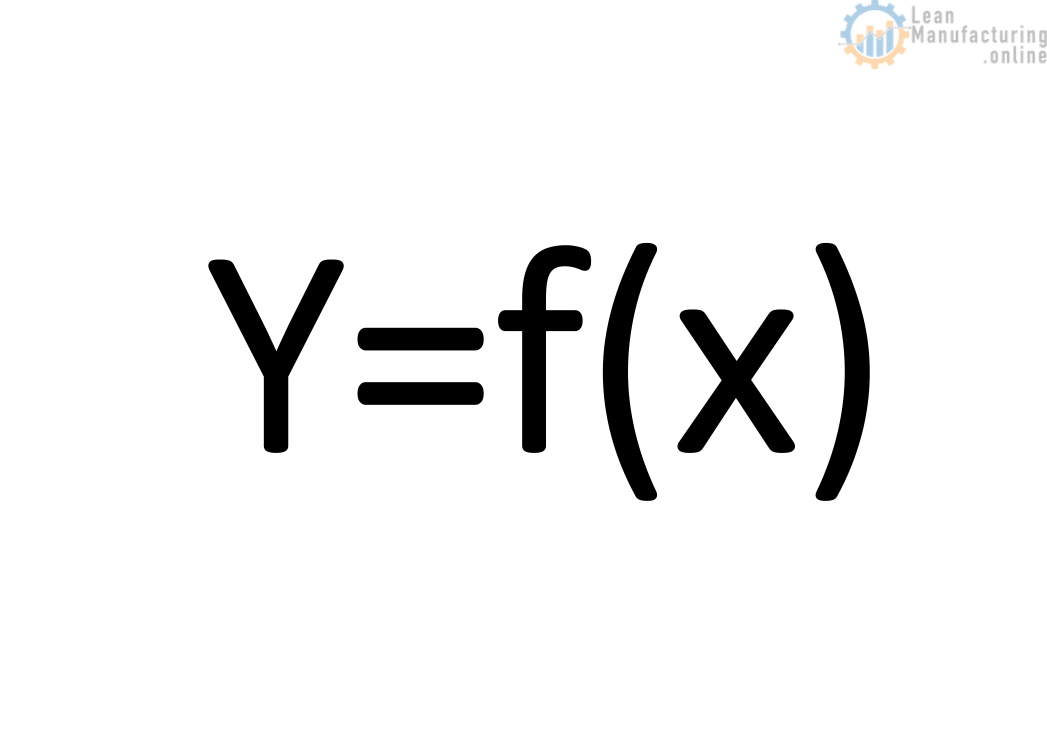Define-Measure-Analyze-Improve-Control is a formal problem-solving process, and a major tool of Lean Six Sigma, based on formula Y= f(X), metric that measures the problem.
Define
The first step is to identify a problem. Lean six sigma approach utilizes Y=f(X), a function that defines one variable in terms of another. The statement “y is a function of x” (denoted y = y(x)) means that y varies according to whatever value x takes on.
Example: Quality=f(Process control, Raw material, Equipment etc.)
- Cost of Poor Quality
- Critical To matrix
- Pareto Chart
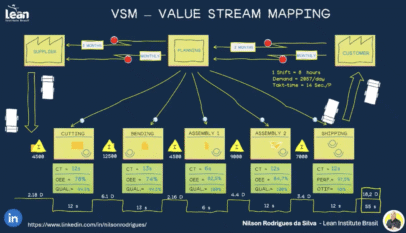
- SIPOC
- Voice of the customer
- Kano Analysis
- Survey Design
Measure
Capture data on the Y metric (if not already available in Define) and “Potentials X’s” that we believe could impact the Y.
- SIPOC
- Stakeholder analysis
- Spaghetti chart
- Check Sheet
- SS Analysis
- Process Capability Analysis
Analyze
Through your process, the graphical and statistical analysis identifies the “Critical X’s” (or Root Causes) that truly impact the Y.
- Ishikawa diagram
- Cause and Effect Matrix
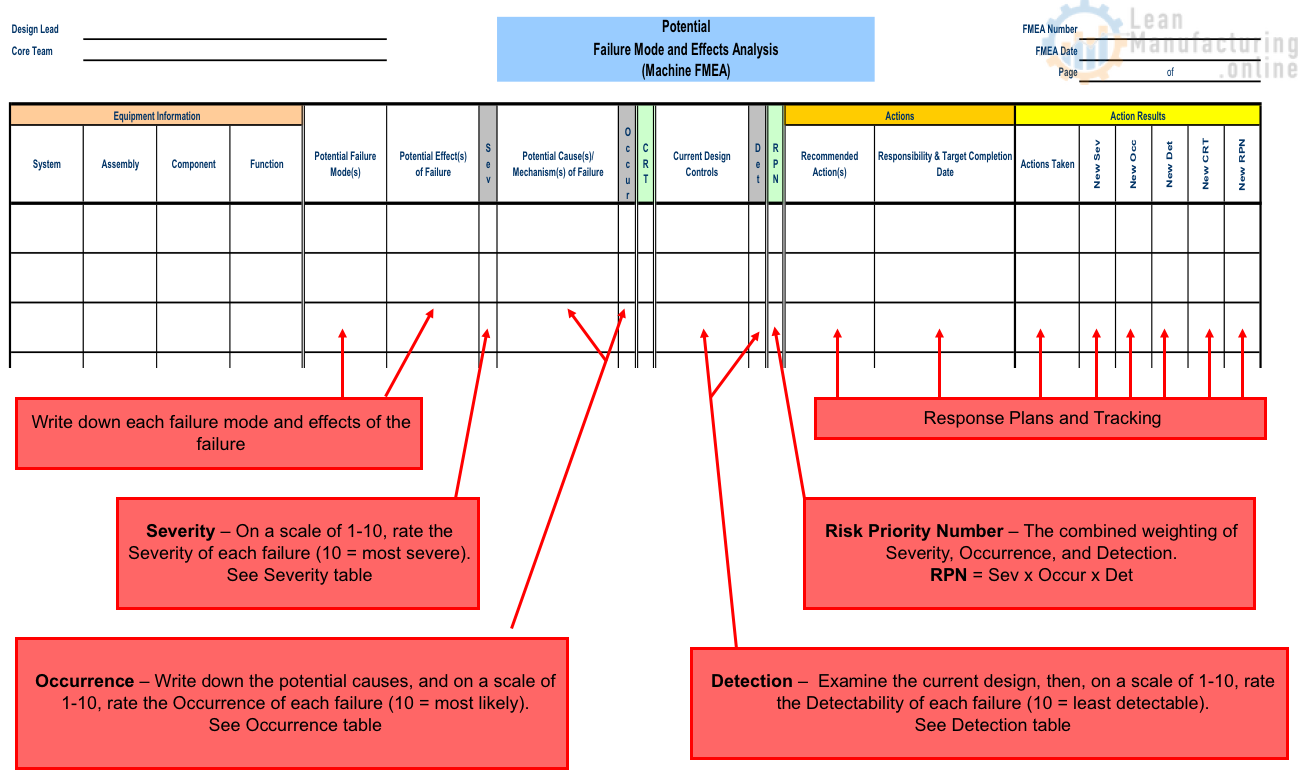
- Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
- Correlation and Regression
- Hypothesis testing
Improve
Identify and test solutions to the Critical X. Rollout out solutions that eliminate the Root Cause
- Regression analysis
- Design of experiment
- Error proofing
- 5S & Visual management
- FMEA
Control
Sustain the improvement by standardizing the new process and monitoring Critical X’s & Y
- Control plan + chart
- Audit plan
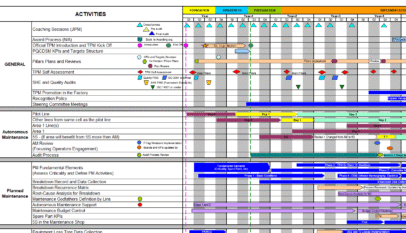
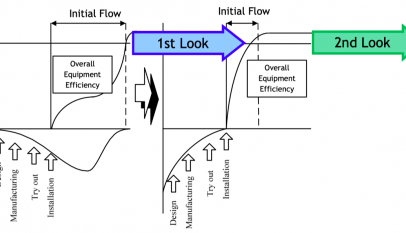
- Total Productive Maintenance
- New process capability analysis
- FMEA