- EEM is not just an Engineering activity but a collective effort with plant technicians, operators, crafts, supervisors, etc.
- EEM learnings are best obtained with one to one discussions with shop floor personnel.
- EEM must become part of the Capital Expenditure process with acknowledgment of EEM consideration similar to Safety and Environmental input.
- The EEM team will address speed to market in all our efforts, knowing the extra upfront time it takes to do EEM right.
Early Equipment Management Goals
- Design production equipment that is easy to use, easy to maintain, highly reliable, and well-engineered.
- Reduce the time from equipment development to production and achieve ‘vertical start-up’
Long Start-up Period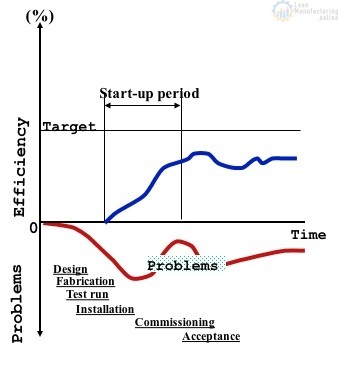
- Lots of teething troubles
- Time to transfer operation skills
- Lack of detail
- Little operational input
Difficult to sustain & improve
- Machines have worn after the warranty period
- Insufficient daily maintenance
- Continuous introduction of new material/product
- Slow skill “catch-up”
Causes of Poor Start-up: 4M’s
- Man
- Machine
- Methods
- Materials
- Other
4 M’s “Man”
Skill
- lack of training
- high level of technology
Organization
- insufficient involvement of factory personnel in the design
- lack of resources
Communication
- language
- no structured process
4M’s “Machine”
Design
- no feedback of improvements
- insufficient consideration of ease of operation, maintenance
- insufficient standardization
- unreliable parts, special parts
Installation
- misalignment
- missing, damaged parts
Supplier
- lack of operational knowledge
- reluctance to incorporate operational knowledge
4M’s “Methods”
Schedule
- no time for design modification
- poor scheduling & resource allocation (commissioning)
- delay in procuring
Procedure
- no standard for commissioning
- insufficient manuals
- unclear handover conditions
4M’s “Materials”
Design
- insufficient consideration of machine dynamics and accuracy
- packaging design change after fixing machine specification
Quality control
- poor source inspection
- defective materials
- poor control (storage) of materials
4M’s “Other”
Budget
- insufficient for design modification
Demands
- insufficient forecasts for future uncertainties
Early Equipment Management Goals
Vertical Start-up
- Short start-up period
- High OEE% that increases steadily
Equipment must be /have:
- Intrinsically reliable design
- Cleaning lubrication inspection standards for AM&PM
- Audit checklists
- Easy to clean, inspect, lubricate and change-over
- Easy to maintain and repair
- Easy to operate (fail-safe)
- Easy to obtain data for predictive maintenance and further improvement
People must have obtained the skills for operation, maintenance, and improvement of equipment
Key Activities in EEM
- Collect Maintenance Prevention Information
- Maintenance Prevention Design
- Safety Activities
- Initial Flow Control
- Project Management
- Commissioning
- Measures
- 30/90 Day Post Completion Audit
- Launching Costs
- EEM Process
MP Information & MP Design
Collect (MP) information about issues with previous equipment designs and use this data to improve the (MP) design of new equipment
- MP function design
- ease of operation, maintenance, monitoring, and safety
- Loss-free design
- elimination of 16 Major Losses (occurred, existing, possible)
- Effective feedback of operational knowledge
- communication between equipment designer and operators/maintenance staff
- equipment designer does not usually have sufficient knowledge on operation/maintenance
- set-up of procedures for gathering MP information
- apply the MP information into new equipment design and standards
Maintenance Prevention Information
MP information is :
“Operational information obtained by conducting technological studies which classify and continuously refine improvements. Such improvements with associated plant history and design modification should be readily transferable”.
MP Information
- SOP (Standard Operating Procedure)
- Changeover procedure
- One-point lesson sheet
- Current major losses
- Trouble records
- Maintenance records
- Improvement records
- Effective maintenance procedure
- Parts (consumption) records
- MP (Maintenance Prevention) sheet
- Why-Why, PM analysis, etc.
- Technical report
- Quality report
- Check sheet (design, spec., commission.)
- Commissioning report
- Cleaning procedure
- Lubrication procedure
- Inspection procedure
- QC procedure
- Suggestion
- Commissioning report
- Skill map
- Training procedure, materials
MP info: Technical reports Best Proven Practice

MP Info: Visual management improvements. Easy inspection, cleaning, lubrication
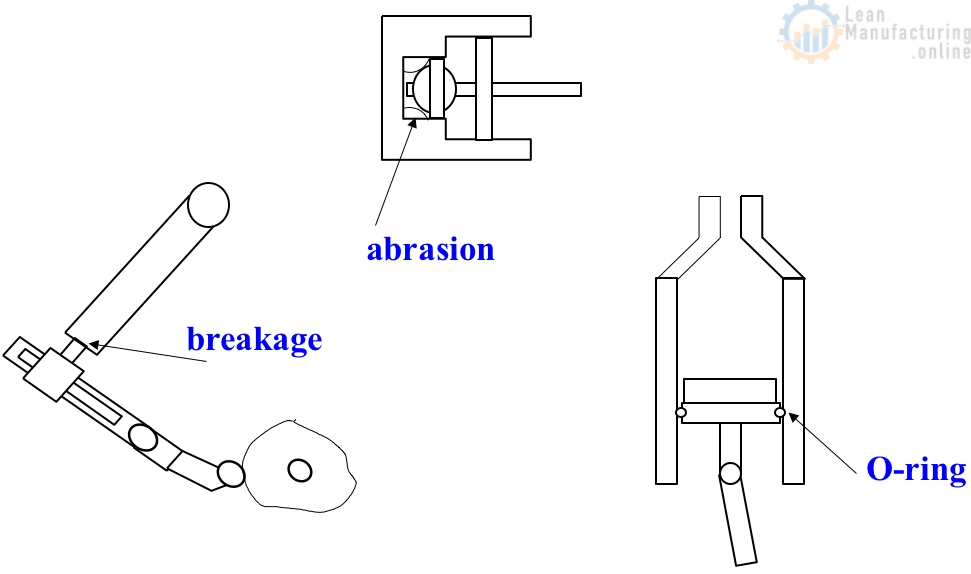
MP Info: Trouble records – design faults
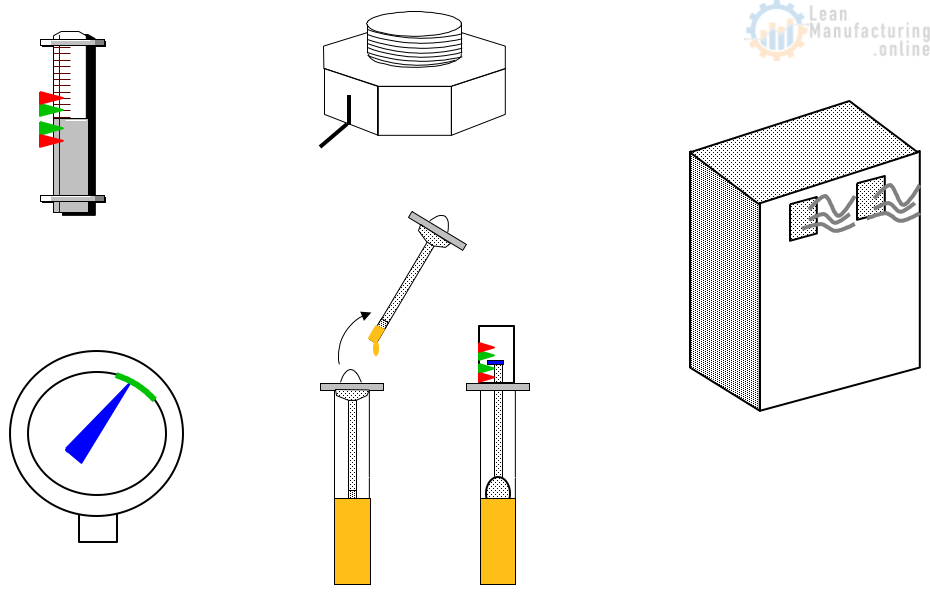
MP Info: Commissioning reports

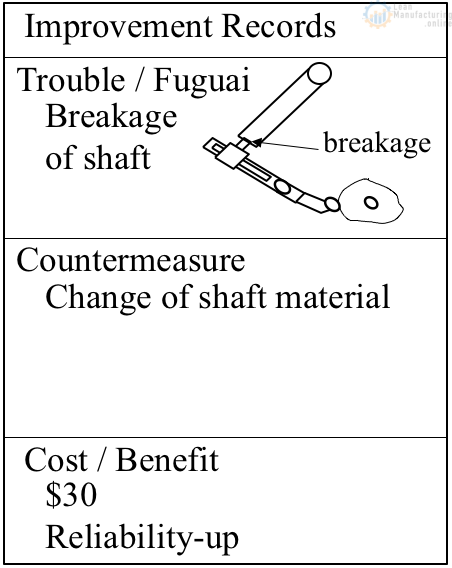
MP info: Improvement records
General
- Easy to understand
- Qualitative
- Drawing/picture
- Transferable
Calculation
- Loss
- Cost
- Benefits
Classification
- Loss
- MP function
- Machine / Products
Information level
Good example?
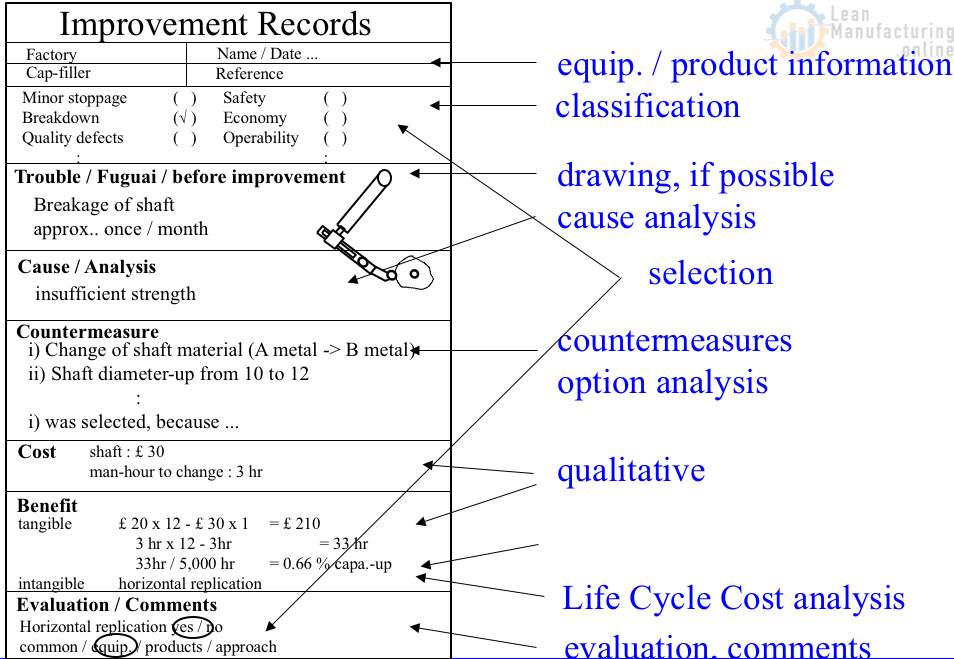
MP Info: Improvement Records Classification
Classification
- Loss
- Breakdown / minor stoppage / set-up & adjustment / speed / defect & rework
- MP function
- Safety / operability / reliability / maintainability – autonomous maintenance / audit/ economy / quality / friendliness to environment, people
- Machine / Products
- Supplier/specification
- Products/property etc.
- Information level
- Horizontal replication / standardization / training / permanent countermeasure
MP Info: Improvement Records Loss / Cost Calculation
Loss
- Losses (less than once / year)
- Production stop (hr / min)
- Rework / scrap (ton / unit)
- Defects / complaints (ton / unit / no. of complaints)
- Other Losses
- Losses x frequency (times/year)
- Reduced speed
- (Specified – reduced speed) x duration
Cost
- Man-hour to fix troubles
- Parts cost
- Subcontractor, equipment supplier costs, etc.
MP Info: Improvement Records Benefits
Benefits
- Production capacity increase
- Man-hour reduction
- Cost reduction
- rework/scrap
- inspection
- parts
- subcontractor
Example
- Breakage of parts
- once / month
- 3 hr for change
- parts cost $20
- Change of materials & design
- once / year
- 3 hr for change
- parts cost $20
- Man-hour reduction
- 3 hr x 12 – 3 hr x 1 = 33 hr
- Production capacity increase
- 33 hr / 5,000 hr(available time) = 0.66 %
- Cost reduction
- $20 x $12 – $30 = $210
Maintenance Prevention Design
MP design is:
“ The use of the latest maintenance data and technology when planning or building new equipment to promote greater reliability, maintainability, economy, operability, and safety while minimizing maintenance costs and deterioration related loss”.
MP Design: 3 Objectives
Main Function Design
- to meet current, future requirements for equipment in terms of quality, cost, capacity, flexibility, and safety.
MP Function Design
- incorporates ease of monitoring, operating, and maintenance so that operators can easily improve the equipment, and identify and solve problems.
Loss-free Design
- to eliminate 16 major losses, such as start-up, breakdown, minor stoppage, set-up, speed. defect/rework, which has been occurring in existing equipment.
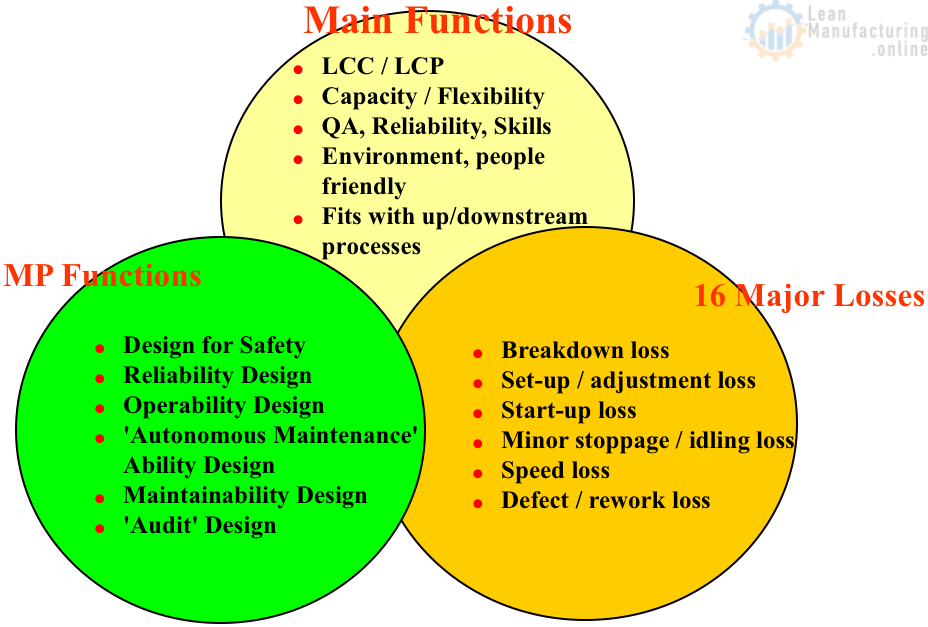
MP Design: Main Functions
- Capacity / Flexibility
- Life Cycle Cost / Life Cycle Profitability
- Quality Assurance / Reliability / Skill level
- Environment/people friendly
- Fits with upstream/downstream processes
MP Design: Main Function Specification
Analyze needs reflected in the production of current products thoroughly before launching into the design of new equipment
Set clear quantitative goals
- Quality
- Costs ( Initial / Running )
- Flexibility
- volume
- mix
- new products
Draft a specific plan for achieving these goals
- The work of designing equipment becomes the work of achieving a mission with specific goals
- Main function design
- Quality Assurance design
- Life Cycle Cost / Life Cycle Profit design
- Flexibility design
MP Design: Main Functions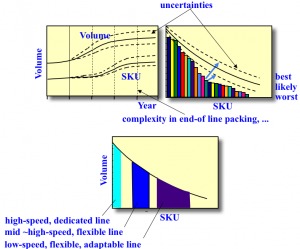
Capacity
- throughput
- balance between processes
Flexibility
- volume
- mix
- complexity
Cost
- IC (Initial Cost)

- RC (Running Cost)
- LCC, LCP
- short-life products vs. long-depreciation change parts
Uncertainties
- volume

- mix
- complexities
- product life cycle
Quality Assurance
–Technology / material selection
- air-clutch/magnet-clutch/servo. for torque control
Reliability
–Dynamic accuracy, tolerance
–Reliable parts
Skill level required
- mechanical or servo drives
Design for Safety
- Intrinsically safe
Reliability Design
- Avoiding operation-stopping failures & operation-deteriorating failures
Operability Design
- Ease of operation, changeovers & adjustments
- Easy troubleshooting, preventing operation-error
‘Autonomous Maintenance’ Ability Design
- Ease of daily maintenance
Maintainability Design
- Ease of maintenance
‘Audit’ Design
- Ease of predictive maintenance
MP Functions: Design Reviews
- Prepare checklists for each MP function
–ease of autonomous maintenance
–ease of planned maintenance
–ease of operation
–ease of monitoring and data collection for kaizen
–etc.
- Study the MP information on existing equipment
- Evaluate equipment specifications
- Identify apparent & possible problems
- Revise the specification (if necessary)
MP Information
- One-point lesson sheet
- Current major losses
- Trouble records
- Maintenance records
- Improvement records
MP function checklists ->
MP Function Checklist: Operability
Operators can do Operation & Changeovers quickly, accurately, and easily.