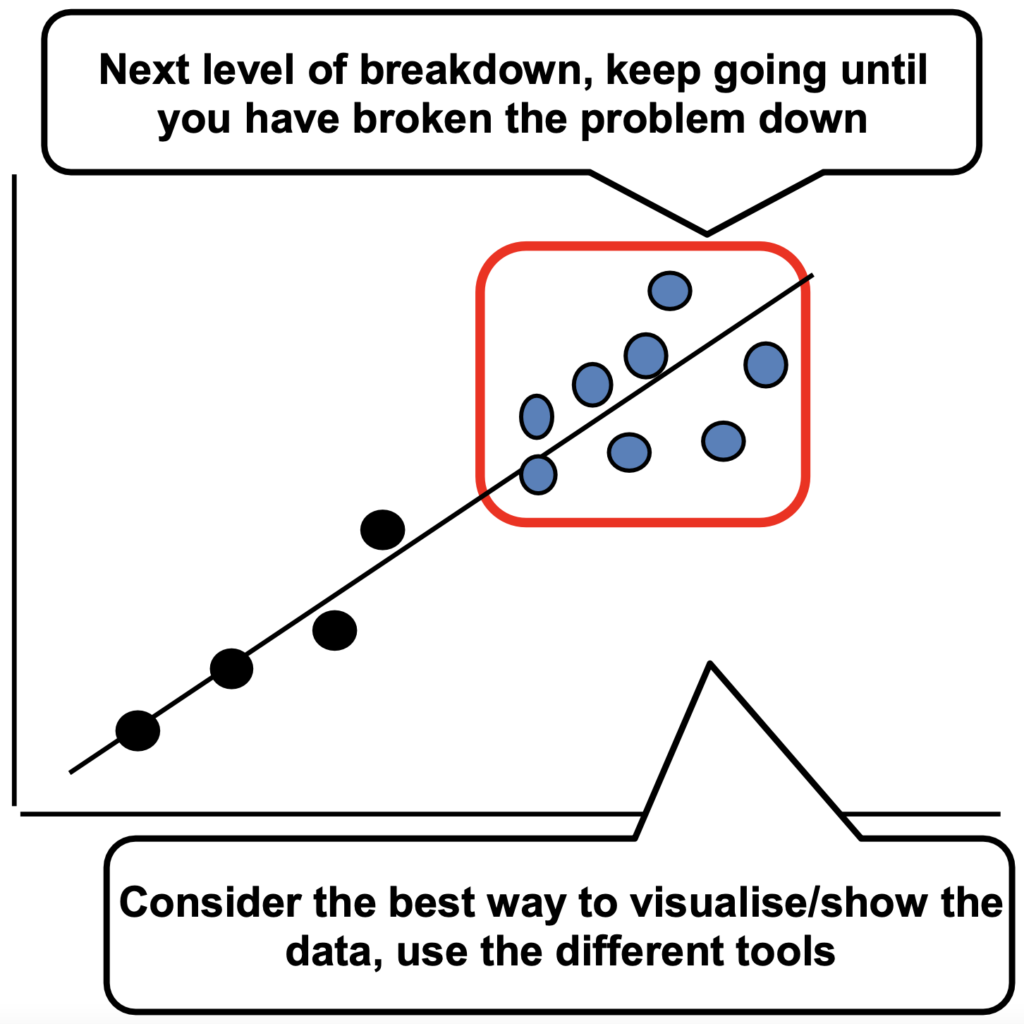
Point of Cause (PoC) – Where is the problem happening?
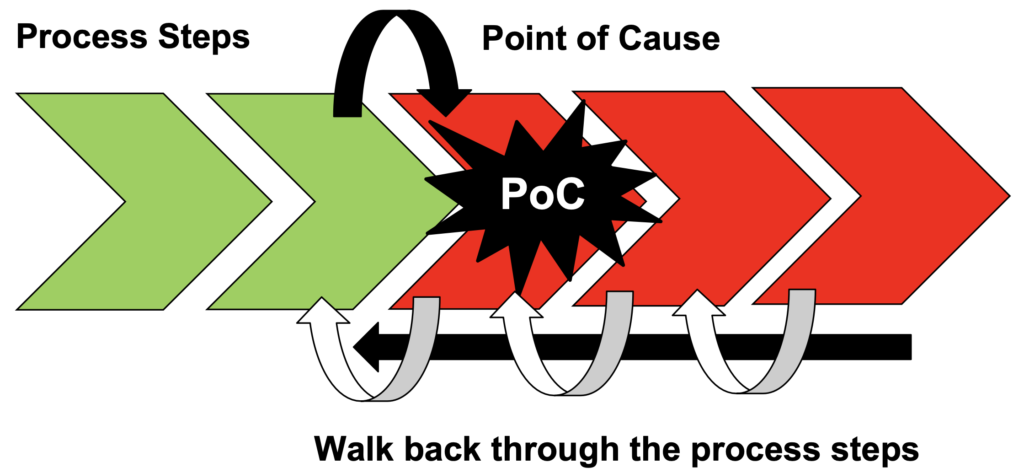
Point of Cause key points:
- Walk back through the process steps – Go and see for yourself
- Find where the problem happens
- Prove with data
Establish the Direct Causes – What switches the problem ON and OFF?
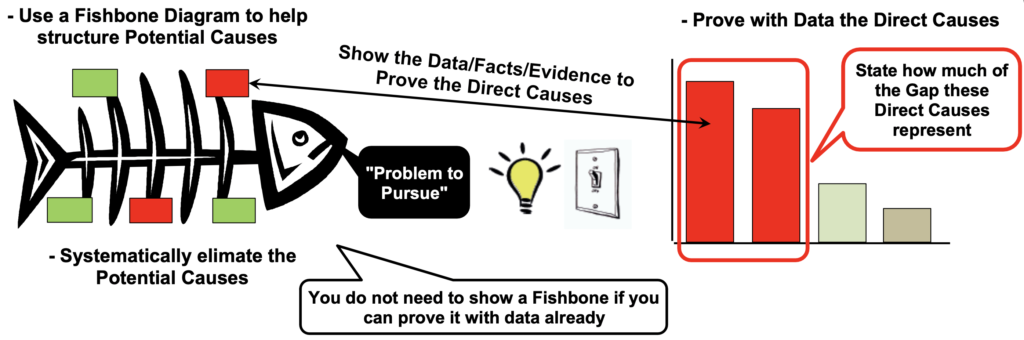
Use data and facts to determine the following:
- What is the problem you are going to tackle?
- When is it happening?
- How is it happening?
- How much of the gap is it contributing to?
Breakdown of critical points:
- Pareto 80:20 rule
- Collect data if you don’t have it
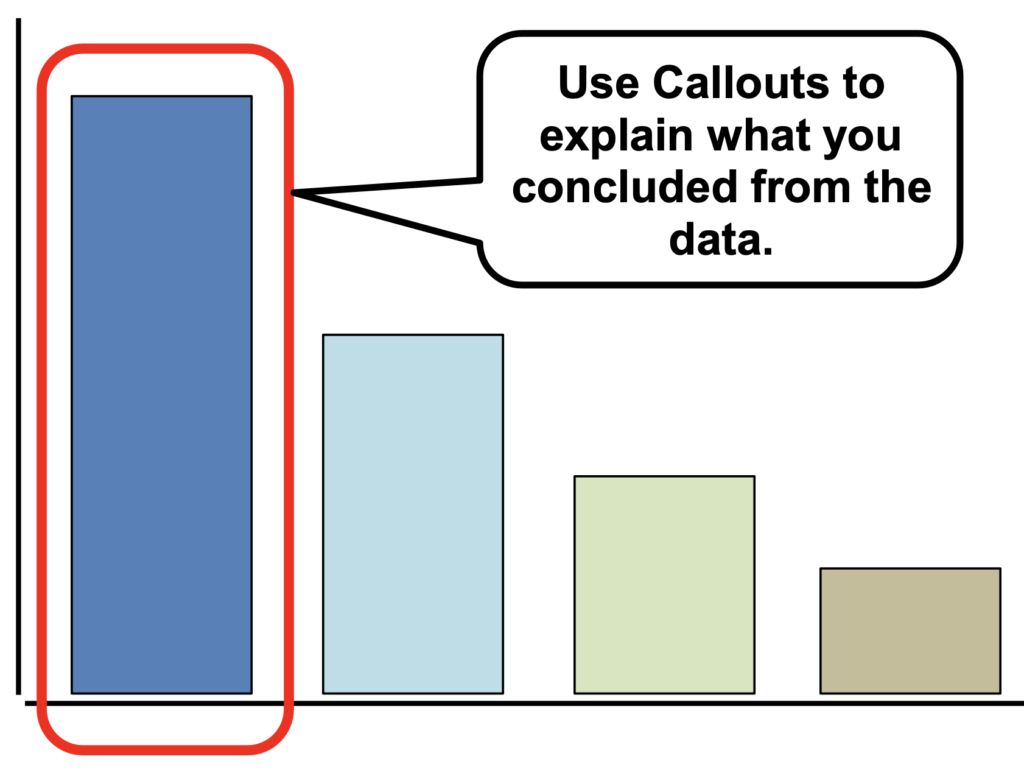
- Use Problem-Solving Tools to analyze the data
- State what the data is telling you!
- Summarise the Problem to Pursue
- A short, simple statement of the problem
- What, Where, When, How, How Much
Direct Causes key points:
- Cause/Effect relationship on the problem
- Light switch test! ON/OFF
- Prove with data or by experiment
- They are the first “Why” in Step 5
Summarise the Direct Cause(s)
- Direct Cause 1
- Direct Cause 2
- How much of the Gap do they represent
Step 4. Target Setting
SMART Target Statement
“By solving the Problem to Pursue by this Date, I will Close the Gap by this much”
Short, simple statement
Always quantify the $, € of the Target and potential look across benefits if initially small.
Visualize your Specific Target Evolution
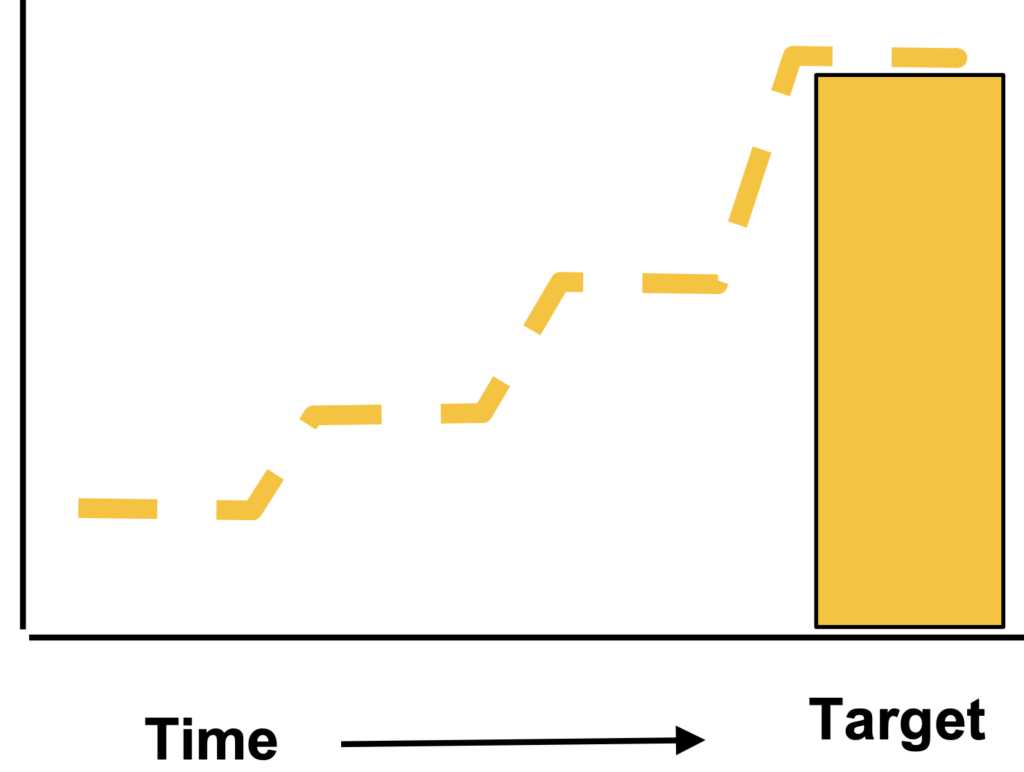
Impact on the Gap

Step 5. Root Cause Analysis

Step 6. Develop and Plan Countermeasures

Step 7. Check results
Result vs your Specific Target
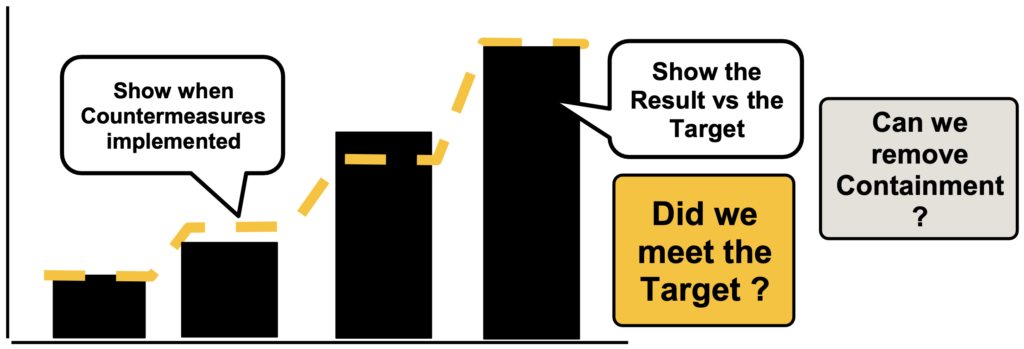
Impact on the Gap

Step 8. Standardize and Share
Standardize
- What did you learn?
- What are the next steps/actions?
- Sustainment: Standardise Countermeasures, update Management Routines
- Update EOS process documents, FMEAs, Control Plans, and other documents…
- MUST be actions (what, who, when)
Share
- How will YOU share the learning points?
- Can we apply the result anywhere else inside your area and outside?
- To similar Products, Processes, Departments, Plants, Regions, Divisions…
- How can we leverage the benefit?
- MUST be actions (what, who, when)
Application of A3 Problem-Solving
The A3 problem-solving process can be applied in manufacturing, healthcare, and service industries. For example, the A3 problem-solving process in manufacturing can improve quality, reduce defects, and improve productivity. In healthcare, the A3 problem-solving process can reduce medical errors, improve patient outcomes, and streamline operations. In service industries, the A3 problem-solving process can be used to improve customer satisfaction, reduce costs, and improve service delivery.
Source: Lean Enterprise Academy
Template here
Updated on May 2, 2023









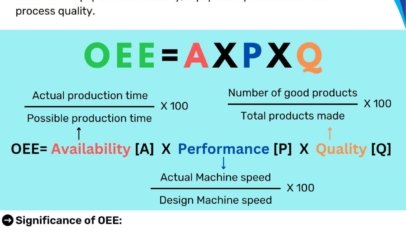

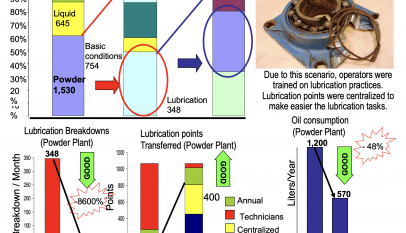







Very good understanding of concepts