Learner Objectives
The main objective of this manual is to be a guideline for training on the principles of Early Equipment Management (EEM).
After you have completed your training you should be able to complete the following activities that make up the EEM process.
- Understand the “Idea Phase” of the process flow and how this process organizes the plants Capital Plan and Total Business Plan. Review the Idea Form and its sources.
- Understand the “Scope Phase” of the process flow and the data gathering required to successfully complete the conceptual engineering review (CER) phase of a project. Review the Customer Brief and its beginnings during the Scope Phase.
- Understand the “Design Phase” of the process flow, collecting MP data, maintaining the MP database, and maintaining and publishing the Design Review Form. Designing safety into the project using the Project Design Safety Checklist and Project Safety Checklist as guide post to insure all of the questions and issues are dealt with in the design phase. Understand Training and PM pillar linkages.
- Understand the “Procurement Phase” and the links to MP data, equipment specifications, contractor qualifications, and the bidding process.
- Understand the “Build and Commission Phase.“ Discuss the meetings and their frequencies to effectively communicate all of the safety, design, installation, and procurement issues of a project. Discuss commissioning requirements.
- Understand the “Completion and Evaluation Phase” using the 30/90 day Project Evaluation Forms and calculation of Launching Costs.
- Understand “Post Project Data Collection and Housekeeping.”
- Updating MP databases
- Calculating and posting KPI’s for the project
- Insuring that all as-builts have been captured and distributed
- Insuring maintenance manuals have been issued
- Forms (Appendix)
- Customer Brief
- Project Safety Checklist
- 30/90 Day Evaluations
- Launching Costs
- MP Form
- Commissioning Information
Section 1. Ideas phase
1.1 DEVELOP IDEA
Resources: EEM Champion, Engineer, Production, TPM, SHE
Checkpoints: Purpose and Necessity
Anyone in the business unit can submit an idea as long as there is a benefit associated with it. If the individual needs assistance formulating the idea, the resources will be able to work as coach or mentor with their idea.
The Supply Chain drives the strategic projects through Manufacturing, Engineering, and other Supply Chain Functions. These projects can be capacity, new projects, flexibility, or to be proposed in nature.
1.2 COMPLETE FORM
Resource: EEM Champion, Engineer, Production, TPM, SHE
Checkpoints: What, When, Where, Who, Which, and How
Document: Idea Form
The purpose of the form is to standardize the beginnings of the CER. By filling out the top section of the form, the person, department, submission date, supervisor/coach, and title of the suggestion are captured. Present situation, proposed solution, and benefits are then formulated.
1.3 REVIEW (Establish Justification)
Resources: EEM Champion, Engineer
Checkpoints: Benefits
Documents: 1.4 Idea Bank
Each Idea Form must be evaluated on its own merit by what benefits it will provide to the business. Either an engineer or the pillar champion will review the idea with the sponsor to determine the benefits.
If the idea doesn’t show enough benefits to be pursued, then the form is reconciled and returned to the originator with comments.
If the idea has a benefits, it is then evaluated on it criticality to the business. If there is no immediate need, it is then put into 1.4 Idea Bank for review periodically for addition into future Capital Plans.
If the idea has benefits and is then evaluated as critical to the business, the idea will be added to the Active List.
1.4 IDEA BANK
Resources: Engineer
Checkpoints: Purpose and necessity
Documents: Idea Bank
All ideas that have no immediate need will be kept in the Idea Bank. This list will be reviewed periodically to evaluate purpose and necessity.
1.5 ACTIVE LIST
Resources: Engineer
Checkpoints: Authorization and Spending Limits
Documents: Active List, Capital Plan
The engineer takes the idea, analyzes the capital requirements for this idea, and sets the authorization and spending limits for the project.
If the authorization and spending limits are within the needs of the project, it can be either put on the Capital Plan or put on the Active List for consideration for the subsequent years.
Section 2. Proposal phase
2.1 DEFINE SCOPE
Resources: Champion, Engineering, Production, SHE, Alliance Engineering Partners, Equipment Suppliers, Construction Management, Purchasing
Checkpoints: Process and Operational Requirements
Documents: Project Scope Form, Project Summary
Defining the scope is also known as Preliminary and Conceptual Engineering. This is an engineering exercise that requires a team effort in process, packing machinery, packing material, quality, development and controls engineering. During this phase, electro-fluid-dynamics, GA’s, P&ID’s, manufacturing standards, and packing material specifications may be generated or reviewed. Request for quotations for packing equipment, tanks, pumps, and other long-lead items may be submitted at this point along with request for construction cost estimates. Historical data from past similar projects is also an important information. It is at this time all municipal, state, and federal regulations and/or permits need to be examined.
The EEM pillar champion and the lead engineer will fill out the following sections of the Customer Brief: Summary, Safety, Design Safety Checklist (Appendix 1), Project Scope (Appendix 2).
2.2 CONCEPTUAL COST AND SCHEDULE ESTIMATE
Resources: Engineering
Checkpoints: Project Scope Form
Documents: Cost Estimate, Technical Analysis
Reviewing the Project Scope Form and affixing the appropriate costs received from vendors and construction management, the engineer develops the cost estimate and defines the technical analysis for the project.
The
engineer then completes the following sections of the Customer Brief: Cost
(Excel Spreadsheet), Operating (Technical Analysis), Engineering
(Technical Analysis), Project Timeline (MS Project Schedule), Management
(Define Project Team)
2.3 LOCAL MANAGEMENT REVIEW
Resources: EEM Champion, Engineer, Production, TPM, SHE, Project Team, Site Management
Checkpoints: Feasibility, Benefits, Scope, Schedule, and Cost
At the Local Management Review the project is reviewed for its value to the business. If it is not approved as a viable project, is will be held in the 1.4 Idea Bank for future reference or consideration. If it is not approved due to scope reasons, it will be put back into the process in Section 2.1 Define Scopefor rescoping. If there is agreement, on the contents of the Customer Brief, by the Project Team, the project will proceed in the process.
2.4 PREPARE PROPOSAL
Resources: Champion, Engineering
Checkpoints: Justification, ROI
Documents: Lead Page, Background, Financial Analysis, Marketing Analysis, MP Forms
The Champion and Engineering, with the assistance of Accounting, calculate the ROI associated with the project. They fill out the Lead Page, Financial Analysis, and Marketing Analysis.
The engineer then completes the Customer Brief Portfolio Section with the Financial and Market Analysis.
2.5 REVIEW CAPITAL PROPOSAL
Resources: EEM Champion, Engineer, Production, TPM, SHE, Project Team, Site Management
Checkpoints: Feasibility, Benefits, Scope, Schedule, Cost
At the Local Management Review the project is reviewed for its value to the business. If it is not approved, it is then moved to Section 2.6 Modification Required. If the project meets the all of the criteria for feasibility, benefits, scope, schedule, and cost, the Plant Project Team in Section 2.8 Project Review 1 will then review it.
2.6 MODIFICATION REQUIRED
Resources: Champion, Engineer
If the project is not approved and modifications are requested, the project will be put back into the process in Section 2.1 Define Scope for modifications. If it is not approved and modifications are not requested, the project will be returned to 1.4 Idea Bank.
2.7 ASSEMBLE PROJECT TEAM
The Project Team must be assembled before the detailed project design commences. All of the team members will not be EEM pillar team members, but the Project Coordinator should be a member of the EEM team or the AM pillar team. The team should consist of the following members:
- Project Manager
- EEM Pillar Champion
- Engineering Leader
- Maintenance
- SHE
- Purchasing
- Development (when required)
- Accounting
- Alliance Engineering Group Leader and Engineers
- Construction Management
- Contractor Representatives
2.8 PROJECT REVIEW 1
Resources: EM Champion, Engineer, Production, TPM, SHE, Project Team,
At the project review the Project Team reviews all of the details of project (drawings, standards, Customer Brief) for completeness and accuracy. If there are any inaccuracies, the appropriate action will be taken to correct and a further review will be scheduled to insure accuracy. Before the document is routed, it must be reviewed to insure that EEM compliance is included and understood by all of the signers of the CER. If there are no issues, the project is then sent for 2.9 Local Approval.
2.9 APPROVAL
Resources: Champion, Engineer
The CER is combined with the Customer Brief and circulated for local approval. When all local stakeholders have signed off, then the CER is sent to the Plant Manager, Supply Chain, and/or Business Team for their approvals.
Local Approvers:
- Department Manager/ Manufacturing Manager
- Engineering Manager
- SHE Manager
- TPM Manager
- Financial Manager
- Plant Manager
Section 3. Design Phase
3.1 PROJECT TEAM MOBILIZATION/COMMUNICATIONS
After the project is approved, the Project Team will assemble and review the EEM principles and how they relate to the approved project. It is at this time that location of the activity board is determined and what role it plays in EEM and the project is explained. A picture of the Project Team is taken and posted on the activity board at this kick-off activity.
3.2 CROSS PILLAR COMMUNICATIONS
Resources: Champion, Engineer, Project Coordinator
Checkpoints: Equipment Operating and Maintenance Requirements
Documents: Customer Brief
The Champion, Engineer, and Project Coordinator review the Equipment List for the project with the PM Pillar Champion. The maintenance requirement sheet will list the equipment numbers and nomenclatures and will serve as a checklist to insure proper communications for development of equipment records, preventive maintenance, spare parts set-ups, and predictive maintenance. The maintenance requirements sheet becomes part of the Customer Brief.
The Champion, Engineer, and Project Coordinator communicates the training needs to the Training and Education Pillar by completing the training plans in the Customer Brief. These training plans define the requirements for the Supervisors, Operators, Electrical Technicians, and Mechanical Technicians. This training should include any safety, operations, technology, quality, and TPM content that is necessary to support the vertical start-up of the project. The training plan documents will become part of the Customer Brief.
3.3 PLAN/SCHEDULE
Resources: Project Team
Checkpoints: Logistics of Material, Equipment, Manpower
Documents: Project Summary, Timeline
After the project is approved, the Project Team will review the project summary and develop the appropriate timeline to guide the project through the remainder of the project. This expanded timeline will become part of the Customer Brief.
3.4 MP DETAIL DESIGN
Resources: Plant Project Team
Checkpoints: Capacity, Reliability, Flexibility, Operability, Maintainability, Life Cycle Costs, Lead Time, Quality, Safety Health & Environment, Core Design.
Documents: MP Data, Hazop, Project Safety Checklist, Design Review Forms, Drawings, Design Documentation
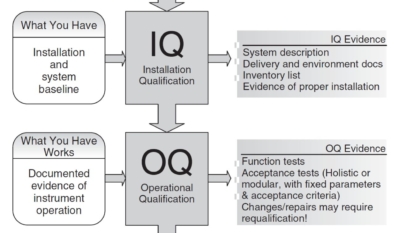
Several safety activities need to be addressed before any designs can be finalized.
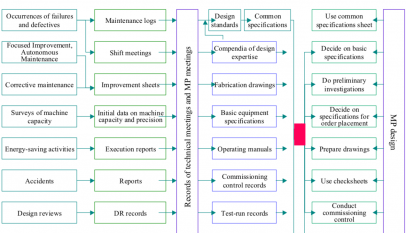
When conceptual engineering is completed, a Process Hazard Analysis, generally a HAZOP, must be completed before detailed design can progress. Any design details will be captured on a design review form to insure inclusion in the engineering. Any training issues will be captured on the Electrical, Mechanical, Operator or Supervisor Training Plans in the Customer Brief. Any maintenance requirements generated will be added to the PM Pillar Maintenance Requirements Sheet in the Customer Brief. Any special requirements that are identified during the Process Hazard Analysis must be funneled to the responsible champion.
Project Design Safety Checklist must be completed in the Customer Brief during the Scope Phase and highlights the areas of safety design that must be focused on during the Design Phase.
The Project Safety Checklist is a document that is reviewed by the Project Team, the department, the Safety Committee, and the SHE representative to the project. The Project Safety Checklist includes safety, mechanical, electrical, training, ergonomics, labeling and signage, operator and process training, hygiene, operating environment, contractors, permits, construction requirements, and environment. The results of this review will be; A Commissioning Sheets will be published for those items that can only be done after construction, like labeling and signage. A Design Review Form will be published for those items that must be included in the Design Phase of the project, the Training Pillar must be notified of any additional training requirements. The SHE Pillar will develop all of the JSAs.
Other TPM activities that must be understood for proper design are MP data, 5s, loss identifications, and countermeasures.
The MP database, on the EEM website, needs to be scanned for modifications made to similar equipment and processes. This information must be put into two areas. One area is Equipment Procurement and along with the EEM equipment attributes is the basis for getting equipment on site that needs no modifications to fit the needs of the project. The other is Initial Design so the modifications to the traditional non-TPM designs meet the needs of the department like clean design, maintainability, and lubrication.
During the Design Phase, regular periodic meetings will occur separately for each discipline and a design status review meetings will be held with all team members to resolve any cross-discipline issues. When contractors and suppliers have been selected, they must be included in theses review meetings.
3.5 DESIGN REVIEW MEETING
Resources: Plant Project Team
Checkpoints: Capacity, Reliability, Flexibility, Operability, Maintainability, Life-cycle Costs, Lead Time, Quality, SHE, Core Design
Docum ents: Design Review Checklist
Design review meetings will be held on a regular basis. At these meetings, the status of each design item will be reviewed in relation to its target date to insure the Design Phase stays on schedule. Any issues that need technical design evaluation will take place only with the required resources.
After this meeting, an updated Design Review form will be published by the engineer and posted on the project activity board.
3.6 PROJECT REVIEW 2
Resources: Plant Project Team, Contractors, Suppliers, AM Pillar
Checkpoints: Capacity, Reliability, Flexibility, Operability, Maintainability, Life-cycle Costs, Lead Time, Quality, SHE, Core Design, EEM Equipment Attributes
Documents: Drawings, Design Documentation, Equipment Specifications
This Project Review meeting is the last meeting before the PO’s are placed for equipment and construction. At this review, all of the safety and TPM requirements must be included in the design. The AM and SHE pillar representatives must insure that all of the requirements are included in the designs. The Engineering group must insure that the MP data and EEM equipment attributes have been included in the machinery and construction specifications.
Section 4. Build and commission phase
4.1 PROCUREMENT
4.1.1 Request for Quotation
Resources: Engineer
Checkpoints: Safety Guidelines, Ergonomics, MP Forms, Standards
Documents: Drawings and Specifications, EEM Equipment Attributes, RFQ
Engineer and Purchasing will develop a RFQ that will meet the main function requirement of the design while employing the qualities of the equipment attributes.
4.1.2 Bidders List
Resources: Engineer and Purchasing
Checkpoints: Vendor Qualifications, Lead Time, Costs
Documents: Vendor Requisitions
Engineering and Purchasing select vendors to bid on RFQ, insuring that contractors and suppliers meet the business, safety, and quality standards required by company.
4.1.3 Requisition
Resources: Engineer and Purchasing
Checkpoints: Approval Limits, Taxes, Insurance, Terms & Conditions
Documents: Purchase Requisition and Letters of Intent
Engineer and Purchasing review each bid, insuring that all of the requirements defined in Section 5.1 Request for Quotation are satisfied and no impact will be made to scope and schedule before placing the purchase order.
4.1.4 Supplier Inspection
Resources: Engineer, Operators, Crafts
Checkpoints: Specifications, Performance
Documents: Factory acceptance test
Project team will run equipment on supplier’s site before shipment, insuring all of the main function design equipment attributes and safety requirements are met before shipment.
4.1.5 Delivery
Resources: Plant Project Team
Checkpoints: Verification
Documents: Receiving Reports
When equipment is received, inspect immediately to insure that none of the equipment is missing or damaged before unloading, if possible. Then either move it into place or put in a secure area protected from elements. Find documentation and distribute to the necessary groups.
4.2 INSTALL
Resources: Plant Project Team
Checkpoints: Schedule, SHE
Documents: Progress Report, Design Review Forms
4.2.1 Activity Board
Before
the project goes to the field, an activity board should be positioned at a
central location that will hold all of the current information. This information will include all safety work
permits, contract progress report, design review forms, project schedule, MP
data, customer brief, accident reports, project safety checklists, and OPL’s
for accident.
4.2.2 Progress Meetings
The Project Team, Project Manager, contractor representatives, and discipline engineers will meet regularly. The agenda of this meeting covers the following items:
- Safety issues
- Contractor coordination issues
- Equipment Deliveries
- Civil/structural
- Mechanical
- Electrical
- Scheduling issues
- Design issues
The minutes of this meeting are published by the Project Manager or Construction Manager and posted on the activity board.
When design review is updated, the Project Engineer will post a copy on the activity board.
4.2.3 Contractor Safety Meeting
Each week all of the contractors are assemble for a safety meeting held by the contractor. It is expected that a member of the Project Team will attend this meeting. Each contractor signs the safety meeting sheet. This sheet is posted with the project progress report on the activity board.
4.3 TRAINING
Resources: Trainers and Trainees both operations and trades
Checkpoints: Trade’s and Operator’s Competencies
Documents: Basic Operating Procedures, Standard Operating Procedures, and Training Certifications
During the Training Phase, all of the items on the operating and trades training plan must be covered and training certified by the testing personnel.
4.4 COMMISSIONING
Resources: Project Team
Checkpoints: Performance Deficiencies
Documents: Commissioning Reports, Deficiency Lists
4.4.1 Assemble Commissioning Teams
Teams need to be assembled along disciplines. Each team needs to have an engineer and at least one craft person to do installation, functional, and safety commissioning.
4.4.2 Develop Commissioning Plan
Commissioning plans will vary as to the type of equipment and the integration and complexity of the controls. Plans should always include the following sections:
- Acceptance Testing
- Installation Checks (civil/structural, mechanical, electrical) – insure properly installed, connected, and rotated
- Functional Testing (mechanical, electrical) – insure that all of the equipment (mixing, pumping, bottle control, case control, e-stops, guarding, mechanical clutches) is functioning as designed
- Safety Commissioning – project safety checklist is completed
- System Integration – all of the upstream and downstream integration properly functions
4.5 DOCUMENTATION
Resources: Plant Project Team
Checkpoints: Update files and drawings, plan PM, attach asset tags
Documents: Project documentation/folder, equipment manuals, PM plan, backed up copies of software and programs
At this point, all of the as-builts should be submitted to update all of the drawings associated with the project. All manuals, PM’s, and programs should be accessible to all operations and craft personnel.
Section 5. Start-up
5.1 START-UP
Resources: Project Team, Supply Chain
Checkpoints: Production Planning
Documents: Start-up Schedule
Project Team and Supply Chain develop a production schedule that reflects the needs of the business.
During the start-up period, all stopss/losses associated withthis project are captured for calculation of the “Launching Costs.”
5.2 START-UP ASSUMPTIONS
- All equipment is commissioned
- All operators are trained
- All necessary spare parts are on site
- All raw materials are on site (process)
- All product is available (packing) and packing materials on site
Section 6. Completion and evaluation phase
6.1 30-DAY FEEDBACK
Resources: Champion, Engineer, Manufacturing, Maintenance, SHE
Checkpoints: Project performance evaluation
Documents: 30/90 day evaluations
Each resource will fill out the 30-day evaluation sheet, rating each section from 1-5 (5 being world class) and filling in appropriate feedback. The 30-day feedback should be used to “clean up” issues needing closure for the project.
6.2 90-DAY FEEDBACK
Resources: Champion, Engineer, Manufacturing, Maintenance, SHE
Checkpoints: Project performance evaluation
Documents: 30/90 day evaluations
Each resource will fill out the 90-day evaluation sheet, rating each section from 1-5 (5 being world class) and filling in appropriate feedback.
6.3 CONSOLIDATE MP REVIEW INTO BEST PRACTICES
Resources: Engineer
Checkpoints: To capture the outstanding and failure of a project as a learning opportunity before project closure
Documents: MP forms, MP form records, standards, and specifications
Engineer should
review all records and insure that all learnings are captured into the MP
database, on the EEM website. Any
standard or specification that has been changed by the MP data should be
modified for future use.
6.4 CONSOLIDATE OPPORTUNITIES
Resources: Engineer
Checkponts: To capture the learning’s, both successes and failure, of a project as a opportunity before project closure
Docum ents: Launching cost
Engineer should capture all of the EEM information and consolidate for review, evaluate all of the assumptions and goals of start up, and calculate launching costs as a percentage of the total project.
6.5 COMPLETION
Resources: Engineer, Capital Engineering Accountant
Checkpoints: Project costs
Documents: PCA (Post Completion Audit)
Engineer will complete a PCA form within two (2) months from the project completion date and forward to and Capital Engineering Accountant. The Engineer and Capital Engineering Accountant will review all costs and insure all invoices have been paid. The Capital Engineering Accountant will then prepare a list of all equipment and services to be capitalized. Based on this list, the Capital Engineering Accountant will issue asset tags for each major piece of equipment per the Engineer’s instructions. It will be the Engineer’s responsibility to insure asset tags are mounted on the equipment.