Section 1
5 WHY Process
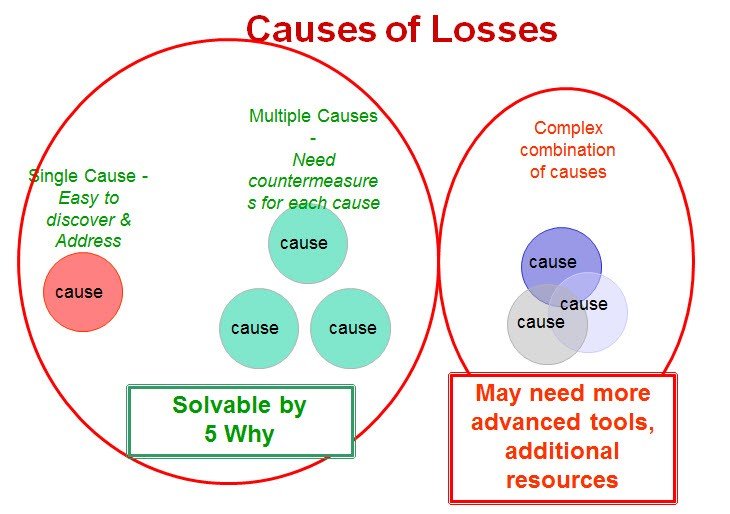
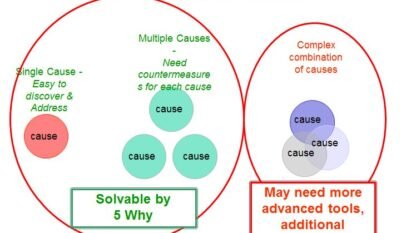
Causes of Losses are Often Complicated:
Common Failure scenario:
1. Management system breakdown
2. Failure to implement countermeasures
3. Premature equipment failure
4. Employees fail to follow the procedure
5. Failure to ID & Respond
6. Large Loss Results
5 Why Analysis is Proactive Addresses the Underlying Causes of Losses:
- 5 Why identifies the Root Causes of Losses
- Supports Implementation of Countermeasures
- Promotes Transfer of Learning
Where Does 5 WHY Fit in the Focused Improvement Process?
Focused Improvement Process
- Collect Data
- Identify, Prioritize & Select Projects.
- Ensure Equipment Is Restored
- Establish the Team
- Use the CAP-Do Process (5 Why is used here)…….. to manage the improvement cycle
- Monitor and Hold the Gains
- Document the Project (Kaizen Summary Sheet, Kaizen database)
- Celebrate Success
- Replicate Where Applicable.
- Share Learnings (Kaizen database, CI and Pillar CoP)
How is 5 WHY used in CAP-Do?
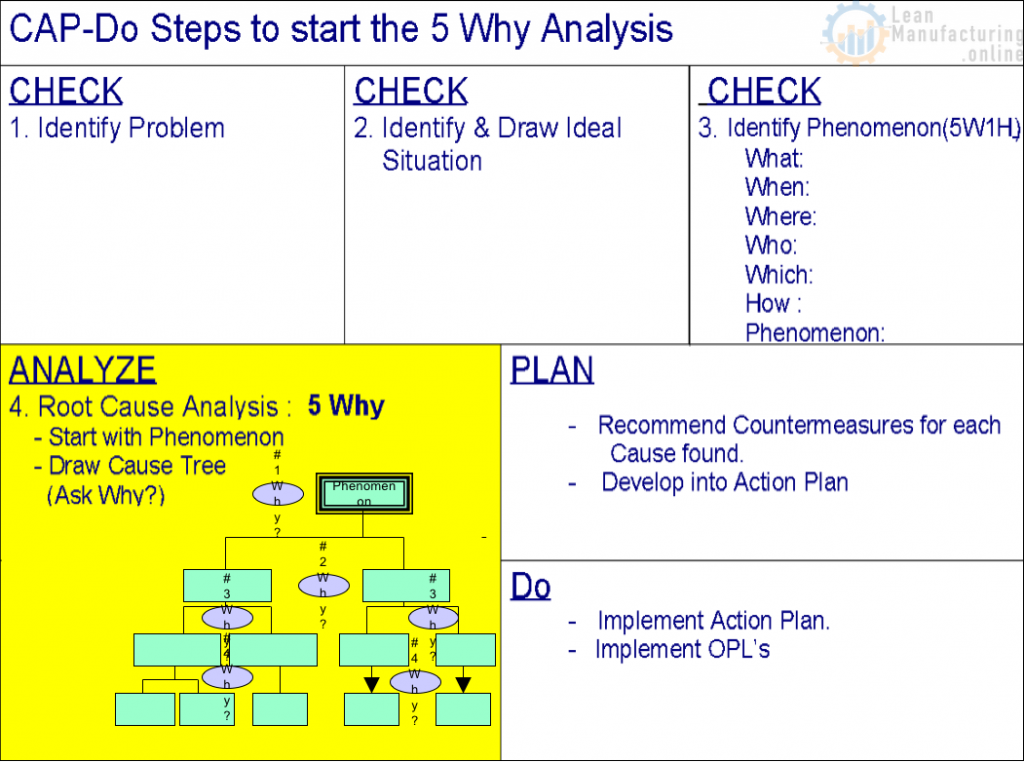
1. CHECK
a. Identify the problem
b. Understand the Ideal Situation
- Machine: equipment sketches and the operational principle
- Material: samples of material involved in the problem
- Method: Flow charts of the process
- Man: Forms, procedures
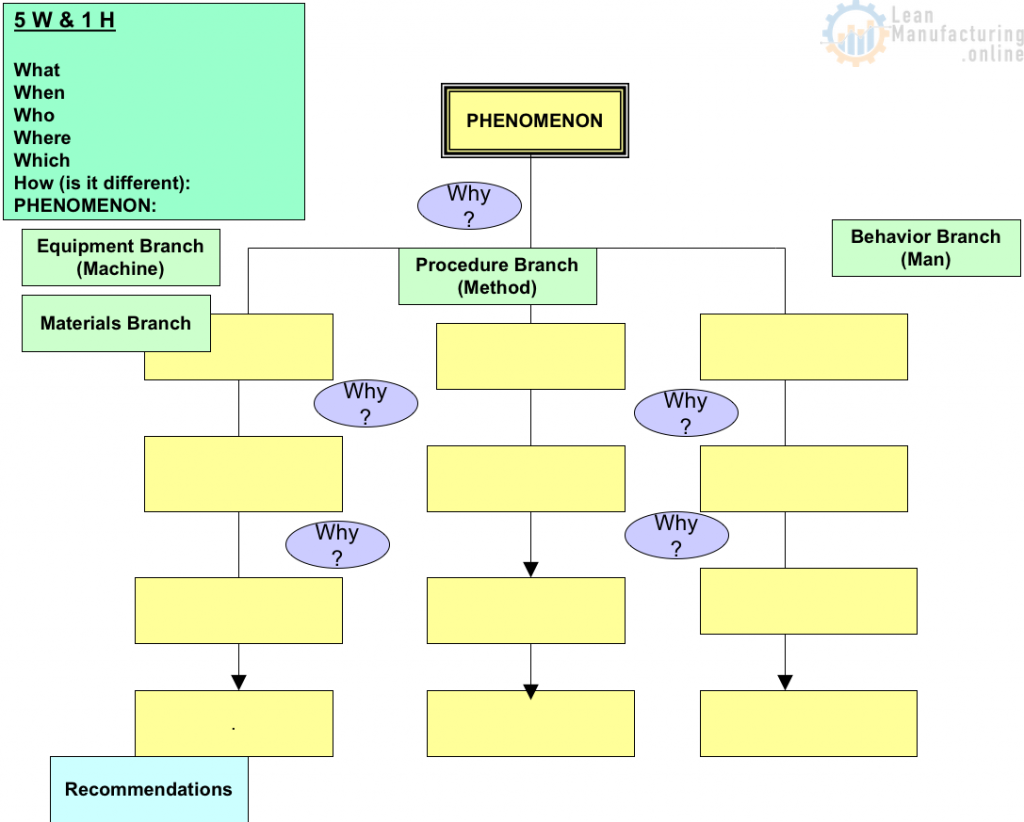
c. Identify the Phenomenon 5W1H Analysis
2. ANALYZE
Root Cause Analysis tools: 5 WHY
3. PLAN
a. Action Plans (Immediate, Intermediate, Long Term)
4. DO
- Safety Comes First!
- OPL’s
- Implement Actions
- Observe Results & Hold the Gains
Before Starting a 5 WHY ANALYSIS …
- The CHECK phase of CAP-Do must be completed . . .
– The problem identified
– The Ideal Situation understood
– The Phenomenon identified through the 5W 1H Analysis
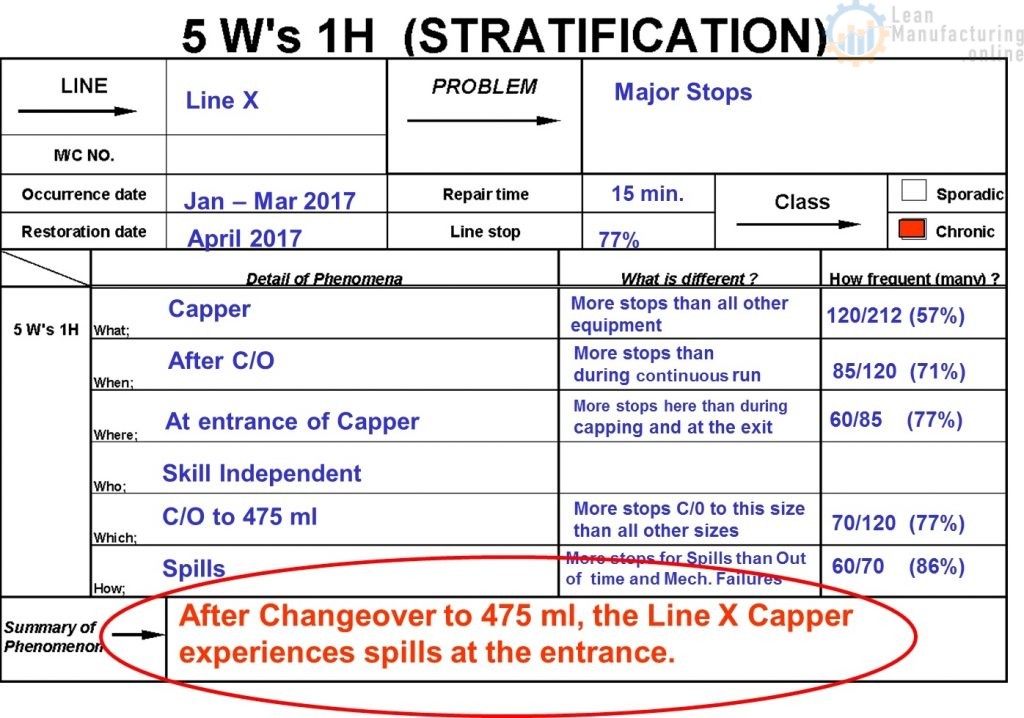
How Do You Start the 5 WHY Analysis once you identify the Phenomenon (5W 1H Analysis)?
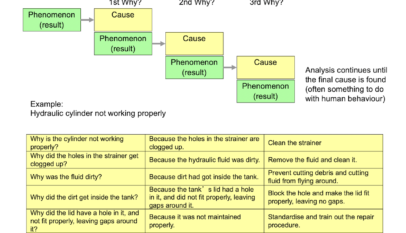
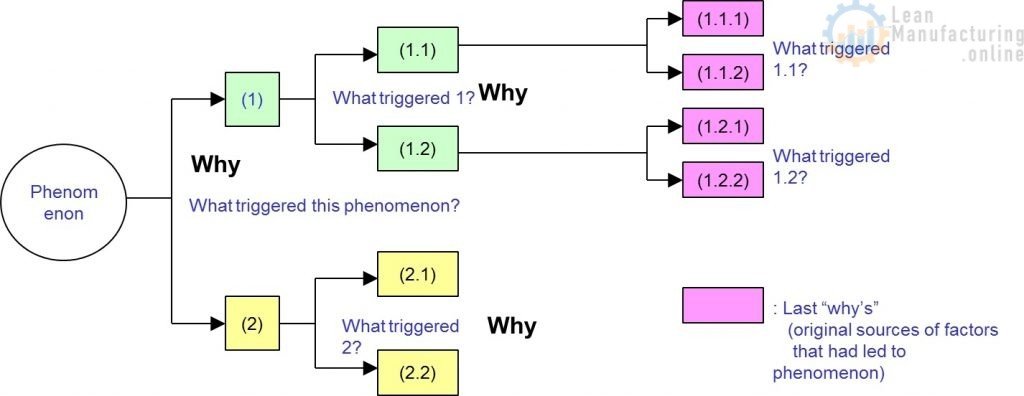
- The 5 WHY Analysis involves asking the question “WHY ?” multiple times (typically 5) until you arrive at the root cause.
- The Phenomenon Statement from the 5W1H is the starting point for the first WHY.
EXAMPLE (see picture above) – Transition from 5W1H (CHECK Phase) to 5 WHY (ANALYZE Phase)
- Why does Line X Capper experience spill at the entrance after the changeover to 475 ml?
Ask Why…? Ask Successive Whys…?
(Follow Phenomenon – (Be)Cause Relationship)
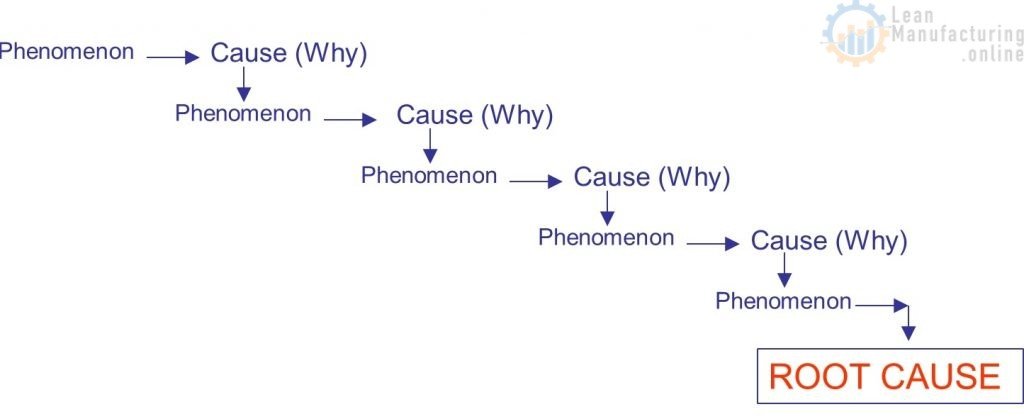
Develop a Cause Tree to Order your Thinking
5 WHY Analysis Using the 4 M’s
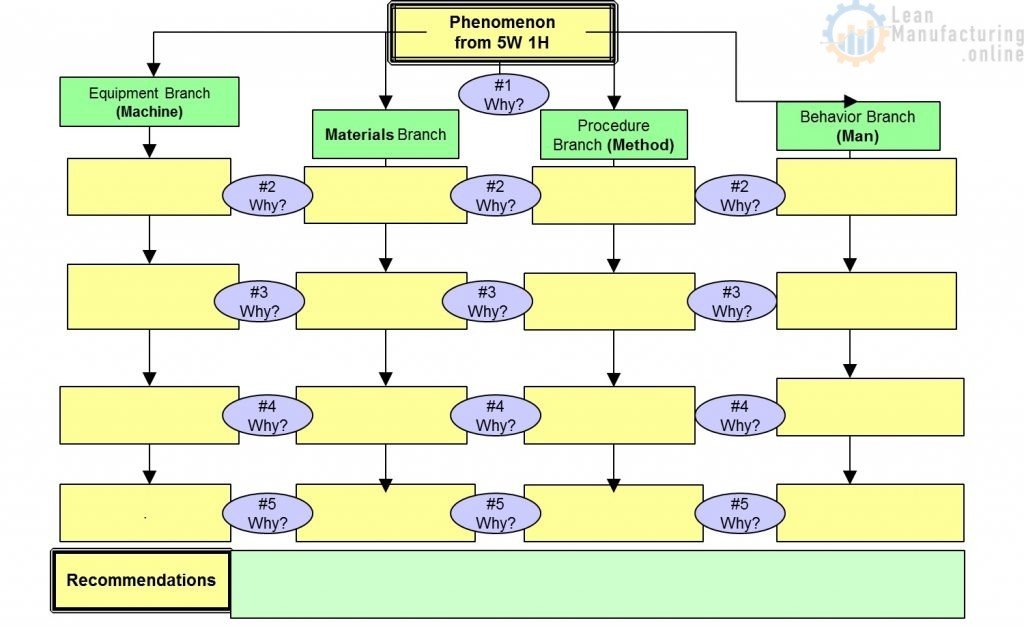
Causes to Consider:
Equipment Branch (Machine)
- Improper Equipment Ordered
- Poorly Designed Equipment
- Inadequate Maintenance
- Wear & Tear
- Abuse or Misuse
Materials Branch (Material)
- Materials out of spec:
- Product
- Packaging
- Ingredients
- Materials damaged:
- by machine
- from storage
- from supplier
Procedural (Method)
- Lack of Procedures
- Inadequate Procedures
- Misunderstood Procedures
- Failure to Warn or Respond
Note: Large losses often occur because of failure to take timely action
Behavioural Branch (Man)
- Lack of Knowledge
- Lack of Skill
- Physically Incapable
- Lack of Motivation
5 Why Analysis Pitfalls to Avoid
- Failure to step SLOWLY and METHODICALLY through the process
- Tendency to jump several “Why” s at once
- Tendency to assign pre-conceived causes
- Failure to consider ALL of the causes
- Use the 4-M approach to help avoid this pitfall
5 Why Analysis – Recommendations
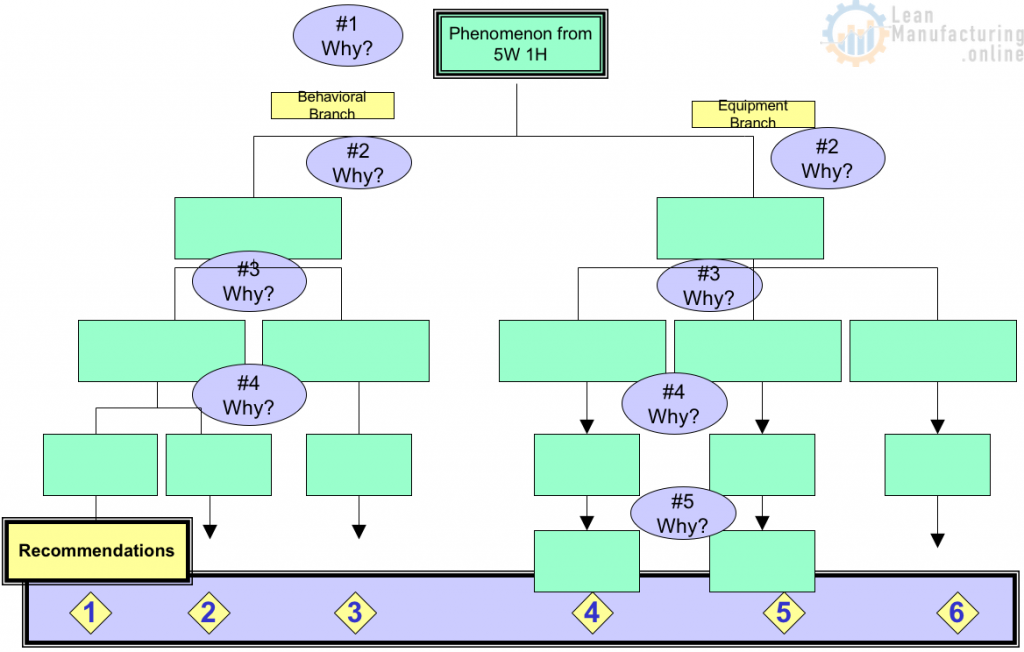
What to do with the Recommendations?
. . .Follow CAP-Do . . .

How to go from 5 Why to the PLAN Phase of CAP-Do?
- For each of the last Why answers, identify recommendation(s) (countermeasures):
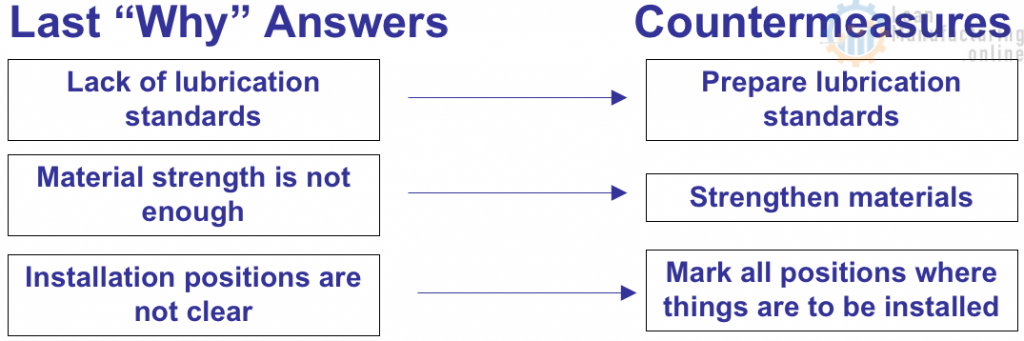
- Develop an Action Plan for each of the countermeasures:
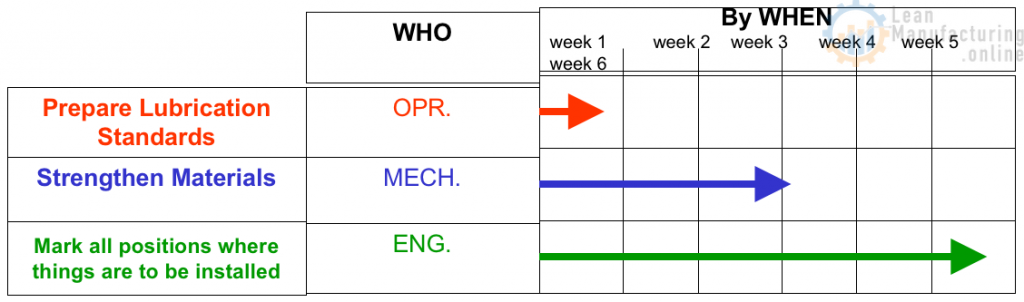
Carry Out “Do” Phase of CAP-Do
Implement the Action Plan
Hold the Gains by Developing Standards:
- Cleaning, Inspection & Lubrication Standards
- Processing Standards
- Maintenance Standards
- Training Standards (i.e. One Point Lessons)
- Engineering Standards
One Point Lesson
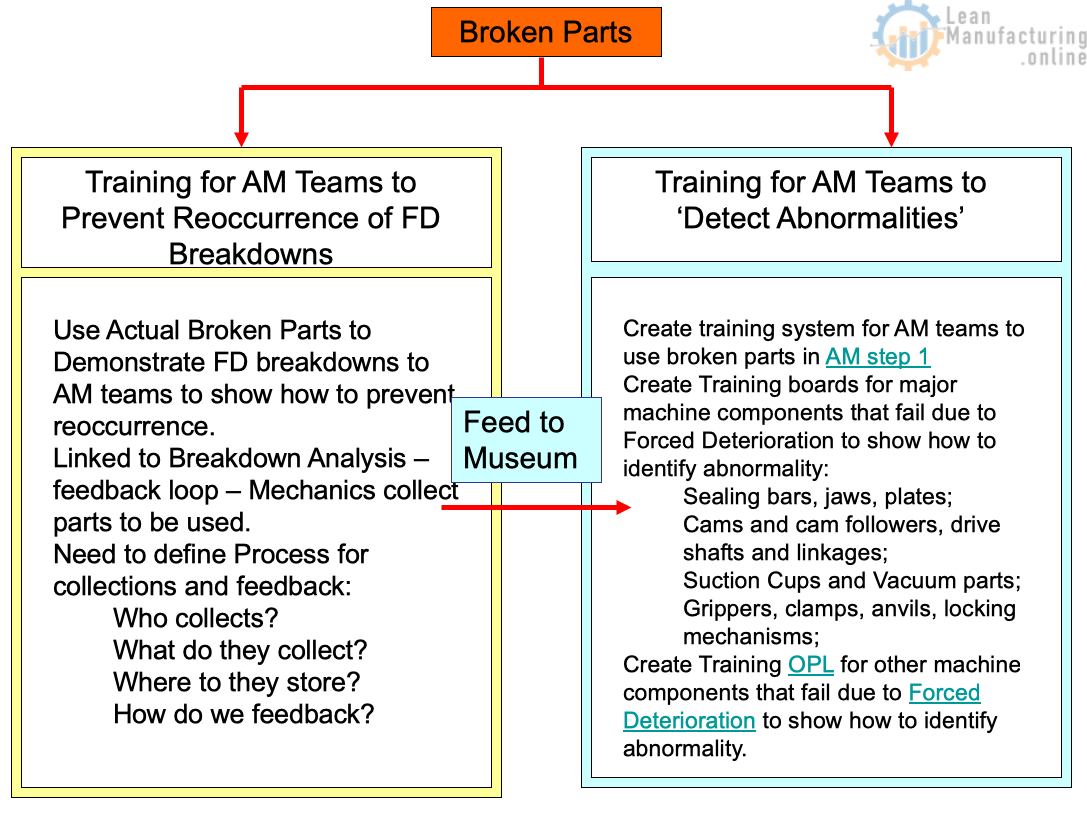
Section 2. Application of the 5 WHY Process
The Loss Pyramid
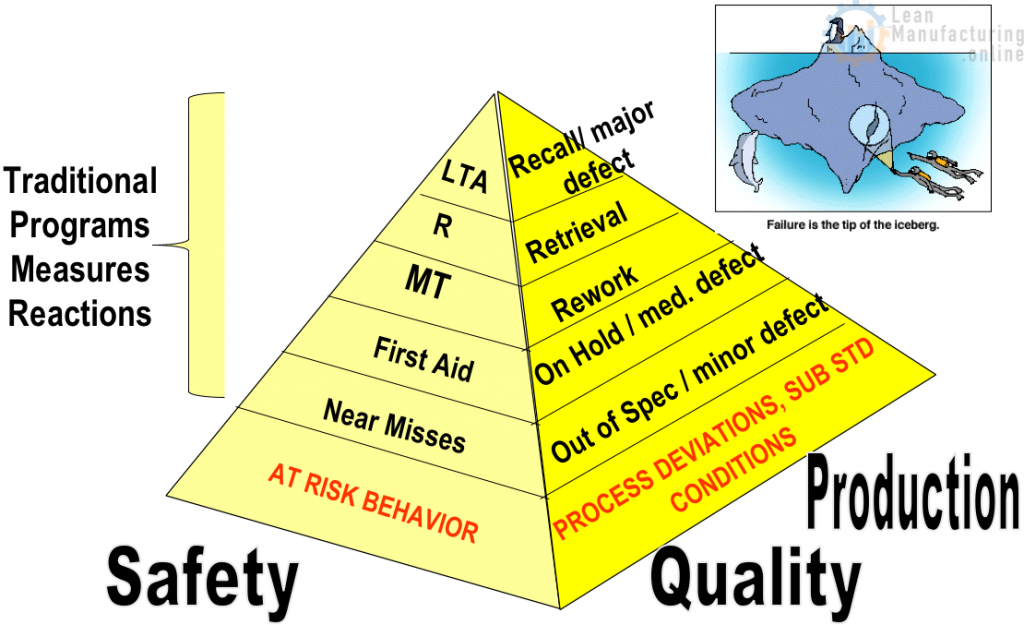
Application of 5 Why
Enables Identification of Problems BEFORE They Escalate Up the Pyramid
- Identifying Sources of Contamination, Stoppages (AM Pillar)
- Tool for Analyzing Cause / Losses in Focused Improvement (FI Pillar)
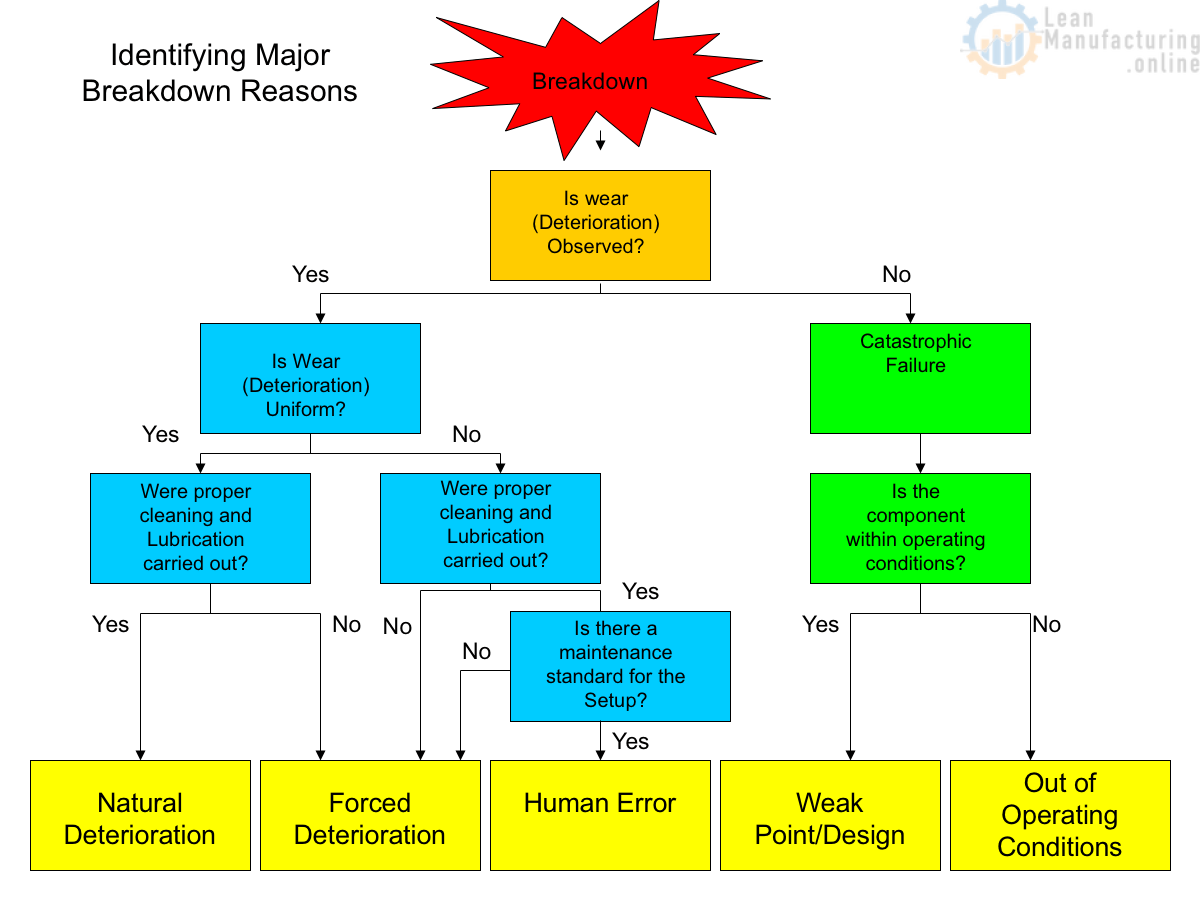
- ID Reasons for Breakdowns (EM Pillar)
- ID Causes of Minor Defects, Out of Spec
(QM Pillar) - ID Causes of Near Misses, First Aids (SHE Pillar)
Section 3 Field Case Studies
Root cause analysis