Planned Maintenance – Introduction
General:
- Provide an overall understanding of Planned Maintenance
- Facilitate the site in developing and refining the PM plan
- Identification of additional training requirements
Develop an understanding of:
- Objectives of the Planned Maintenance Pillar
- The support required for Autonomous Maintenance, T&E, and EM Pillars
- The objectives and approach of each of the PM elements
Prepare:
- Develop a 3 Year Pillar Master Plan
- Detail for each of the 8 PM elements
- Pillar Goals, Targets, and KPI’s
Presentation:
- Presentation of workshop results to Site Steering Committee
TPM Health Check
- Must be able to plan, organize, lead and control;
- Planning the work by predetermining the expected quality and quantity of output for every job;
- Organize the work by specifying the appropriate ways and means to perform each task;
- Leading and influencing others to engage in work behaviors to achieve the desired results;
- Controlling the work by:
- selecting and training qualified individuals;
- overseeing the actual job performance;
- verifying that the output meets the expectations.
Purpose
To establish and maintain optimal equipment and process conditions, cost-effectively and efficiently.
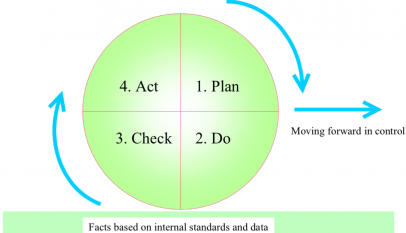
Plan
- PM and AM are clearly defined. Both maintain the equipment with shared responsibilities.
- Time-Based Maintenance (TBM) and Condition-Based Maintenance (CBM) is being selectively used.
- Specialized maintenance techniques such as lubrication control and root cause analysis are being used.
- Reliability, maintainability, and availability are being measured.
- Corrective maintenance is pursued and utilized in the creation of MPs.
- Maintenance equipment is under control.
- Data concerning downtime, man-hours, MTBF, MTTR, etc is being analyzed.
- CMMS is being effectively utilized.
- Equipment diagnosis techniques are studied and used.
- Maintenance costs are understood and controlled.
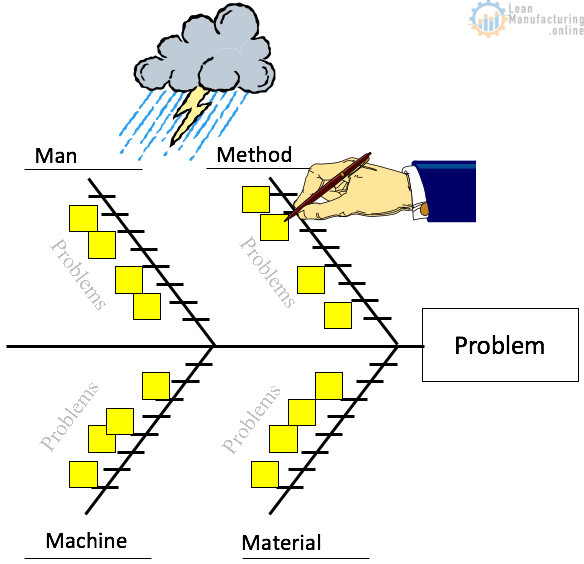
The 6 steps for effective maintenance
Step 1. Evaluate and understand current conditions
- Prepare or update machine log
- Evaluate and prioritize the equipment
- Rank failures
- Understand the failure situation and set maintenance goals
Step 2. Restore deterioration & correct weaknesses
- Help operators restore the equipment
- Correct weaknesses and lengthen equipment life using focused improvement methods
- Prevent recurrent major failures
Step 3. Build an information system
- Build a failure data management system
- Build a system for controlling parts and materials
- Build a system for controlling technical information
Step 4. Build a periodic maintenance system
- Select equipment and components for periodic maintenance
- Prepare maintenance plans
- Formulate periodic maintenance standards
Step 5. Build a Predictive maintenance system
- Select key equipment for predictive maintenance
- Introduce equipment diagnostics
- Vibration, Temperature, Lubricant sampling
- Roll out to other equipment
Step 6. Evaluate the maintenance system
- Evaluate improvement on
- reliability
- maintainability
- maintenance cost savings
- Review the whole system
Agenda
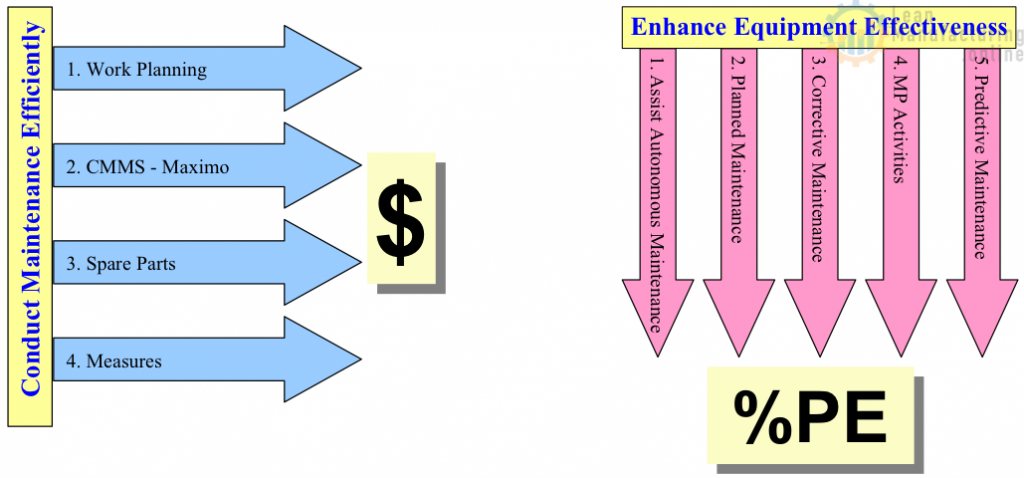
The concept of Planned Maintenance is designed to lower costs by conducting maintenance efficiently and eliminate breakdowns by enhancing equipment effectiveness.
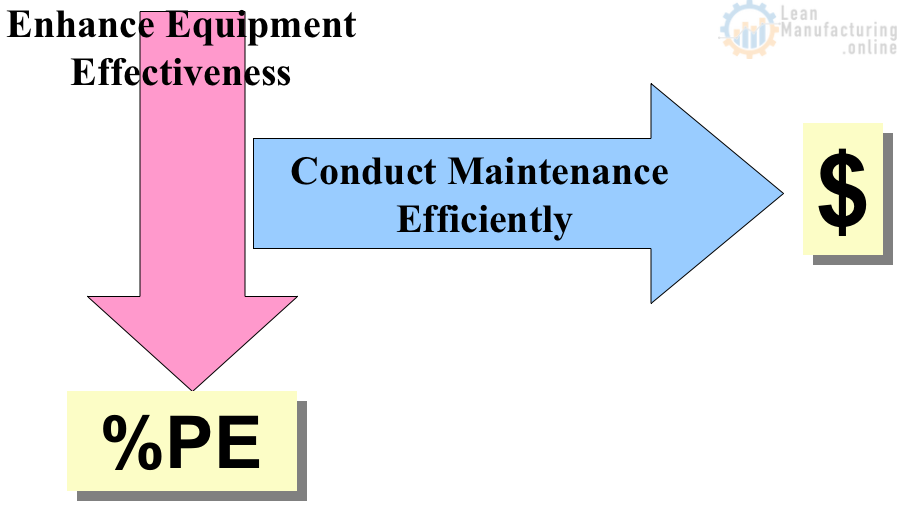
Continuously improving maintenance activities and performing them in a systematic, efficient, and effective manner.
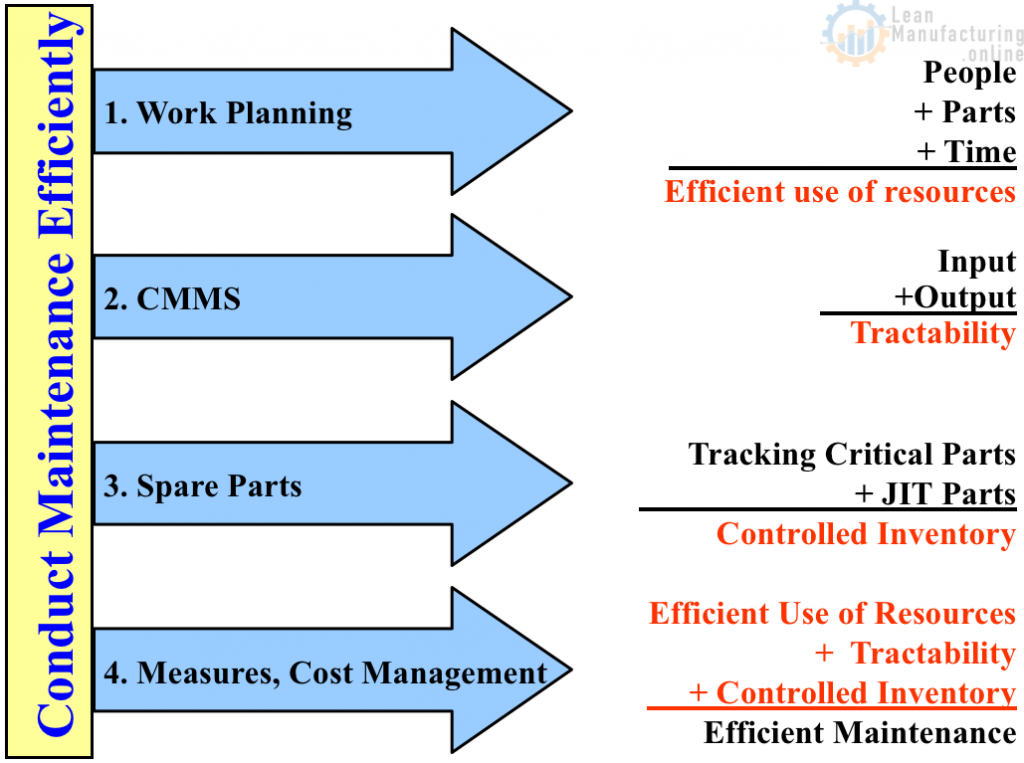
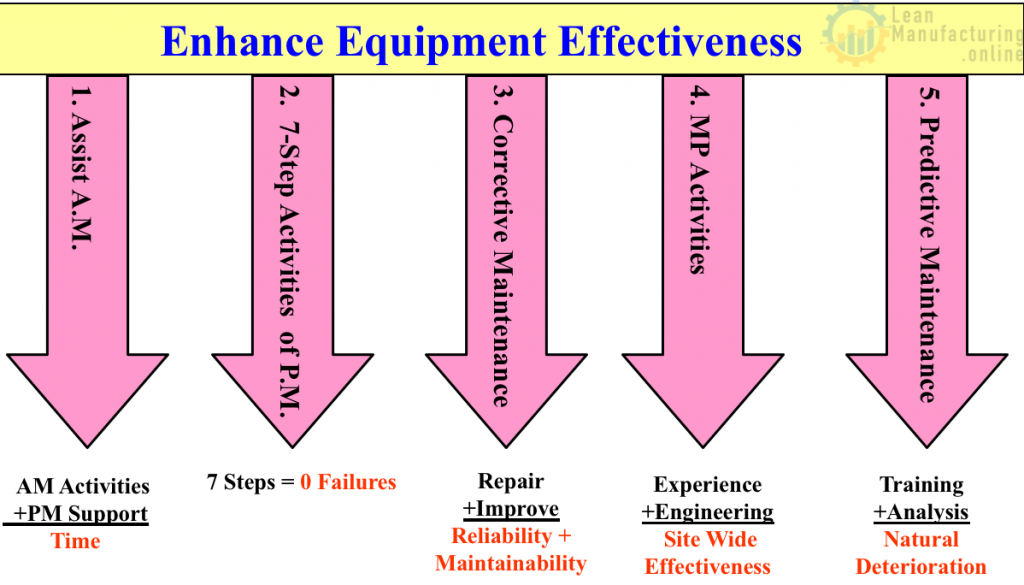
System
A step by step approach for achieving zero breakdowns:
- Return to and maintain the equipment in its basic condition
- Extend the equipment’s effective service life
- Prevent future breakdowns
- Predict equipment’s natural limits
Best Practice
- 100% – Maintenance person time is covered by a work order
- 90% – Work orders generated through PM inspections
- 30% – Work is predictive
- 90% – Planned and scheduled compliance
- 100% – Capacity reached 100% of the time
- Spare Part stock-outs less than 1 per month
- Overtime is less than 2% of total maintenance time
- Backlog for each trade in each department
+/- 2 % Maintenance budget within +/- 2%
Approach to Maintenance
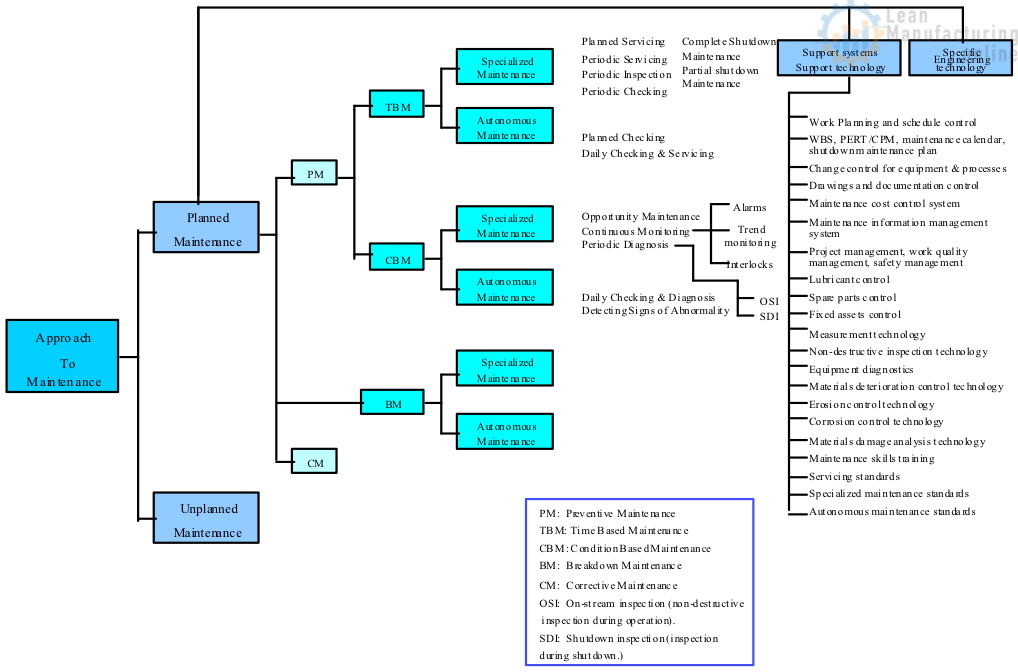
Reliability-Centered Maintenance (RCM)
A process used to determine the maintenance requirements of any physical asset in its operating context…
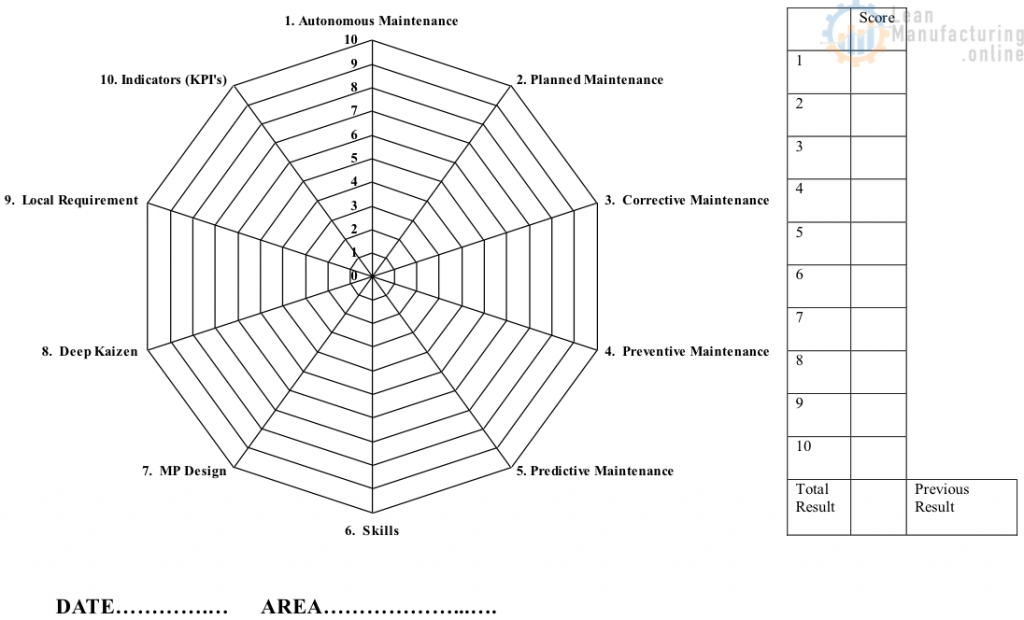
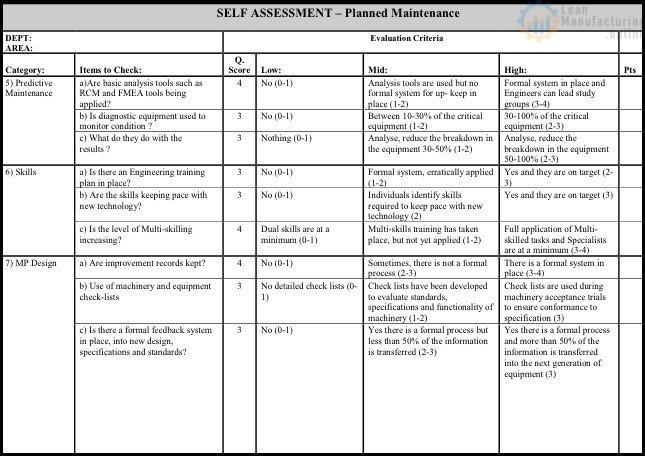
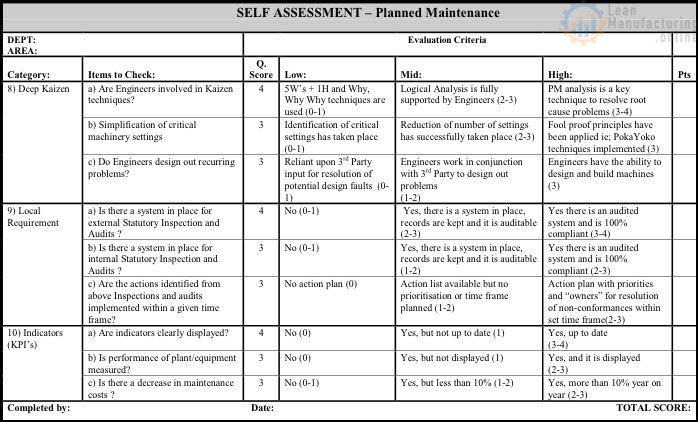
Self Assessment – Planned Maintenance
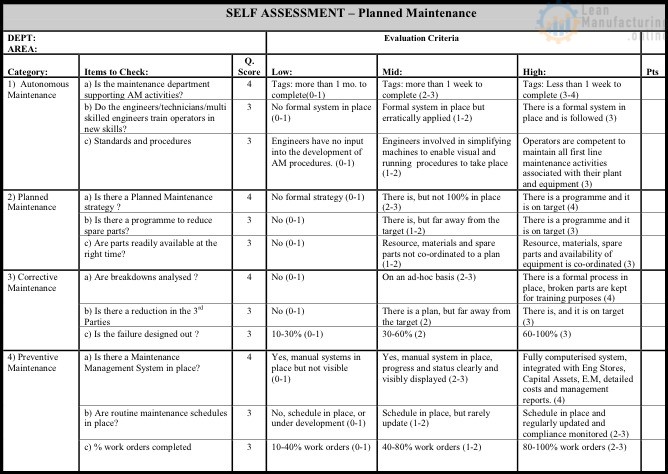
SELF ASSESSMENT FINDINGS – PLANNED MAINTENANCE