AM – Step 6 Activities – Standardization
- Objective
- Standardize Routine Operation to sustain & prevent Problems.
- Activities
- Develop Sub-step Activities
- 6.1 Quality
- 6.2 Change Over
- 6.3 Cyclic Operation
- 6.4 Safety
- Develop Sub-step Activities
- Review the Role of Operators, and Efficiency Improvement and Standardization of Related Work
- Maintain an Effective Autonomous Inspection System
AM – Step 7 Activities – Autonomous Management
- Objective
- Establish Line Management system by First line Team – Autonomous Management
- Control Cost – develop Annual Budget by Team
- Use “Policy Deployment – “Hoshin Kanri”
- Maintain Optimal Equipment Condition
- Striving to Meet the Targets of Zero Failures and Zero Defects
- Maintaining a Proactive Attitude To Equipment Maintenance
12 Key Points in A.M. Implementation
- Collaboration between departments is important
- Thoroughly educating members during the introductory stage at each department, to ensure their understanding of what AM is;
- Sharing roles to attain common targets and exerting maximum efforts
- Leadership of Managers results in practice
- AM is work in itself;
- Placing emphasis on hands on experience, unconcerned with theory.
- The precedent of manager models represents the initiative
- The Managers initiative and shining example is an essential requirement;
- Understanding the essence of AM at the workshop through the use of actual equipment.
- The manner of diagnosis leads to activation
- Directing the people to the tasks to be done in the future;
- Evaluation of what has been done.
- Through education, it is understood that to teach is to learn
- Adopting new ideas for carrying out education;
- Understanding the necessary knowledge personally, to ensure subordinates’ understanding.
- Enhancing understanding through One Point Lessons
- Basic Knowledge: Info that must be shared;
- Problem Case: What was lacking and recurrence prevention;
- Improvement: Cases leading to positive results.
- The experience of success leads to a challenging mind-set
- Accumulating many successful cases;
- Experiencing what has not been carried out help us overcome difficulties.
- Giving Focused Improvement themes to teams for implementation
- Themes related to routine work;
- Minor stoppages, set-up, failure analysis.
- The TPM Activity Board is a communication tool between the Manager and the team members
- Showing the participants plans, ways of thinking, status of execution, and achievements in an immediately understandable way;
- The activity board allows Managers to get a sense of team members efforts.
- Meetings are a barometer of the activity level of the team
- Creating good ideas through all members participation and expression of their opinions;
- Forum of reflection, study, and proposal.
- Work should be executed promptly
- Delay in the execution of requested work will impede the activation of circles;
- Review of the maintenance sector’s response.
- Implement thoroughly
- The degree of thoroughness determines the quality of maintenance and management.
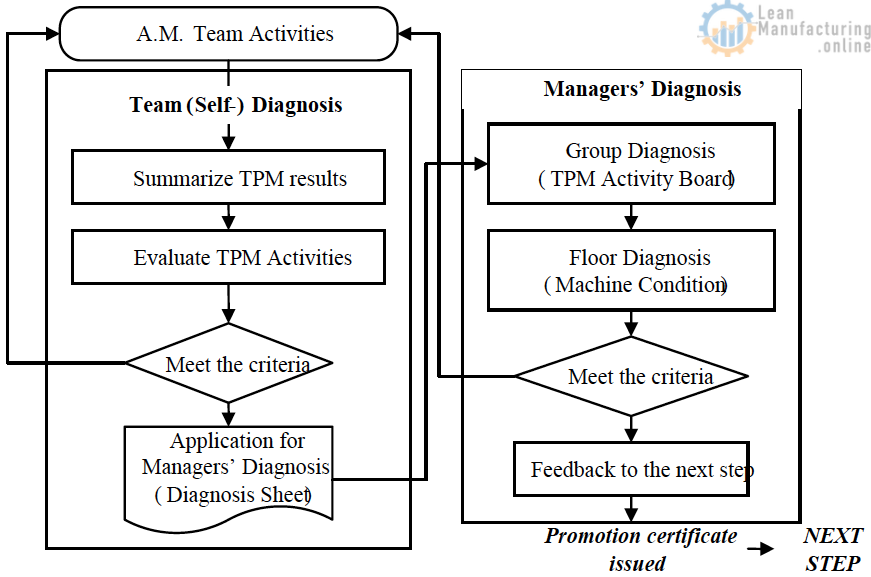
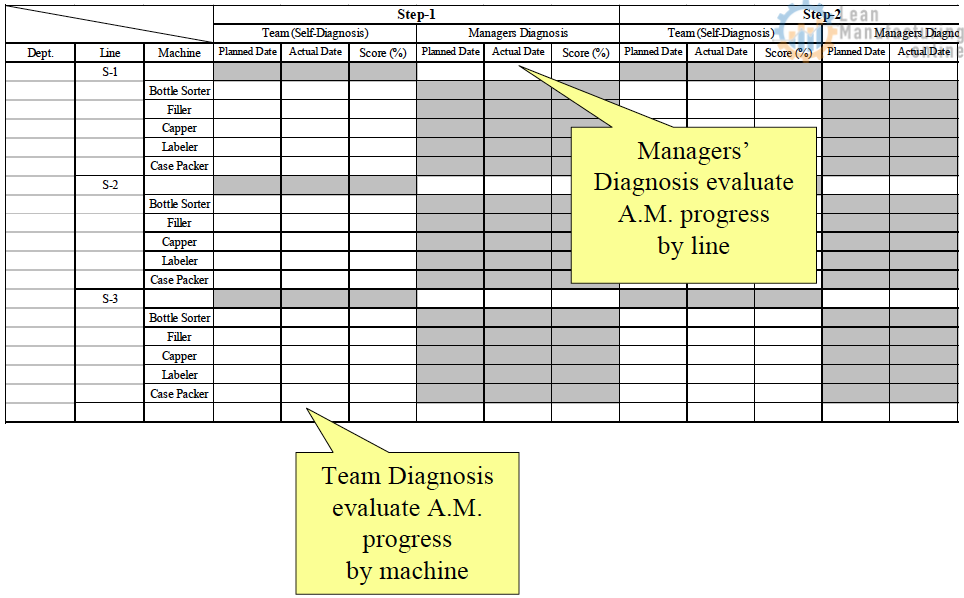
Step Diagnosis
This is the important goal-sharing process.
- Each team evaluates the progress of Kaizen/TPM.
- Control timeline (Deadline)
- Evaluate Kaizen/TPM activities from the viewpoints of “Need to Improve” – Weakness & Opportunity.
- Align the direction with the plant-wide master plan.
- Managers evaluate the progress of Kaizen/TPM form the viewpoints – how each team drive the right direction onto the plant-wide target & goals and managers’ target & goals.
- Plan & Analyze the resource for a team to move on the right direction & the right on time.
- Analyze the connection with AM and other pillars. – Move smoothly such as AM and T&E using F-Tags, … etc.
Step Diagnosis Flow
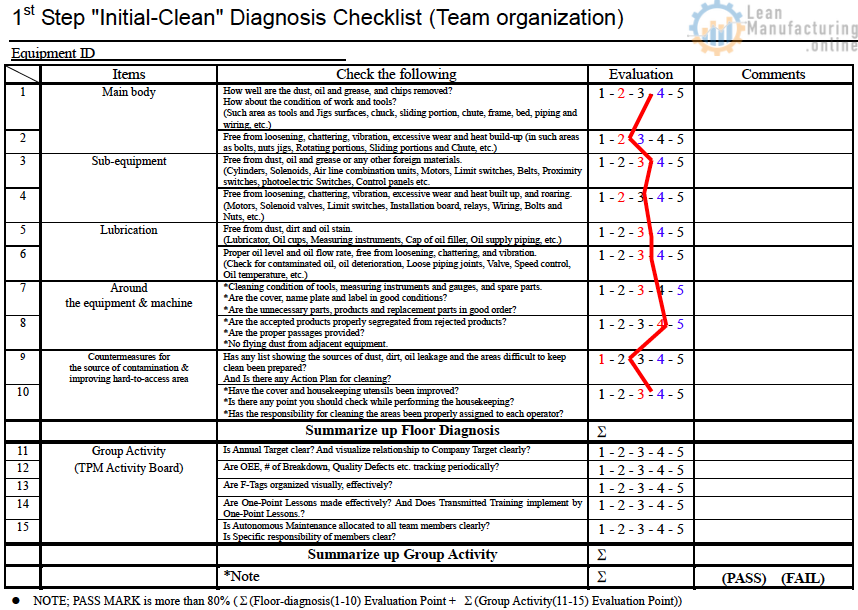
Step Diagnosis Checklist
AM Step Progress Control
Elements of an Activity Board
TPM Activity Board Requirements (Activity Board for First-line Small Group)
- Policy & Implementation plan
- Policy & Target
- Company / Factory policy & target / Department / Team policy & target (Annual, quarterly) / Action plan; TPM Master plan (Plant-wide and long term) / Team implementation plan (Annual plan and Quarterly)
- Indicators (Measurables)
- Tracking data (Daily & Monthly)
- Productivity (Output per hour person)
- Quality (# of scrap and type of scrap)
- Cost (Overall Equipment Efficiency – Bottle neck machine)
- Delivery & Availability – Zero Breakdown calendar
- (On-time delivery ratio, # of unscheduled breakdown, downtime, change over time
- Safety (Lost time injury)
- Data collection (Daily or Every shift)
- # of Major stops (Equipment Failures)
- # of scrap and type of scrap, rework
- Safety Information (# of Near Miss Report, LTA / MA)
- * Change over time , Time and Operation Analysis Chart
- # of minor stoppage
- Tracking data (Daily & Monthly)
- AM & FI Activities Process
- AM Activities at each step – SOCS &HTA, Visual Control
- One Point Lesson (Basic knowledge / Improvement case / Troubleshooting)
- Trend chart – # of F-Tag (Blue / Red ) & F-Tag log (Fuguai list)
- FI Topics Register – 5-why analysis / P-M Analysis
- Autonomous Maintenance standards
- Review of action taken
- # of One-point lesson / # of Tag (Blue / Red)
- Step Diagnosis comment, score & sticker